SUPERCHARGE YOUR Online VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
Zombie pages are a common issue affecting websites, especially those with a vast amount of content. These are pages that provide little to no value to users or search engines but still get indexed, leading to inefficiencies and potential ranking penalties. This guide breaks down the concept of zombie pages, their impact on SEO, and actionable strategies to deal with them effectively.
1. Introduction: Understanding Zombie Pages
Zombie pages are the excess pages indexed in search engines that provide little or no value to users. These pages are identified when you perform a site-specific search query such as site:xyz.com. In many cases, the number of pages indexed in search engine results pages (SERPs) exceeds the actual valuable content your website has.
For instance, if your website hosts 1,000 meaningful pages but the SERPs show 1,500 indexed pages, the additional 500 are likely zombie pages. These surplus pages dilute your site’s overall quality score, reduce crawl efficiency, and can negatively impact organic traffic.
By eliminating zombie pages, you can streamline your website’s structure, improve crawl budgets, and increase the chances of driving more organic traffic to the pages that truly matter. In essence, having fewer but higher-quality pages reduces SEO challenges and improves your site’s overall performance.

2. Mostly seen Zombie Pages:
Zombie pages typically fall into the following categories:
1. Pages with Thin Content
- These pages contain minimal or irrelevant content that doesn’t provide value to users or search engines. Examples include:
- Placeholder pages.
- Auto-generated pages with little text.
- Pages with low word counts and no meaningful insights.
2. Search Result Pages
- Some websites mistakenly allow internal search result pages to be indexed. These pages often duplicate content from other parts of the site and provide no unique value to users coming from search engines.
3. Category and Tag Pages
- Blogs and content-heavy websites often create numerous category and tag pages to organize their content. However, when these pages are indexed without meaningful descriptions or unique content, they become zombie pages.
4. Archive Pages
- Monthly or yearly archive pages on blogs and forums are common culprits. These pages usually offer redundant information and are rarely useful for users or search engines.
5. Pages That Serve No User Value
- Examples include outdated policy pages, expired promotions, or test pages accidentally left accessible to search engines.
Zombie pages not only clutter search engine indexes but also mislead users by presenting irrelevant or low-value results.
3. Elimination process:
Removing zombie pages is a critical step in improving your site’s SEO health. Here’s how you can systematically eliminate these pages:
1. Using Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool to identify and de-index zombie pages.
- Navigate to the Index Coverage report to identify excluded or low-performance pages.
- Use the Remove URLs tool to temporarily remove zombie pages from Google’s index.
- Disavow unnecessary pages using the Disavow Tool for low-quality backlinks pointing to zombie pages.
2. Robots.txt
- The robots.txt file allows you to disallow search engine bots from crawling specific pages.
- Add directives like:
txt
Copy code
Disallow: /category/
Disallow: /tag/
Disallow: /search/
This prevents zombie pages from being crawled and indexed.
3. XML Sitemap
- Regularly update your XML sitemap to ensure only high-value pages are included.
- Remove zombie pages from the sitemap to signal search engines to stop prioritizing them.
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush to audit your sitemap for irrelevant or outdated URLs.
4. Meta Robots Tags
- For pages that should be accessible but not indexed, add a noindex meta tag:
html
Copy code
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
- Apply this to pages like search results, thin content pages, or outdated content.
5. Monitor and Reevaluate
- After eliminating zombie pages, monitor your site’s performance using Google Analytics and Search Console.
- Regularly conduct audits to identify and address new zombie pages that might emerge as your site grows.
4. Merger Process:
In some cases, zombie pages contain partial value or unique content that can be repurposed. Instead of outright elimination, consider merging these pages with existing, high-performing pages.
Steps to Merge Zombie Pages Effectively:
1. Identify Valuable Content on Zombie Pages:
- Analyze zombie pages to determine if they contain any useful information, keywords, or backlinks.
2. Select a Relevant Destination Page:
- Find an existing page on your website that aligns with the topic or intent of the zombie page.
3. Consolidate Content:
- Incorporate the valuable portions of the zombie page into the destination page, ensuring a natural and seamless integration.
4. Implement 301 Redirects:
- Redirect the zombie page to the updated destination page to retain any link equity and avoid 404 errors.
5. Update Internal Links:
- Replace internal links pointing to the zombie page with links to the merged page.
6. Communicate Changes to Search Engines:
- Update your XML sitemap and submit it to Google Search Console to ensure search engines recognize the changes.
By repurposing zombie pages, you not only declutter your site but also strengthen the authority and relevance of your main pages.
Here is a real-time process for fixing and eliminating Zombie Pages
Zombie pages are pages on a website that generates little or no traffic and are difficult or impossible to access through search engine results.
The performance difference between Normal live pages and Zombie page pages is easy to spot. Take a look at the following metrics:
- Total visits (Pageviews)
- Unique Pageviews
- Avg. Time on Page
- Bounce Rate
- Exit rate
- Pages per session (Pages/Session)
Step 1:
From Google analytics, we need to go to Behavior à then Site Content and then All pages data.
