SUPERCHARGE YOUR Online VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
There is a widespread belief among traditional SEOs today that SEO has become far more difficult than it used to be. Many assume that building authority and acquiring a strong backlink profile is the only way to outperform competitors in SERP rankings. If your day-to-day SEO work makes you feel this way, I’d encourage you to pause and consider the following example.

For a relatively straightforward keyword like “business outsourcing”, which carries high commercial intent, an IT outsourcing company called boutsourcing.com is ranking impressively in the 3rd position. This is ahead of major players such as Wikipedia and even a government website, despite the fact that its domain authority and backlink profile are nowhere close to those competing domains in the SERPs.
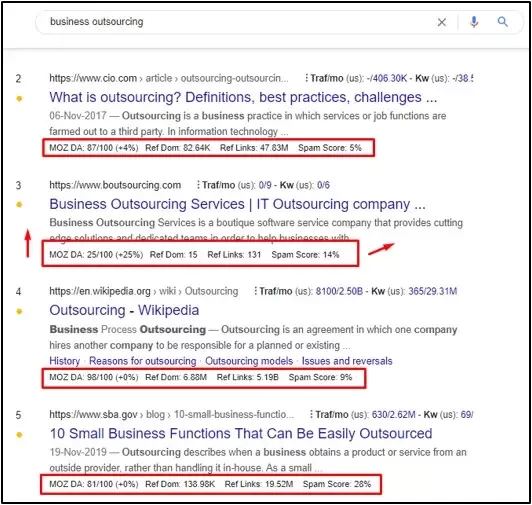
The reason behind this is simple: domain authority no longer holds the same weight it once did—relevance does. Google has been reinforcing this idea from the very beginning.
When someone searches for the term “business outsourcing,” there is a strong likelihood that they are looking for actual service providers rather than purely informational resources. Since the entire outsourcing website is dedicated to business outsourcing, it makes far more sense for Google to rank it prominently, alongside or even above domains that only offer general or informational content.
As a search engine that processes millions of queries every second, Google is fully capable of understanding and predicting search intent. It can make these assumptions about a keyword’s intent based purely on large-scale statistical data.
Learn more about how to optimise for Keyword intents using Customer Journey Map to better align your content with user intent at every stage of the search process.
To further reinforce this point, Googler John Mueller himself has clearly stated that Domain Authority is not a metric used within Google’s algorithm. You can read more about this in John Mueller Rebuts Idea that Google Uses Domain Authority.
Google’s noticeable shift in focus from backlinks toward relevancy has pushed SEOs to closely analyze the algorithm and discover smarter ways to achieve faster rankings in recent years. This ongoing evolution has also motivated our team at Thatware to explore, develop, and implement advanced SEO strategies powered by software, AI, and data-driven insights to remain competitive in an ever-changing SEO landscape.
Many of these approaches and techniques will be shared throughout this article, so I encourage you to stay with me as we dive deeper into them.
👉Crawl Depth
Crawl depth refers to the number of clicks required for a user to reach a specific page on your website starting from the homepage. In simple terms, it measures how deep a page sits within your site’s structure.
Google’s John Mueller has clearly addressed this concept in one of his webmaster hangouts. In the discussion, he responds to an eCommerce store owner who is unsure whether multiple store pages should be linked directly from the homepage or accessed through an intermediate page such as “/stores.” His explanation highlights the importance of keeping critical pages easily accessible, reinforcing how crawl depth can influence discoverability and indexing.
👉Here’s John Mueller’s response:
“In general, both of these setups would work. So I don’t see any big advantage in having the URLs in separate sub-directories even further. From our point of view, we don’t count slashes in the URLs. If you put it into ‘/stores’ and then ‘/location’ and that’s how you want to kind of keep your website on your server that’s perfectly fine.
What does matter for us a little bit is how easy it is to actually find the content. So especially if your homepage is generally the strongest page on your website, and from the homepage, it takes multiple clicks to actually get to one of these stores, then that makes it a lot harder for us to understand that these stores are actually pretty important.
On the other hand, if it’s one click from the home page to one of these stores then that tells us that these stores are probably pretty relevant, and that probably we should be giving them a little bit of weight in the search results as well.
So it’s more a matter of how many links you have to click through to actually get to that content rather than what the URL structure itself looks like.”
Here’s a video of the full response:
In other words, the closer a particular page is to the home page, the more likely it is to rank for relevant search terms.
An easy solution is an “HTML Sitemap”
👉What is an HTML Sitemap?
An HTML sitemap is essentially an HTML page that contains links to all (or most) of the important HTML pages on your website. By doing this, it significantly reduces crawl depth, often bringing it within Google’s recommended standard of fewer than three clicks.
Here’s a simple example of how an HTML sitemap helps reduce crawl depth. Suppose we want to reach the page “https://thatware.co/managed-seo/” on the ThatWare website. With an HTML sitemap in place, the number of clicks required to access this page is reduced to just two, making it easier for both users and search engines to discover and crawl the page efficiently.
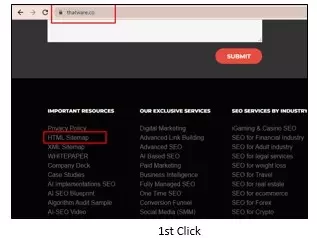
1st Click
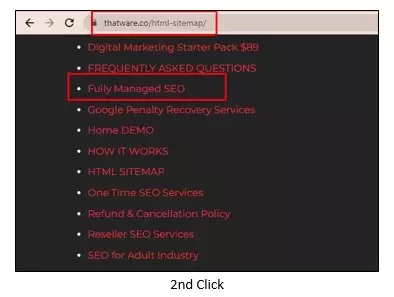
2nd Click
You can clearly see how an HTML sitemap page that lists all the URLs on a website significantly lowers the crawl depth across every page. For this reason, creating an HTML sitemap has become essential for modern-day SEOs.
Here’s the link to Thatware’s HTML Sitemap.
👉Optimising for Voice Search using MREID
Ever since Google transitioned from understanding search queries in the “context of keywords” to interpreting them in the “context of object and entities”, the way it processes information has fundamentally changed.
Let’s take a quick look at the difference between entities and strings. Consider a person’s name such as “Jason Barnard.” Under Google’s older algorithm, this query would have been treated simply as a string of characters or a set of keywords. As a result, Google would return documents that matched those keywords, largely influenced by authority signals such as backlinks.
With the introduction of the Hummingbird algorithm, Google now recognizes “Jason Barnard” as an entity in its own right. It assigns a unique identifier—ID = /g/11cm_q3wqr—which represents the Machine Readable Entity ID (MREID) associated with this individual. This allows Google to understand who the person is, rather than just matching text strings across web pages.
By assigning real-world objects as distinct entities, Google is able to understand them in real time and map semantic relationships between multiple entities within a document. This enables Google to better grasp the overall context of each document rather than relying on isolated words or phrases.
The same principle applies to search. By analyzing the semantic relationships between entities in a query, Google can accurately interpret user intent and surface the most relevant document that fulfills that intent—rather than simply matching keywords.
As a result, search optimization has evolved to focus far more on intent, shifting away from a purely keyword-driven approach.
👉How to get MREIDs of an Entity?
An entity is an object either real or abstract for which Google generates separate search engine features which can define the entity fully. It can be a product, a person or a company.
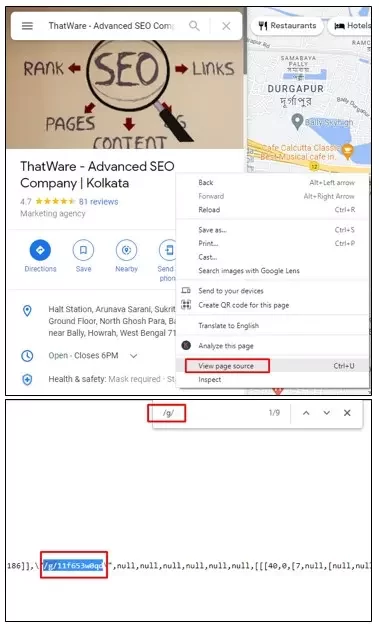
For example, Google understands Thatware by its entity id = “/g/11f653w0qd”.
This can be found by typing Thatware in Google, going to the Google My Business Listing and right-clicking to view the source code.
By searching for “/g/” using Ctrl + F we can find the MREID of that keyword.
It can also be found using Google Trends such as for Macbook Air, we can get the MREID from Google Trends
Type Macbook in Google Trends and select the product
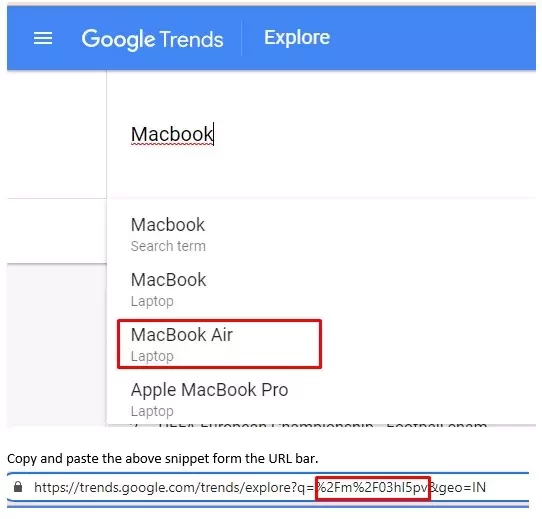
Copy and paste the above snippet from the URL bar.
%2Fm%2F03hl5pv
Now replace the “%2F” with forwarding slashes as /m/03hl5pv.
Hence we get the MREID for Macbook Air.
Another Way to find MREID is by inspecting the knowledge panel for an Entity. For example, for an instrument “Keystar” the MREID is found within the card_id of the page source.
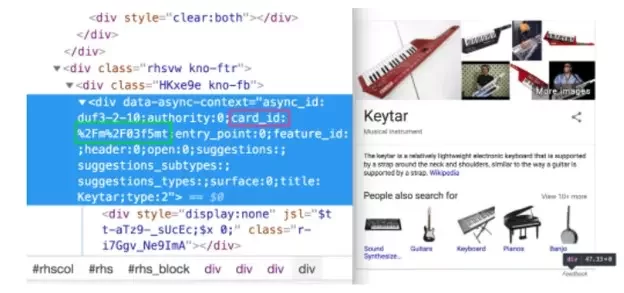
👉How to Implement MREIDs with Schema Codes?
Google’s algorithm is designed to collect and understand as much contextual information as possible about a webpage. The clearer the signals you provide, the easier it becomes for Google to match your content with relevant search queries. One of the most effective ways to supply structured information is through Schema markup.
This becomes even more powerful when MREIDs are included alongside your structured data. Below are three practical methods to integrate MREIDs using different schema types.
👉 Embedding MREIDs into Product Review Schema
One straightforward approach is to insert the MREID within the Product Review Schema using the “sameAs” property.
For instance, if you are marking up a product such as the Apple MacBook Air, you can incorporate the MREID directly into its Product Schema.
To do this, generate a Google Search URL that includes the MREID along with the kponly parameter (which ensures only the Knowledge Panel is displayed). Then, add this URL under the sameAs field in your schema markup.
This method connects your product entity to Google’s Knowledge Graph representation, strengthening entity association and contextual clarity.
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”:”https://schema.org/”,
“@type”:”Product”,
“brand”:{
“@type”:”Brand”,
“name”:”Apple”,
“sameAs”:[ “https://www.apple.com/”, “https://www.google.com/search?q=Apple&kponly&kgmid=/m/0k8z”,]
},
“name”:”MacBook Air M1″,
“sku”:”macbook-air-m1″,
“gtin8″:”macbook-air-m1”,
“image”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/images/macbook-air-m1.jpg”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/macbook-air-m1-review/”,
“description”:”This MacBook Air M1 review puts Apple’s latest MacBook to the test.”,
“sameAs”:[
“https://www.apple.com/macbook-air/”, “https://www.google.com/search?q=MacBook+Air&kponly&kgmid=/m/03hl5pv”,
],
“review”:{
“@type”:”Review”,
“datePublished”:”2021-05-26″,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/macbook-air-m1-review/”,
“inLanguage”:”en-US”,
“description”:”This MacBook Air M1 review puts Apple’s latest MacBook to the test.”,
“publisher”:{
“@type”:”Organization”,
“name”:”MyAffiliateSite”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/”,
“logo”:{
“@type”:”ImageObject”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/images/logo.png”
}
},
“reviewRating”:{
“@type”:”Rating”,
“ratingValue”:”4.5″,
“bestRating”:”5″,
“worstRating”:”0″
},
“author”:{
“@type”:”Person”,
“name”:”Joe Doe”,
“sameAs”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/author/joe-doe/”
}
}
}
</script>
We also know that Google often references Wikipedia to generate knowledge graphs. So we can add that reference too.
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”:”https://schema.org/”,
“@type”:”Product”,
“brand”:{
“@type”:”Brand”,
“name”:”Apple”,
“sameAs”:[ “https://www.apple.com/”, “https://www.google.com/search?q=Apple&kponly&kgmid=/m/0k8z”, “https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apple_Inc.” ]
},
“name”:”MacBook Air M1″,
“sku”:”macbook-air-m1″,
“gtin8″:”macbook-air-m1”,
“image”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/images/macbook-air-m1.jpg”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/macbook-air-m1-review/”,
“description”:”This MacBook Air M1 review puts Apple’s latest MacBook to the test.”,
“sameAs”:[
“https://www.apple.com/macbook-air/”, “https://www.google.com/search?q=MacBook+Air&kponly&kgmid=/m/03hl5pv”, “https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MacBook_Air”
],
“review”:{
“@type”:”Review”,
“datePublished”:”2021-05-26″,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/macbook-air-m1-review/”,
“inLanguage”:”en-US”,
“description”:”This MacBook Air M1 review puts Apple’s latest MacBook to the test.”,
“publisher”:{
“@type”:”Organization”,
“name”:”MyAffiliateSite”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/”,
“logo”:{
“@type”:”ImageObject”,
“url”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/images/logo.png”
}
},
“reviewRating”:{
“@type”:”Rating”,
“ratingValue”:”4.5″,
“bestRating”:”5″,
“worstRating”:”0″
},
“author”:{
“@type”:”Person”,
“name”:”Joe Doe”,
“sameAs”:”https://myaffiliatesite.com/author/joe-doe/”
}
}
}
</script>
👉Implementing MREIDs in Local Business Schema.
For a Business called Insta Global Travel, we can inject the MREID into the Local Business Schema as follows.
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “http://schema.org”,
“@type”: “LocalBusiness”,
“@id”: “http://g.co/kg/g/11f653w0qd”,
“image”:”https://lh5.googleusercontent.com/p/AF1QipM8e6SYYY2Oa9IaYeF4rz9iWuaare9oOtFWJwv7=w408-h333-k-no”,
“address”: {
“@type”: “PostalAddress”,
“addressLocality”: “Halt Station, Arunava Sarani, Sukriti Appartment – Ground Floor, North Ghosh Para, Bally, Landmark:, near Bally, Howrah, West Bengal 711227, India”,
“addressRegion”: “IND”
},
“mainEntityOfPage”: “https://www.google.com/maps?cid=6324742204996025982”,
“description”: “ThatWare LLP is a group of smart digital marketing professionals who are excellent at handling advanced IT solutions and high tech digital marketing goals. Based out of Kolkata, ThatWare LLP has experience in several digital marketing services such as SEM, SEO, ORM, CRO, Schema, Penalty Recovery, SMO, SMM and much more.
Professionals at ThatWare LLP have several years of expertise in managed IT solutions, outsourcing, technical consultancy and much more.
One of the core areas in which ThatWare LLP is expertise is advanced online marketing strategies and improving the business’s sales funnel.
We claim to provide state of the art SEO services making us one of the best SEO agencies in Kolkata.”,
“name”: “ThatWare”,
“telephone”: “+917044080698”,
“email”:”info@thatware.co”,
“priceRange”: “$$”,
“hasMap”: “https://g.page/thatware?share”,
“geo”: {
“@type”: “GeoCoordinates”,
“latitude”: “22.6513316”,
“longitude”: “88.3349138”
},
“areaServed”: {
“@type”: “State”,
“name”: “West Bengal”,
“url”: “https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Bengal”
},
“sameAs” : [
“https://www.google.com/search?q=thatware&kponly&kgmid=/g/11f653w0qd”,
“https://www.facebook.com/thatware.co”,
“https://twitter.com/thatware”,
“https://in.linkedin.com/company/thatware-llp”,
“https://www.youtube.com/TuhinBanika2z/videos”,
“https://www.instagram.com/thatware.co/”
],
“currenciesAccepted”: “DU”,
“paymentAccepted”: [
“Cash”,
“Check”,
“Invoice”,
“Visa”,
“MasterCard”,
“American Express”,
“Discover”,
“Insurance”
]
}
</script>
This way we can inject MREIDs into different Schema formats.
👉Optimising for Google Rankbrain AI using Rankbrain Schema
With Rankbrain rolling Google made significant advances in its algorithm. With hummingbird, Google was able to understand the existence of entities as opposed to real-world objects. Rankbrain gave Google the ability to find meaning and extrapolate various intents by looking at the entities of a document as a whole.
In its most basic interpretation, Rankbrain’s job is to furnish Google with enough information about the documents in its index to enable it to show those documents which are contextually relevant to the intent of the search query.
So basically to implement Rankbrain Schema is to simply compile all types of Schema Information that we can furnish for a specific document. Here’s one example for
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “http://schema.org”,
“@type”: “WebPage”,
“breadcrumb”: “Home > Blog > High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”, //Breadcrumb
“mainEntity”:{
“@type”: “Article”,
“name”: “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“headline”: “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“author”: “Heavyglare Eyewear”,
“image”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”,
“inLanguage”: “English”,
“publisher”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“logo”: {
“@type”: “ImageObject”,
“name”:”Heavyglare Eyewear Logo”,
“height”:”50″,
“width”:”200″,
“url”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/media/wysiwyg/logo.png”
}
},
“datePublished”: “2018-5-12”,
“dateModified”:”2018-5-14″,
“mainEntityOfPage”: {
“@type”: “WebPage”,
“@id”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog”
}
}
}
</script>
<script type=”application/ld+json”>
{
“@context”: “http://schema.org”,
“@type”: “BlogPosting “,
“publishingPrinciples”:{
“@type”:”Table”, //Contents
“name”:”Contents”,
“sameAs”:[“1.Functionality of your lenses is imperative”, “2.Quality lens materials make a difference”,”3.High performance sport sunglasses need to fit properly”]
},
“headline”: “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “Heavyglare Eyewear”
},
“image”: [
“https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”
],
“publisher”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Heavyglare Eyewear”,
“logo”: {
“@type”: “ImageObject”,
“name”:”Heavyglare Eyewear Logo”,
“height”:”50″,
“width”:”200″,
“url”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/media/wysiwyg/logo.png”
}
},
“datePublished”:”2018-5-12″,
“dateModified”:”2018-5-14″,
“mainEntityOfPage”: {
“@type”: “WebPage”,
“@id”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog”
},
“keywords”:”lens,sunglass lens characteristics,sunglass lenses,sunglass lens issues”,
“wordCount”:”1800″, //wordcount
“mainEntity”:{ //Anchortext
“@type”:”brand”,
“name”:[“shop.heavyglare.com”,
“heavyglare eyewear”,
“heavyglare”,
“sports eyewear”,
“prescription sunglasses”,
“heavyglare.com”
]
},
“workExample”:{ //Quora questions
“@type”: “Question”,
“text”: “What is the colour of sky?”,
“dateCreated”: “2018-5-12”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “A”
},
“acceptedAnswer”: {
“@type”: “Answer”,
“text”: “blue”,
“dateCreated”: “2018-5-14”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “A”
}
},
“mainEntity”:{ //loop
“@type”:”HowToStep”,
“name”:”suggested answers”,
“itemListOrder”: “http://schema.org/ItemListOrderAscending”,
“itemListElement”:[
{
“@type”: “Answer”,
“position”: “1”,
“text”: “black”,
“dateCreated”: “2018-5-14”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “B”
}
},
{
“@type”: “Answer”,
“position”: “2”,
“text”: “red”,
“dateCreated”: “2018-5-14”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “B”
}
}
]
}
},
“potentialAction”:{ //questions with loop
“@type”: “AskAction”,
“agent”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “John”
},
“recipient”: {
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “Steve”
},
“object”:{
“@type”:”HowToStep”,
“name”:”Queries”,
“itemListOrder”: “http://schema.org/ItemListOrderAscending”,
“itemListElement”:[
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“position”: “1”,
“text”: “What’s 2 + 2?”