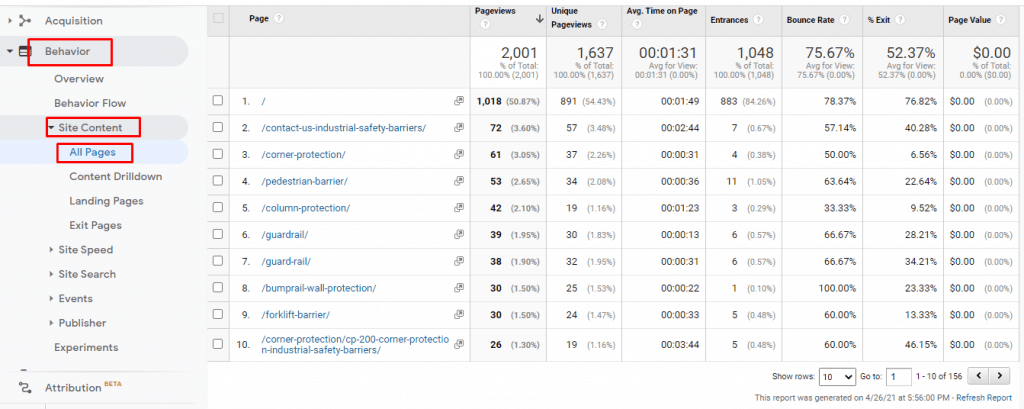
Step 2:
Need to export the full file on excel:
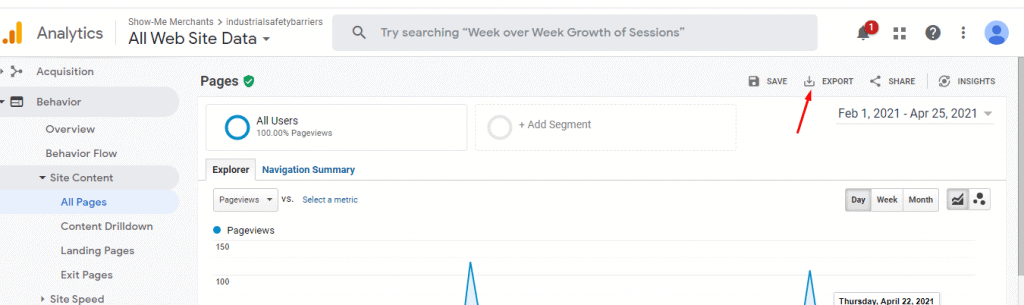
Step 3:
Shortlist the Avg. time from smallest to largest to get the low-timing pages. As shown below, the low-time pages have a high bounce rate:
As shown below, the low-time pages have a high bounce rate!
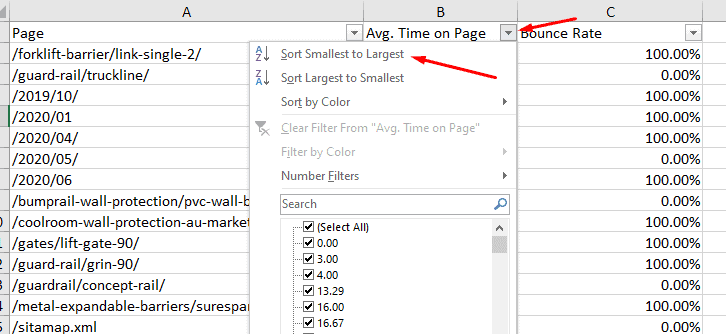
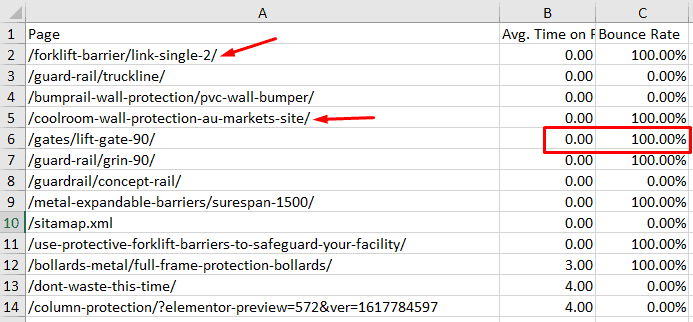
Suggestion:
We need to delete or redirect those pages to relevant pages to reduce the bounce rate of the website.
Best Practices for Preventing Zombie Pages
A. Establishing Content Guidelines and Governance Policies
- Define Clear Guidelines for Content Creation, Publication, and Maintenance:
- Outline specific criteria for creating new content, including tone, style, formatting, and target audience.
- Establish standards for content quality, accuracy, and relevance, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and brand identity.
- Provide guidelines for content maintenance, including procedures for updating, archiving, and retiring outdated or obsolete content.
- Establish Roles and Responsibilities for Content Creators, Editors, and Administrators:
- Clarify the roles and responsibilities of individuals involved in the content creation and management process.
- Assign accountability for content ownership, review, and approval at each stage of the content lifecycle.
- Define workflows and escalation procedures to streamline content creation, review, and publication processes.
- Implement a Content Review and Approval Process to Ensure Quality and Relevance:
- Develop a structured workflow for content review and approval, including designated checkpoints and sign-off procedures.