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“position”: “2”,
“text”: “What’s 21 + 22?”
}
]
}
},
“exampleOfWork”:{ //how to
“@type”:”HowTo”,
“name”:”How to choose a good sunglass for better performance?”,
“url”:”https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/high-performance-sport-sunglasses-guide/”,
“description”:”Read the article to know the process of choosing a good sunglass”,
“image”:”https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”,
“inLanguage”:”en-US”,
“keywords”:”lens,sunglass lens characteristics,sunglass lenses,sunglass lens issues”,
“steps”:{
“@type”:”HowToStep”,
“name”:”Queries”,
“itemListOrder”: “http://schema.org/ItemListOrderAscending”,
“itemListElement”:[
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “1”,
“name”:”Aim to protect your eyes first and foremost.”,
“description”:”Excessive exposure to UV radiation can cause a variety of problems for your eyes such as cataracts, burns, and cancer.”
},
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “2”,
“name”:”If you want your sunglasses to protect you from these risks, look for pairs that block at least 99% of UVB rays and at least 95% of UVA rays.”,
“description”:”Also look for the amount of cover the sunglasses provide. Look at how much you can see around the frames––will the sunglasses let in sun from the top or sides?”
},
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “3”,
“name”:”Don’t buy sunglasses if they’re labeled as ‘cosmetic’ or don’t provide any information on UV protection.”,
“description”:”Look for scratch resistance, many lenses have very fragile coatings. If you are spending much money, you want them to last. Fortunately damaged lenses can be replaced for most models.”
},
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “4”,
“name”:”Choose scratch-resistant lenses.”,
“description”:”Scratched up sunglasses are useless sunglasses. Lenses made from NXT polyurethane are impact-resistant, flexible, lightweight, and have great optical clarity, but they’re expensive.”
},
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “5”,
“name”:”Check for distortion.”,
“description”:”Hold the lenses up to a fluorescent lamp. As you move the sunglasses up and down, check that wave distortion doesn’t happen. If it doesn’t happen, this is a good sign.”
}
]
}
},
“video”: { //video
“@type”: “VideoObject”,
“description”: “Get a visual idea about the high performance sport sunglasses.”,
“uploadDate”:”2018-05-14″,
“duration”: “T1M33S”,
“name”: “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“thumbnail”: “High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”,
“thumbnailUrl”:”https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”
},
“encoding”:{ //infographic
“@type”: “ImageObject”,
“name”: “Infographic on High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide”,
“author”: “Heavyglare Eyewear”,
“contentUrl”: “https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”,
“datePublished”: “20018-05-12”,
“description”: “Get a visual idea about the high performance sport sunglasses.”
}
}
}
</script>
The main part in the entire above schema is shown below “How to section”
“object”:{
“@type”:”HowToStep”,
“name”:”Queries”,
“itemListOrder”: “http://schema.org/ItemListOrderAscending”,
“itemListElement”:[
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“position”: “1”,
“text”: “What’s 2 + 2?”
},
{
“@type”: “Question”,
“position”: “2”,
“text”: “What’s 21 + 22?”
}
]
}
},
“exampleOfWork”:{ //how to
“@type”:”HowTo”,
“name”:”How to choose a good sunglass for better performance?”,
“url”:”https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/high-performance-sport-sunglasses-guide/”,
“description”:”Read the article to know the process of choosing a good sunglass”,
“image”:”https://shop.heavyglare.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/High-Performance-Sport-Sunglasses-Guide.jpg”,
“inLanguage”:”en-US”,
“keywords”:”lens,sunglass lens characteristics,sunglass lenses,sunglass lens issues”,
“steps”:{
“@type”:”HowToStep”,
“name”:”Queries”,
“itemListOrder”: “http://schema.org/ItemListOrderAscending”,
“itemListElement”:[
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “1”,
“name”:”Aim to protect your eyes first and foremost.”,
“description”:”Excessive exposure to UV radiation can cause a variety of problems for your eyes such as cataracts, burns, and cancer.”
},
{
“@type”: “HowToDirection”,
“position”: “2”,
“name”: “If you want your sunglasses to protect you from these risks, look for pairs that block at least 99% of UVB rays and at least 95% of UVA rays.”,
This set of different schemas gives all possible information about the blog “High Performance Sport Sunglasses Guide” which can be picked up by the Rankbrain algorithm and can massively boost ranking and traffic generated for that website page.
👉Optimizing for Voice Search using Passage Indexing
Sometimes people are looking for specific answers to a very specific search query. For example: for those of you wondering “What is passage indexing”.
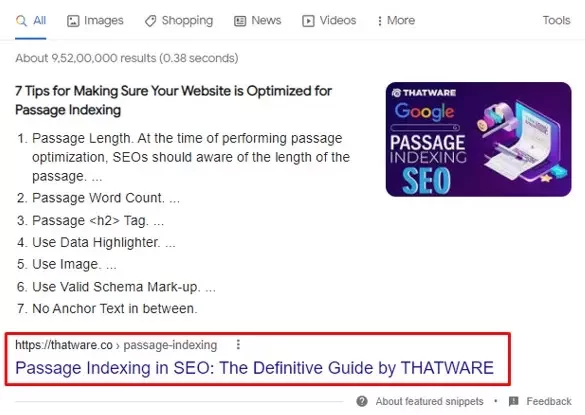
This is a new kind of search feature which allows Google to answer oneliner queries such as above.
Google Martin Splitt was excited when he announced the breakthrough of Google where they can now not only index web pages but also can index individual passages in content.
This allows Google to answer very specific search queries by simply showing the most relevant passage above all serp results. Thus satisfying the searcher’s intent to gain a quick answer.
👉How to Optimise for Passage Ranking
We at Thatware have tried with several contents and tried to optimise our pages for passage ranking.
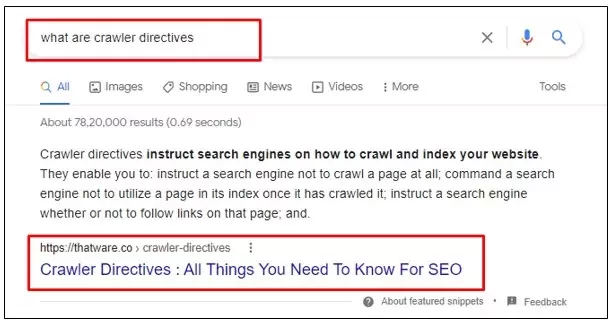
After several experiments, our passages rank for several search terms as above.
Here are our observations regarding how to optimise passage indexing.
1. PASSAGE LENGTH
Let us assume that a particular page has 3000 words worth of content. We organize passages intended for passage ranking not more than 1% or 2% of the total word count. This means each passage should have 30-60 words at most. In other words, passage segregation should be around 1-2% of the intended word count. Such a passage is ideal to serve as an answer to specific queries.
2. PASSAGE <H2> TAG
If a passage consists of a <H2> tag then it should have an LSI keyword in the tag. In other words, if a passage is followed by any h-tag then it’s recommended to use an LSI keyword within the H-tag whether it be <h1> or H2> or etc.
3. USE DATA HIGHLIGHTER
If you are optimising a certain passage from the content then you have to use data highlighter with the help of Google Search Console’s Data Highlighter tool. The option varies in the list from site to site, suppose you are optimising a passage for an article based website, then you have to choose an article from the given list in GSC.
You can check out more about Passage Indexing below:
5. USE IMAGE
It is recommended that you use at least one image for the particular page that you are optimizing for passage indexing. And it should be placed below a passage. For reference, please see the attached layout by end of this article!
6. USE VALID SCHEMA MARK-UP
It is recommended that you use the specific passage into the schema code for which you are optimizing the page. It’s advised to use JSON-LD for the markup!
7. NO ANCHOR TEXT IN BETWEEN
The passage should not contain anchors but there should be internal and external hyperlinks above or below. Well, there is no such rule still it’s our practical experience that having no anchors within the passage helps with the optimization. Moreover, having an internal link / external link above or beyond also helps with the process.
Wrapping up this section you can learn more about Passage Indexing and its benefits here.