- Involve subject matter experts, stakeholders, and legal/compliance teams in content review processes as needed.
- Establish criteria for evaluating content quality, relevance, accuracy, and compliance with regulatory requirements or industry standards.
- Regularly Communicate and Educate Stakeholders About Content Standards and Best Practices:
- Provide ongoing training and resources to content creators, editors, and administrators on content guidelines, standards, and best practices.
- Foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement by promoting awareness of content governance policies and procedures.
- Encourage open communication and collaboration among team members to share insights, feedback, and lessons learned.
B. Regularly Updating and Refreshing Content
- Schedule Regular Content Audits to Identify Outdated or Irrelevant Pages:
- Establish a cadence for conducting content audits, considering factors such as website size, industry dynamics, and content velocity.
- Utilize automated tools and manual reviews to identify pages with outdated information, broken links, or low engagement.
- Document audit findings and prioritize action items based on content relevance, strategic importance, and resource constraints.
- Set Up a Content Calendar to Plan and Schedule Updates and Revisions:
- Develop a centralized content calendar to track planned updates, revisions, and new content initiatives.
- Allocate resources and assign responsibilities for content maintenance and revision activities according to the content calendar.
- Incorporate key dates, events, and seasonal themes into the content calendar to ensure timely and relevant updates.
- Monitor Industry Trends and Audience Preferences to Ensure Content Remains Current and Valuable:
- Stay informed about industry trends, market developments, and emerging topics of interest to your target audience.
- Monitor competitor activity and benchmark your content against industry peers to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
- Leverage data analytics and audience insights to track content performance metrics and identify areas for optimization.
- Encourage User Feedback and Engagement to Identify Areas for Improvement and Updates:
- Solicit feedback from website visitors through surveys, polls, feedback forms, and social media channels.
- Monitor user engagement metrics such as bounce rate, time on page, and click-through rate to assess content effectiveness.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement by actively responding to user feedback and incorporating user-generated content ideas and suggestions.
C. Implementing Canonical Tags and Redirects to Prevent Duplication
- Utilize Canonical Tags to Indicate Preferred Versions of Similar Content or Pages:
- Implement canonical tags to signal to search engines the preferred URL for indexing when multiple URLs contain similar or duplicate content.
- Ensure consistency in canonical tags across all versions of duplicate content to avoid confusion and maintain search engine visibility.
- Implement 301 Redirects to Consolidate Multiple URLs That Lead to the Same Content:
- Set up 301 redirects to redirect traffic from obsolete or duplicate URLs to the canonical version of the content.
- Regularly audit website URLs and update redirect rules as needed to ensure all redirects are functioning correctly.
- Regularly Check for Duplicate Content Issues and Address Them Promptly to Maintain Search Engine Visibility:
- Use website auditing tools and search engine webmaster tools to identify instances of duplicate content.
- Take immediate action to consolidate duplicate content by implementing canonical tags, redirects, or content consolidation strategies.
- Ensure Consistency in URL Structure and Internal Linking to Prevent Confusion and Duplication:
- Establish a standardized URL structure and naming convention to ensure consistency and clarity across the website.
- Implement robust internal linking practices to guide users and search engine crawlers to the most relevant and authoritative content.
- Monitor and update internal links regularly to reflect changes in content structure and navigation.
D. Monitoring and Maintaining Content Quality Over Time
- Set Up Analytics and Tracking Systems to Monitor Key Performance Metrics for Content:
- Configure web analytics tools to track content performance metrics such as traffic, engagement, conversions, and bounce rate.
- Establish custom dashboards and reports to monitor content performance trends and identify areas for improvement.
- Establish Benchmarks and Goals for Content Quality, Engagement, and Effectiveness:
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring content quality, relevance, and user engagement.
- Set realistic goals and benchmarks for content performance based on industry benchmarks, historical data, and organizational objectives.
- Conduct Regular Content Reviews and Assessments to Identify Areas for Improvement:
- Schedule periodic content reviews and assessments to evaluate content quality, accuracy, relevance, and alignment with business objectives.
- Use content audits, user feedback, and performance metrics to identify areas for content optimization, refinement, or retirement.
- Stay Vigilant for Changes in Search Engine Algorithms and Industry Standards That May Impact Content Quality and Relevance:
- Stay abreast of updates and changes to search engine algorithms, content ranking factors, and best practices for SEO and content optimization.
- Monitor industry publications, forums, and conferences for insights into emerging trends, technologies, and strategies relevant to content management and optimization.
By implementing these best practices for preventing zombie pages and maintaining content quality and relevance over time, websites can enhance their search engine visibility, user experience, and overall effectiveness in achieving business objectives.
End Note
The content outlines the concept of zombie pages and provides a comprehensive guide on identifying, dealing with, and preventing them. It highlights the importance of addressing zombie pages to maintain a high-quality website and maximize organic traffic. By offering strategies such as content audits, keyword analysis, user engagement metrics evaluation, and implementation of canonical tags and redirects, it equips website owners with the tools necessary to tackle this issue effectively.