Semantic Topic Clustering
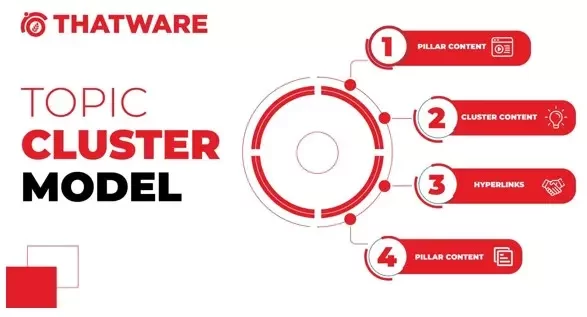
https://thatware.co/passage-indexing/
Why does Topic Cluster Model Work
The effectiveness of the topic cluster model stems from the fact that Google no longer ranks websites purely based on individual keywords. Instead, it evaluates whether a website demonstrates sufficient authority and credibility to cover a topic comprehensively, aligned with user search intent.
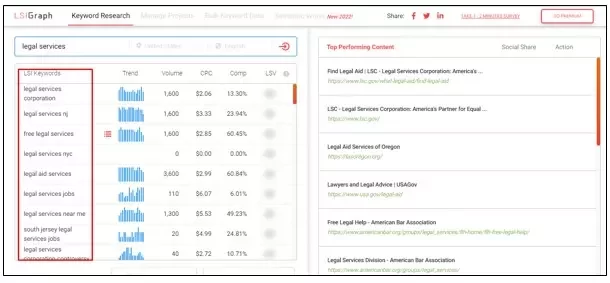
To illustrate, let’s consider a practical example. Suppose we want to target the keyword “Legal services” (with a search volume of 9,600/month). We can create a dedicated landing page that addresses various aspects of the legal services our organization provides. This landing page serves as the main topic or pillar page.Beneath the pillar page, we can develop clusters of content targeting more specific, yet related, keywords, such as:
- Pro-bono legal services (1500 searches/month)
- commercial property lawyer (1400 searches/month)
- Community legal services (3300 searches/month)
- Legal aid services (2200 searches/month)
- Immigration Legal Services (600 searches/month)
And so on.
HubSpot takes the concept even further. For instance, the cluster “community legal services” has enough search volume to be considered a topic on its own. This can be expanded into additional content, such as:
- eastside legal assistance program
- northern community legal service
- neighbourhood legal services
- Latino legal services
- LGBTQ legal aid
- Suncoast community legal services
This demonstrates how clusters can themselves evolve into sub-topic clusters, forming a Tier 2 topical cluster within the broader content structure.
Since these clusters target specific long-tail keyword variations, they not only increase overall keyword coverage but also address individual questions and aspects related to the overarching topic of “legal services.”As these cluster pages start attracting traffic from Google searches and gain rankings, the links pointing from these pages to the main pillar page—optimized for the keyword “Legal services”—signal to Google that the pillar page is an authoritative source. Over time, this helps the pillar page rank for the broader keyword as well, consolidating topical authority across the site.
👉Tools to find Cluster Keywords.
Soovle – Soovle is an excellent tool for discovering long-tail and semantic variations of any keyword. It provides auto-suggestions and commonly used keywords related to your query, pulling data from 6 different search engines: Wikipedia, Amazon.com, Answers, YouTube, Bing, and Yahoo.
👉Bag of Words
The Bag of Words model is a powerful tool for generating keyword ideas that your competitors may be using but you haven’t yet tapped into. It’s an information retrieval model that extracts keywords from large volumes of data and records the frequency of each keyword within a document. In SEO, we use it to create a cloud of Keywords with varying weightage based on their popularity and then compare it with competitor keyword clouds to identify meaningful keyword opportunities.
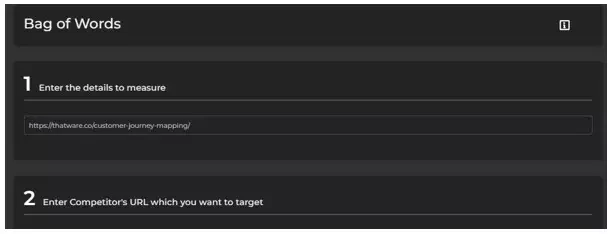

These keywords are organized so that their size reflects their relative importance, making them ideal candidates for cluster topics.
👉Use LSI Graph Tool to generate LSI Keywords
LSI Keywords are keywords that are semantically related to a target keyword or search query. When optimizing a document, it’s important to include a focus keyword but also LSI variations to clearly convey the intent that the content fulfills.
These keywords help Google gain a deeper understanding of the context of your web content. Additionally, they serve as excellent ideas for cluster content, since the main goal of a topic-cluster model is to develop cluster pages around low-difficulty keywords that are semantically connected to the main pillar keyword or keyphrase.
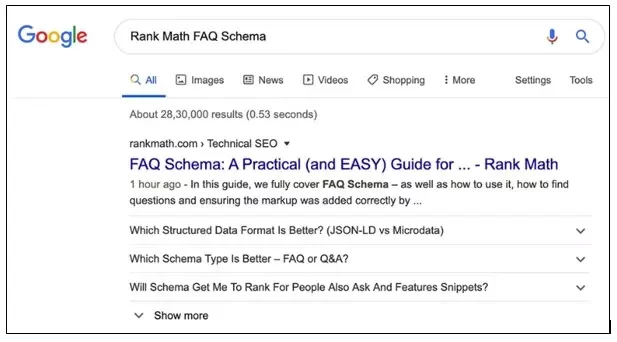
👉FAQ Schema is a MUST!
Have you ever wondered how users most commonly search on Google? The answer is—they ask questions! That’s why, as SEOs, it’s essential to include an FAQ section at the end of service or blog pages, optimized to provide answers to the most frequently asked questions on a topic.
An FAQ page or section contains a list of questions along with relevant answers related to a specific topic. When these pages are properly structured and marked up, Google can display them as rich snippets in the SERPs, making your content more visible and engaging. It looks something like this:
👉SEO Benefits of FAQ Schema and Rich Snippet
- Increase in SERP Visibility: Implementing FAQ schema adds more content to your search listing, making it larger and more noticeable, which can boost your website’s click-through rate. Additionally, users can quickly jump to the specific question they find most relevant, improving the overall user experience.
- Optimizing for Voice Search: FAQ schema also supports voice search optimization by providing structured information that Google Assistant can use directly. This allows your content to become a reliable source for answers to common questions, increasing the chances of appearing in voice search results.
👉How to Implement FAQ Schema
The easiest and most straightforward way to implement FAQ Schema is by using a schema markup generator and then applying it through a WordPress plugin to insert the code into the header and body sections. For example, HFCM is a reliable plugin that can help manage these schema insertions efficiently.
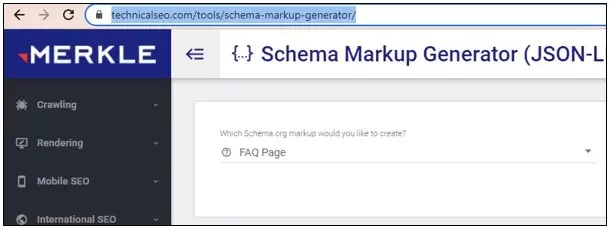
- Select FAQ Page in the Schema Categories
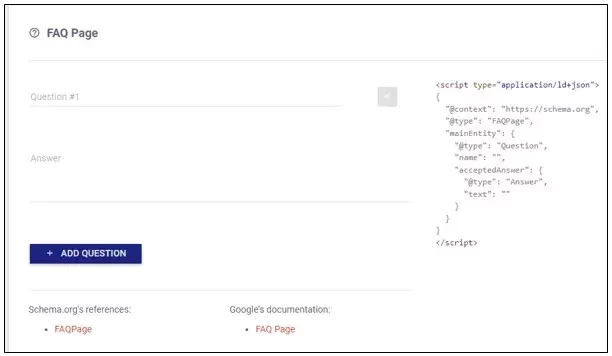
- Simply write each question along with its intended answer, and the schema markup will be generated automatically. Once complete, you can copy the generated code and insert it into the header or body tags of your website.
👉Using Topic Relevant Quotes using Quotes HTML
Quoting content from external sources generally does not harm SEO; in fact, it can add significant value to your content.
An SEO-friendly way to implement this is by using the inline quotation tag <q>.
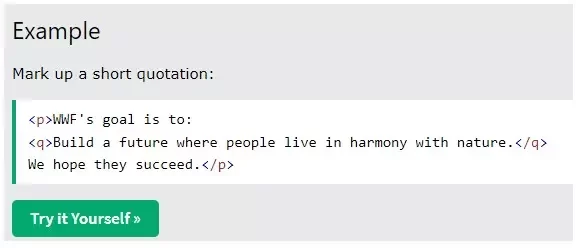
This signals to Google that the content is a quotation from an external source, allowing you to safely include references with a high likelihood—around 90%—of no negative impact on SEO.
👉N-Gram
N-Gram is a technique used to measure the significance of keywords within a document. It shows how often a sequence of n words appears in the text.
- A 1-gram is a single word, such as “life” or “tie.”
- A 2-gram is a keyphrase made up of two words.
- And so on for longer sequences.
N-Grams are particularly useful for optimizing content around a focused keyword, especially in documents containing hundreds or even thousands of potential keywords.
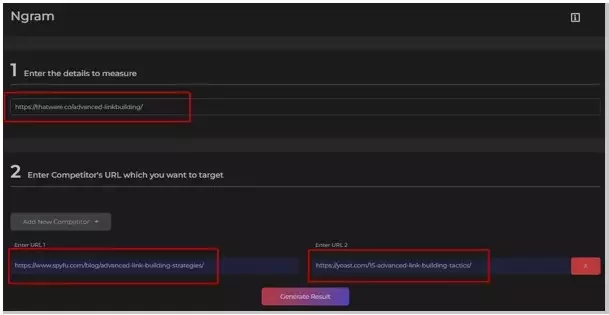
👉How does it Work?
Using an N-Gram analysis tool is simple.
- First, we enter the url of the document which we want to optimise.
- Add two or three competing URLs.
- The algorithm analyses and find the most used Keywords not only in our document but also the most weighted words on the competitor’s pages.
- On the basis of this analysis, the tool then provides keyword suggestions based on Weightage which the document can be optimised for.

👉TF – IDF Measurement
What is TF-IDF?
Let’s learn about TF or Term Frequency. As the name suggests it is a measure of the number of times a particular keyword occurs in a document.
TF = (No. of times a keyword appears in a document) / (Total Number of Words)
DF Score or document frequency = (Number of docs) / (Total Number of documents where the keyword appears in a Database)
IDF = log(DF)
When TF is multiplied by the IDF, then the resulting score is lower for commonly used words and higher for niche-specific or intent specific topics.
When we use Keywords that have a high TF-IDF scores, those words indicate to Google the context of the page more than regular words.
👉Benefits of TF-IDF Optimization
First, to clear it our, TF-IDF is not a ranking signal. But what Google cares about is Semantic search.
For example, let us be a search engine that does not know the meaning of Trout. Let us analyse the following sentences.
- Trout is rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Trout has tender flesh and a mild, somewhat nutty flavour.
- When choosing trout we pay attention to a clear red-orange colour.
Also, let us assume we understand what a Salmon is. That when we encounter the following lines,
- Salmon is a popular type of fish in Western cuisine, which goes well with white wine.
- Tender salmon meat can be added to pasta.
- Salmon skin is super nutrient-dense, so keep it why you cook.
The mere occurrence of the word Trout with words like “Omega 3, flesh, salmon, pasta” gives us an idea that Trout might be some type of edible fish.
These are called Co-occurrence words. Google uses co-occurrences to determine semantic relationships between various words for a long time. This is exactly where TF-IDF comes to play.
Using a TF-IDF tool we can find various such Co-Occurrence suggestions based on their high TF-IDF score. This way we can optimise our content with such co-occurrences, hence making sure Google interprets the context of the document correctly and more specifically increase the weightage of some keywords as we desire.
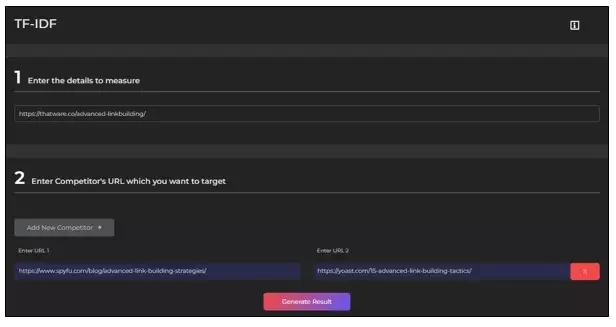
👉How to Use a TF-IDF Tool
- First, we enter the document URL we want to optimise.
- Then we enter 2-3 competitor URLs which are relevant and ranking for our target keywords.
- The tool will analyse the TF-IDF value of various words and identify those with high Tf-IDF Scores.
- It will show a chart of words weighed according to their TF-IDF value for each URL along with competitors.
- At last, it will suggest possible keywords which are not currently in our document that we can implement to make sure our document is optimised for all relevant co-occurrences.

👉Capitalising on Phrase-based Indexing by Leveraging Co-Occurring Words
This section is based on the same idea of Co-occurrence that we determined using the TF-IDF technique. Search engines like Google process millions of documents and search queries every minute. Hence it is not just able to index pages and keywords, but individual phrases too.
Hence it has the ability to predict that certain phrases occur with certain co-occurring phrases more often. Through the presence of these Co-occurring phrases together in a document, Google gets a better idea about the topic of focus for that particular document.
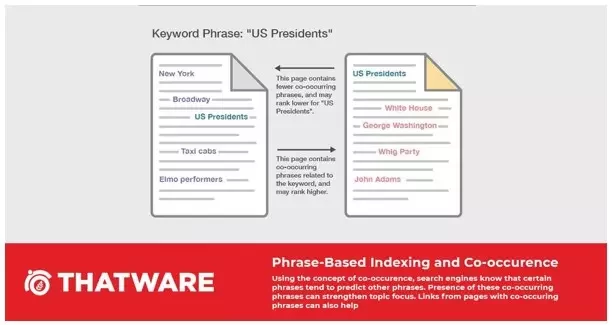
Hence if a tool gives us a set of all relevant co-occurring words around our target keyword, then all we have to do is to optimise our document with the relevant suggestions, hence we can indicate the context of the document more strongly and improve its SERP visibility for the intended set of queries.
👉Using a Co-occurrence Suggestion Tool to Optimise for Phrase Indexing
- First, we enter the document URL we want to optimise.
- Then we enter the target keyword.
- The Tool returns a set of co-occurring keywords commonly appearing for the target keyphrase on the internet.
- Optimising our document for these words will help us improve the SERP visibility of the page for the intended target keyphrase and relevant variations.
👉Topic Modelling with LDA Algorithm
Topic Modelling is the process of identifying distinct Topics or Words with topical significance in a group of text. It is essentially useful in the context of topic clustering. Despite several techniques that help us do this, most data scientists prefer the LDA method.
“LDA assumes documents are produced from a mixture of topics. Those topics then generate words based on their probability distribution. Given a dataset of documents, LDA backtracks and tries to figure out what topics would create those documents in the first place.”
Let’s visualise how the algorithm is able to identify this in real time. We ran an analysis on a set of SERP data for the keyword “yoga for beginners”.
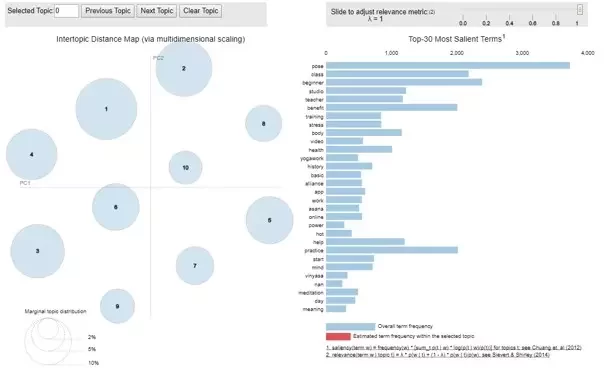
We visualized the output using the PyLDAvis package.
The left-hand side shows all the major identified topics covered in the document. If you are interested you can check how the visualisation works here. Basically the further away these topics are the more distinct it is. The right-hand side contains words that create these topics.
This is very interesting as, at a glance, we can understand what search topics is Google most interested in. It can also be used to make content recommendations all over the website and create long term content and topic model around which we can centre our content marketing strategies.
If this tool can give us so many content suggestions, imagine how much more efficient Google is in identifying topics and content hubs. Using the LDA algorithm to find content and topic suggestions can greatly enable us to find and optimise our pages on the basis of on-demand searchable content.
👉How do you know your Topic Modelling is Wrong?
Another Note to check is whatever we do, make sure our Web pages don’t look like this:
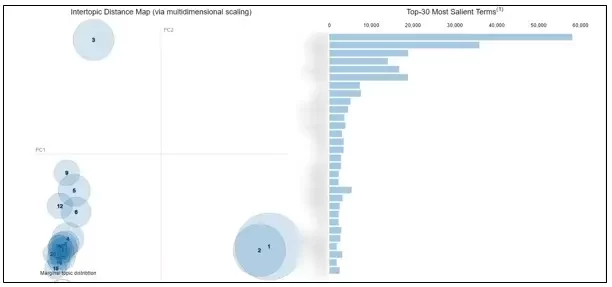
This excessive overlapping shows that the topics are not distinct enough, hence our original search term might not have enough semantically related but distinct subtopics.
👉Keeping Passages Unique using SMITH Algorithm Tool
Google recently published a research paper based on a new Algorithm that it claims, outperforms BERT. It stands for Siamese Multi-depth Transformer-based Hierarchical Encoder.
In a very basic sense, while BERT is able to understand the relationship between words and short sentences, the SMITH algorithm can understand and index long queries and passages.
There is no official confirmation of the SMITH rollout as a Google update. However, that does not stop us from assuming that Google doesn’t already use it.
👉How does it Work
The Algorithm is a set of rules that when satisfied increases the chances of it showing up in “passage ranking”. Here’s a basic outline of its working.
- We first take a long content with lots of passages. Probably a landing page of a website
- Then we check passage density in the content.
- Then we check the word count of each passage.
- Check any long-tail keywords if it’s available in the passage or not
- The check similarity distance between two passages.
- Check, If the similarity distance is high, has a long tail keyword available & satisfies the density criteria then the passage fulfils the SMITH algorithm in search engine optimization.
The rules to be satisfied are as follows:
- word count of passage: 30-70
- Long-tail keyword present = greater than 1
- Similarity Should be above 0.5
Below we have taken an example content from https://thatware.co/about-us/
After running this content through a python program that specifically checks the above three criteria and also measures the passage density.
👉Output
P.S: The code triggered 7 passages and whilst counting the word the stop words have been ignored!
- [There are many technical seo companies around the world but THATWARE is recognized as a leader in it.]
- Word count: 9
- Passage Density 4.411764705882353
- [Traditional marketing never provided a better opportunity in understanding the customer’s need. Moreover, with old school marketing, proper analysis and handling of data were a lot difficult. As a result, the ROI and efficiency were much lower as compared to the AI-based marketing model. 4 key benefits are highlighted here as to why seo services should use the ai model over the traditional approach.]
- Word count: 39
- Passage Density 19.11764705882353
- [AI gives a positive influence on SEO. With AI, corporations can boost the precision, efficiency, and performance of search engine optimization techniques, comprising the content generated for SEO. While some SEOs may fear that AI will replace their role, AI fulfils a supporting role as equipment. AI in SEO assists to enhance your recent SEO strategy by finding out chances, like related keywords. Its algorithms, as well as rate, help businesses expedite the method and improve the precision of keyword research, competitor analysis, search intent analysis, and much more.]
- Word count: 59
- Passage Density 28.921568627450984
- [There are many technical seo companies around the world but THATWARE is recognized as a leader in it. From advanced off-page services to professional seo services we are the market leader. ]
- Word count: 18
- Passage Density 8.823529411764707
- [Our main value-added proposition is ai seo optimization & business seo with cutting edge technologies such as data science, machine learning, semantic engineering, advanced search, and much more.]
- Word count: 23
- Passage Density 11.27450980392157
6. [While some of the SEOs may fear that AI will replace their role, AI fulfils a supporting role as an equipment.AI in SEO assists to enhance your recent SEO strategy by finding out chances, like related keywords. Its algorithms, as well as rate, help businesses expedite the method and improve the precision of keyword research, competitor analysis, search intent analysis, and much more. ]
- Word count: 39
- Passage Density 19.11764705882353
- [Its algorithms, as well as rate, help businesses expedite the method and improve the precision of keyword research, competitor analysis, search intent analysis, and much more. ]
- Word count: 17
- Passage Density 8.333333333333332
THE NUMBER OF LONG-TAIL KEYWORDS AVAILABLE IN THE PASSAGES IS AS UNDER:
For Passage 1:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 6
For Passage 2:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 14
For Passage 3:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 6
For Passage 4:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 7
For Passage 5:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 5
For Passage 6:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 3
For Passage 7:
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 2
👉THE SIMILARITY SCORE’S FOR THE PASSAGES HAVE BEEN GIVEN BELOW:
P.S: Every passage has been compared with their subsequent passages for a similarity comparison
For Passage 1:
- In passage 2, Score is 0.243
- With passage 3, Score is 0.214
- In passage 4, Score is 0.8
- With passage 5, Score is 0.172
- With passage 6, Score is 0.218
- With passage 7, Score is 0.162
For Passage 2:
- With passage 3, Score is 0.356
- In passage 4, Score is 0.283
- With passage 5, Score is 0.209
- With passage 6, Score is 0.341
- With passage 7, Score is 0.315
For Passage 3:
- In passage 4, Score is 0.21
- With passage 5, Score is 0.152
- With passage 6, Score is 0.915
- With passage 7, Score is 0.622
For Passage 4:
- With passage 5, Score is 0.197
- In passage 6, Score is 0.206
- In passage 7, Score is 0.159
For Passage 5:
- In passage 6, Score is 0.15
- With passage 7, Score is 0.219
For Passage 6:
- With passage 7, Score is 0.686
👉CONCLUSION AND FINAL RESULT
After checking each passage with our code we can say that only one paragraph follows closely the SMITH algorithm. Here it is:
[While some of the SEOs may fear that AI will replace their role, AI fulfils a supporting role as an equipment.AI in SEO assists to enhance your recent SEO strategy by finding out chances, like related keywords. Its algorithms, as well as rate, help businesses expedite the method and improve the precision of keyword research, competitor analysis, search intent analysis, and much more.]
- Passage similarity Score 0.915
- Number of long-tail keywords present: 3
- Word count: 39 (without stop words)
- Passage Density 19.11764705882353
Only the above passage fulfils all conditions of the SMITH algorithm here. Hence this passage has a higher chance of being used in Google passage ranking.
👉Google MUM Update | Refined Search
MUM or Multitask Unified Model is Google’s approach to answering complex search queries. We all agree that Google is able to surface good results when it comes to topic-based keywords or 3-4 gram queries. But when it comes to complex questions or queries, Google might not be able to share straight or always relevant results.
Let’s understand this with an example. Let’s say a hiker searches “I’ve hiked Mt. Adams and now want to hike Mt. Fuji next fall, what should I do differently to prepare?”
When you check the SERP result for this query? Here’s the result
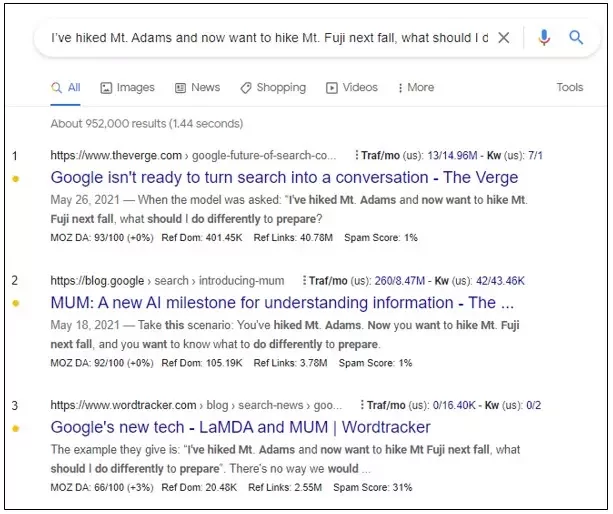
Since MUM has not rolled out yet, you can see that Google is not able to give any definite search result.
MUM is being developed to address just that. MUM not only will try to understand the context of the query better to surface relevant pages to answer the question definitively, but in addition MUM can surface insights based on a deep knowledge of the world, meaning it could point out information like fall is the rainy season on Mt. Fuji so the user might need a waterproof jacket.
“Today’s search engines aren’t quite sophisticated enough to answer the way an expert would. But with a new technology called Multitask Unified Model, or MUM, we’re getting closer to helping you with these types of complex needs. So in the future, you’ll need fewer searches to get things done.”
- Google hangout.
Perhaps the most important aspect of MUM is that it can understand queries across content formats and languages. Hence it is claimed to be better prepared to answer complex queries than BERT could ever do.
“MUM not only understands language, but also generates it. It’s trained across 75 different languages and many different tasks at once, allowing it to develop a more comprehensive understanding of information and world knowledge than previous models.
And MUM is multimodal, so it understands information across text and images and in the future, can expand to more modalities like video and audio.”
- Google hangout
👉How should we Prepare for the MUM Update?
When fully implemented MUM will have a huge impact on the way search results are delivered. That being said it is to be noted that MUM is an opportunity and not a threat. Since MUM is multi-modal and can understand and find context between searches across different formats, it will open much more avenues for content marketing than ever before.
👉Classic SEO will still Rock
Although the considerations over how search results will deliver will change, still you will have to provide all the information to Google that you can about your content. There’s no better way to do that but to keep following Google SEO Webmaster guidelines, and create a schema for different kinds of content. Ultimately the goal is to provide as much information to Google as possible.
👉Local SEO might be a Priority
Since complex searches tend to be local, hence optimizing for MUM would primarily mean optimising for complex and specific searches. Hence Local SEO will be vital to boost your rankings and have a greater chance to get organic visibility not just in Google Maps but in various other formats as well.
👉Create Content-focused around Long-tail Keywords and Specific Queries
With Google preparing itself to answer specific queries with MUM updates, it will now become vital to expand our content marketing efforts. Make sure to create content for all possible and related search queries around your target keyphrase.
Also, it will create content in multiple formats and languages. Since MUM is multi-modal it understands information across text and images and in the future, can expand to more modalities like video and audio.
Hence for specific queries, MUM can surface relevant videos, pictures and even short-form content to not only deliver the best possible answer to the user but also room for deeper exploration that might further satisfy his intent.
All the more reason to stay omnipresent in our content marketing efforts.
👉Leverage Image Search in Google Lens
Users may presently execute a few basic image-based searches with Google Lens, such as finding things for sale online based on a photo of the product. The MUM upgrade will expand these capabilities by allowing users to search for products that have the same pattern, colour, or shape as the reference image, as well as add more image query criteria.
Remember that MUM will remove language as a criterion in search, allowing non-native clients access to foreign marketplaces. Users will be able to search for extremely precise products based on their individual preferences, with more alternatives than ever before. This is an excellent opportunity for e-commerce companies to accommodate the increased demand. Include a lot of high-quality product photos.
Determining Keyword Relevance to Page Content using Cosine Similarity
👉Preface to Word Vectors
Word vectors or word embedding helps to better understand the text as it not only shows the word but helps to determine some context around it. You can learn how vectors can be used to represent real-world concepts here.
Vectors work by mapping the position of each token in different sentences and by calculating the probability of finding a given token in the same position.
As a simple example lets take the query “I would love to hang out with my _______”.
From our perception the blank word would be “friends, family, boyfriend, BFF etc.” However one can expect its most certainly not “pants” or “drills”. Good thing is Google understands it too.
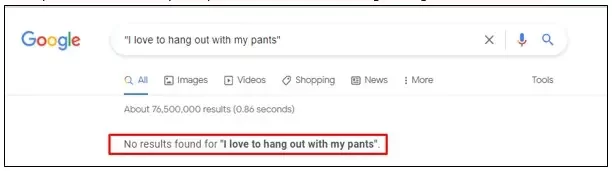
In a multidimensional space, words like boyfriend, BFF, friends would appear much closer rather than words like “pants” and “drills”. Hence clusters of words can be used as vectors and distances can be calculated between them.
Another reason why the vectorized text is great is that vectorization takes into consideration the sentence’s syntactical structure‡. Word embeddings capture not only the lexical similarity but also syntax and some degree of semantics.
👉Meet Cosine Similarity
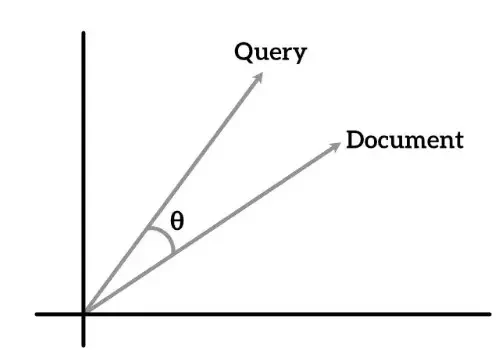
The biggest novelty of using the vector approach is that with word embeddings we can use distance or cosine distance to discover if documents, tokens, or sentences are similar.
It merely consists of calculating the distance or cosine distance to discover if queries and documents are similar. A smaller angle means more similarity.
👉Using Cosine Similarity Tool to find Content Relevance between Focus Keyword and Document
- Enter a document and its focus keyword.
- Enter competing URLs to compare their relevancy with ours.
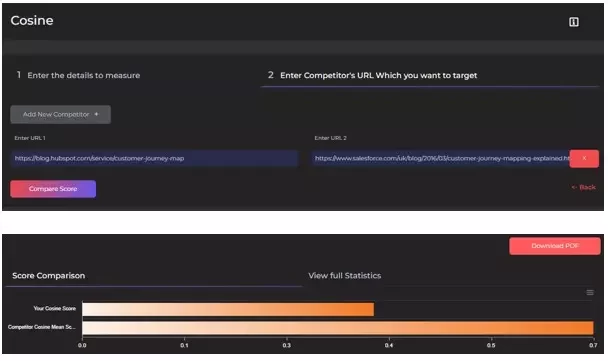
Lower our cosine angle more the relevance of the Keyword to the document.
👉Semantic Proximity and Semantic Score
Semantic proximity measures the distance between similar words or searches terms within a specific document set. It works on a different algorithm which is known as Euclidean cosine.
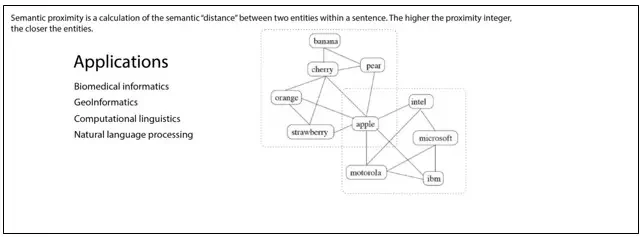
Here’s an example that illustrates its ability more clearly.
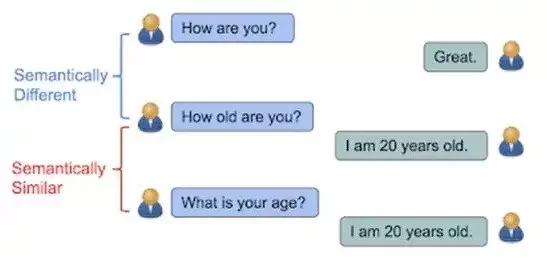
In seo, semantic proximity is very important. As per the generic rule – each of the semantic keywords within a document set should be equally spaced and balanced.
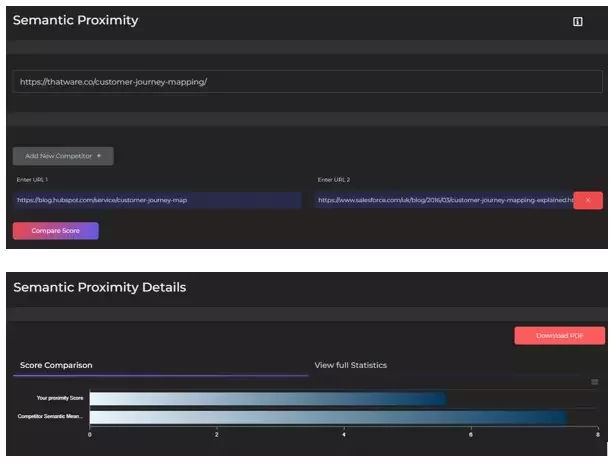
👉How to use the Semantic Proximity Tool
- Add the URL needed to be analysed.
- Then check if the landing page proximity score is less than the mean value of the competitor’s score. If our score is less than that of competitors, then our semantic proximity is optimised. Else we need to re-optimize the content to get an ideal score.
👉Semantic Score
Semantic is an overall score assigned to a keyword to validate its intent specification in search. It uses the different Semantic-based algorithms like LDA, Cosine Similarity, and Word cloud to have an overall idea of semantic relevance.
It is to be noted that having a good semantic score of your Keyword to your content is not a ranking factor. It only highlights the level of semantic relevance of your content to the target keyword which may work in favour of you since Google AI algorithms claim to populate SERPs on the basis of semantic relevance.
👉How it Works
- We take the landing page and calculate the search term’s frequency, relevancy score, and cosine similarity score by making a word cloud, LDA, and Cosine similarity algorithm.
- Then repeat the above thing for your competitor to check its score. Take a single competitor only!
- Now test for conditions. If the landing page score is greater or less than the competitors. If the score is greater than no action is needed else suggest adding the search terms on the landing page.
👉Are Keywords Still Relevant?
At the beginning of everything, there were only keywords. The idea was simple, if you wanted to rank on a particular search query it was imperative to strategically place all relevant keywords along with the target keyword in your document and voila! Based on the competition, you are sure to get a ranking.
Despite significant advances of Google in semantic search it is still safe to say that the influence of keywords is not totally dead. This is because keywords are fundamental in understanding what the user is searching for. This is a concept so fundamental that cannot possibly be eroded away.
Understanding the user’s query starts with Keywords, hence it is fundamentally imperative to have good keyword research before beginning a website.
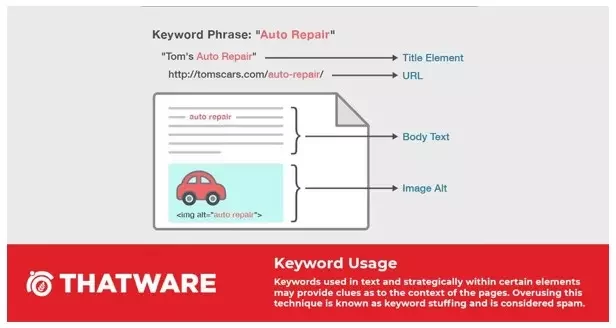
This leads us to evaluate Keyword density. Although there is no official statement from Google regarding Keyword density, it is generally a best practice among SEOs to maintain a keyword density of 2%.
However, let me warn you that maintaining a keyword density doesn’t mean using the same phrase this many times. It simply is a benchmark that can be used to include helpful semantically related keywords in your document but not to overuse it.
You can determine Keyword Density in a document using our keyword density tool.
👉Analysis:
By counting word occurrences the numbers of occurrences represent the importance of the word. More frequency means more importance. First, we tokenize each and every word in the text document then we use the tokenized words for each observation and find out the frequency of each token. After that, we can determine the frequency of a particular word which will, later on, indicate the relevancy of a keyword to a particular site.
Taking a corpus (collection of documents) which contains text related to the site, we vectorized all the words in a corpus and separated them, each and word has a value (integer) that indicates their occurrences, later on, we have created a visualisation to clear out which word stands for out the most. In the end, to get a fine anchor text from particular content we extracted the highest most frequently occurring words from the corpus.
👉Bag of Words
The bag-of-words model is an information retrieval approach used to extract keywords from large volumes of data while also measuring how frequently those keywords appear within a document.
In SEO, this model is commonly applied to generate tags and compare them with competitors’ tags, helping identify and include missing search terms that competitors may already be targeting.
It’s important to note that the more relevant search terms you optimize for, the greater your potential visibility across the SERPs.
👉Analysis:
By counting word occurrences, we can determine the relative importance of each word—higher frequency generally indicates greater importance. The process begins by tokenizing every word in a text document. These tokens are then analyzed across each observation to calculate how often each one appears. This frequency helps identify how relevant a specific keyword is to a particular website.
Next, we take a corpus (a collection of documents) containing text related to the site and vectorize all the words within it. Each word is separated and assigned an integer value that represents its number of occurrences. We then create a visualization to clearly highlight which words appear most prominently. Finally, to derive well-optimized anchor text from the content, we extract the most frequently occurring words from the corpus.
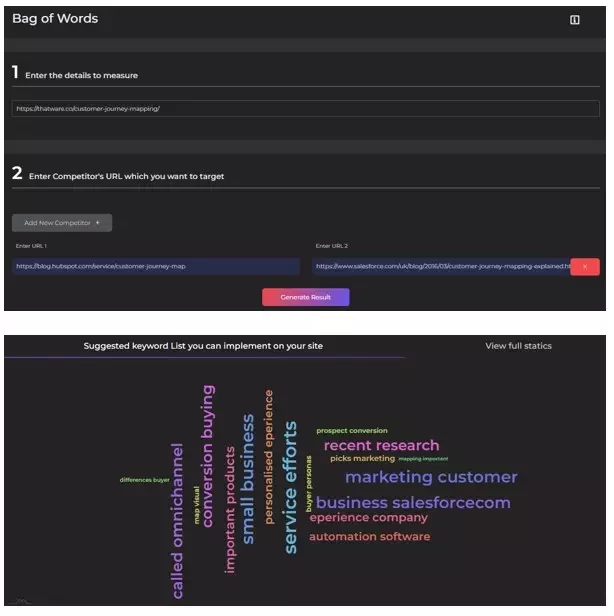
👉How does it Work
- Create a model for the landing page you want to target and extract the top 10 words based on frequency.
- Apply the same process to competitor pages, identifying the top 10 high-frequency words for each competitor.
- Merge all competitor high-frequency terms to form a single superset of word tags, ensuring the list is unique with no repeated words.
- Compare your landing page’s word set against this final superset and identify the terms missing from your page.
- The result is a refined list of unique terms, which can then be added to your landing page to better optimise the overall context.
👉Is Sentiment Analysis a Ranking Factor?
Googler Bill Slawski was once asked a similar question, and the following was his response:
“Sentiment is like a flavour, like vanilla or chocolate. It does not reflect the potential information gain that an article might bring.
Information gain can be understood by using NLP processing to extract entities and knowledge about them, and that can lead to a determination of information gain.
The sentiment is a value that doesn’t necessarily reflect how much information an article might bring to a topic.
Positive or negative sentiment is not a reflection of how much knowledge is present and added to a topic.”
– Bill Slawski – Google Expert
Sentiment represents the emotional tone conveyed by the writer or speaker in a piece of content. While sentiment analysis plays a role in understanding the broader context of topics and search queries, Google has consistently stated that it does not apply sentiment bias when generating SERP results.
To illustrate this, let’s look at a simple example. Consider the following two search queries:
“are reptiles good pets”
“are reptiles bad pets”
At their core, both queries are asking the same fundamental question: whether reptiles make good pets. Based on the assumption of no sentiment bias, one might expect the same SERP or featured snippet to appear for both searches. In reality, however, this is not what happens.
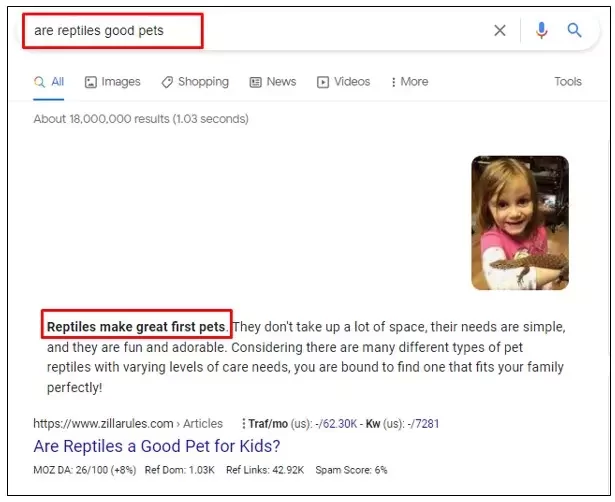
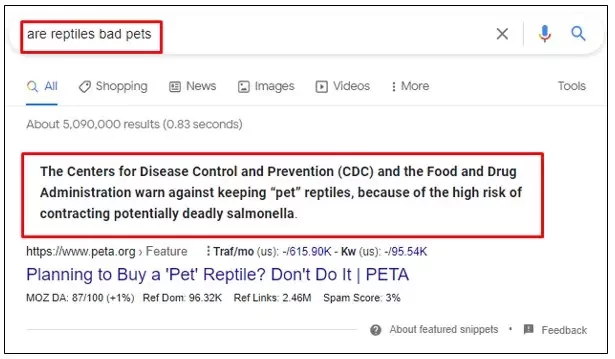
As you can observe, the featured snippet displayed for the query “are reptiles good pets” presents a very different viewpoint compared to the result shown for the query “are reptiles bad pets.”
From these featured snippets, it becomes evident that Google is ranking pages whose sentiment—or at least contextual alignment—matches what the user is explicitly searching for. This behavior appears to contradict Google’s earlier stance on not applying sentiment bias.
Google expert Danny Sullivan addressed this issue by stating:
“…people who search for “are reptiles good pets” should get the same featured snippet as “are reptiles bad pets” since they are seeking the same information: how do reptiles rate as pets? However, the featured snippets we serve contradict each other.
A page arguing that reptiles are good pets seems the best match for people who search for them being good. Similarly, a page arguing that reptiles are bad pets seems the best match for people who search for them being bad. We’re exploring solutions to this challenge, including showing multiple responses.”
The key takeaway here is that Google is actively exploring ways to present multiple perspectives or solutions for such queries.
👉 So how do we analyze the Sentiment of Content?
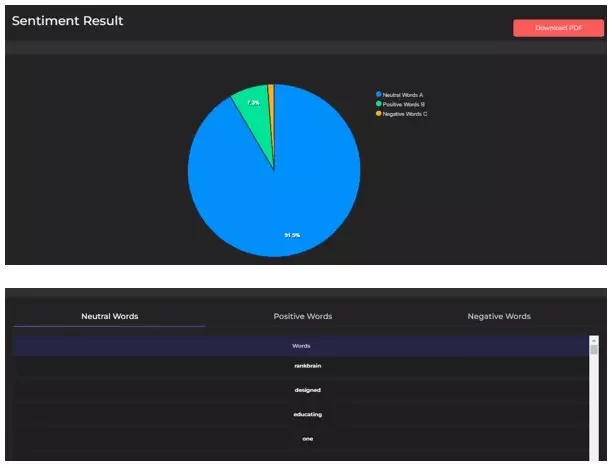
The most effective approach is to use a sentiment analysis tool. At Thatware, we have developed a solution that identifies different types of words within a document based on sentiment—positive, negative, and neutral.
Based on this analysis, the tool then generates an overall sentiment score for the content, helping you better understand how your message aligns with user intent.
Entity Salience
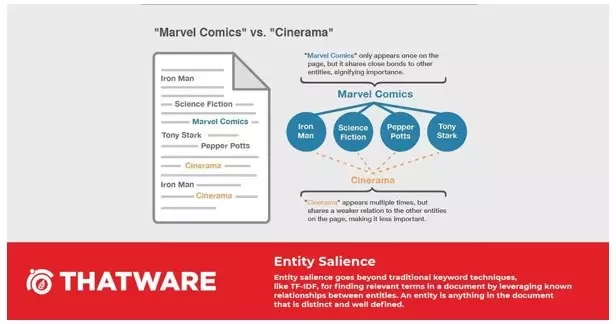
In the earlier sections, we discussed how Google began recognizing entities rather than just keywords with the introduction of the Hummingbird algorithm. Google’s primary objective has always been to accurately understand the context behind search queries.
One method Google uses to achieve this is a technique known as entity salience. This approach goes far beyond traditional models like TF-IDF, which focus mainly on identifying relevant keywords or phrases. Instead, entity salience leverages the existing relationships between multiple entities within a document to determine contextual importance.
The significance of entity salience can best be analyzed using Google’s Knowledge Graph API. For example, when you enter a query such as “Marvel,” the API returns a list of related entities and assigns each one a confidence value—commonly referred to as the salience score.
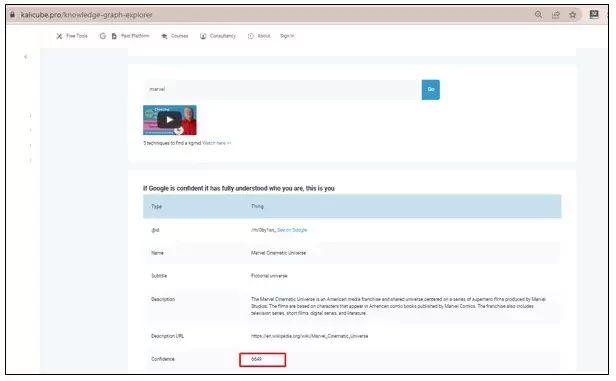
Although Google has never officially defined what a salience score represents, here’s what we believe it is used to measure:
- How confident Google is that the entity identified truly matches the query (in other words, whether the string of characters has been correctly mapped to the intended entity).
- In cases of ambiguity, which entity Google considers the most likely match based on its interpretation of user intent.
- When the identified entity does not directly correspond to the query, how closely related that entity is to others connected to the query.
It’s important to note that salience scores alone do not imply that Google relies on them to construct SERPs. Google uses a combination of over 200 ranking factors—along with additional signals—to generate search results for any given query.
👉 What SEOs Can Do?
Based on the insights above, we can consider salience as a type of authority score. Therefore, the natural goal of SEO efforts should be to gradually improve the salience score over time.
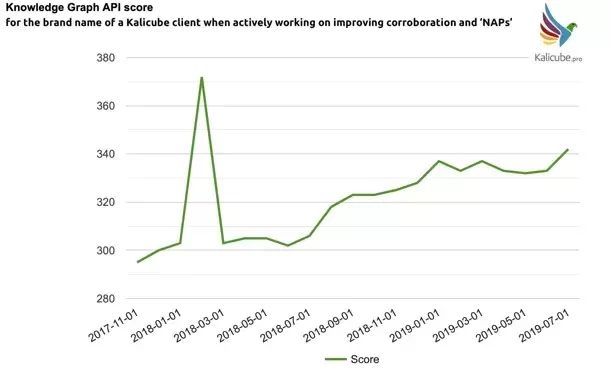
This aligns closely with Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines, where higher salience scores often reflect the trustworthiness and credibility of a brand or content. Here’s how salience scores can be effectively enhanced:
- From research and practical experience, we’ve observed that a brand’s salience score tends to rise with more references across the web. This means that backlinks, along with related signals such as social presence and the volume of searches for the brand, can positively impact salience.
Salience scores are also highly responsive to fresh popularity, meaning that recent mentions, trends, and engagement can further boost a brand or content’s perceived authority.

