Get a Customized Website SEO Audit and SEO Marketing Strategy
Traditional search no longer works the way businesses and marketers once understood it. For years, online visibility meant targeting specific keywords, optimizing pages for algorithms, and competing for those coveted blue links on a search results page. That approach is quietly fading. Today, users ask full questions and expect direct, concise answers rather than a list of websites. Modern search systems interpret meaning, context, and intent before determining which information to display. As a result, simply appearing on a results page is no longer enough—your brand must be recognized as a reliable source of insight. Instead of clicking through multiple links, users increasingly receive a single, consolidated response that feels authoritative and complete. Achieving this level of relevance requires strategic LLM optimization, ensuring your content clearly communicates expertise, maintains consistent visibility across public sources, and aligns closely with real user intent.

The result is a transformed search landscape where authority outweighs optimization gimmicks and clarity matters far more than clever phrasing. Brands that continue to rely solely on keyword placement and ranking positions are gradually losing relevance—not because their content lacks quality, but because it was designed for a system that no longer defines how people discover information. Partnering with a Custom LLM agency can help ensure your content aligns with modern search behavior, establishing your brand as a trusted and authoritative source.

From Keywords to Intent: How AI Search Thinks Differently
The Limits of Keyword-Based Thinking
For a long time, search success depended on identifying the right keywords and placing them strategically across a page. This approach worked because older search systems matched words more than meaning. If a page repeated the same phrase often enough and earned enough links, it stood a good chance of appearing at the top. Over time, this led to predictable practices where content was shaped around search terms rather than real questions. While this method brought visibility, it rarely ensured that users found the most helpful or complete information. As search behavior evolved, the gap between what users wanted and what keyword-focused pages delivered became increasingly obvious.
Search Has Shifted Toward Understanding Purpose
Modern search no longer interprets queries as isolated keywords. Instead, it focuses on understanding the underlying intent behind each search. A user typing a short phrase could be researching, comparing options, or seeking expert guidance. Even when two people enter the same words, their goals may be entirely different. Today’s search systems strive to detect this purpose before deciding which content to surface. As a result, content built solely to match phrases often falls short, while content that explains a topic comprehensively and thoughtfully gains preference. Collaborating with an LLM model creation agency can help brands develop content that aligns with real user intent and stands out in this intent-driven search environment.
How Intent Is Interpreted
Intent interpretation involves reading between the lines of a query. A search for “best accounting software” is not just about a list of names. It suggests comparison, trust, and experience. A search for “how accounting software works” points to learning and explanation. Modern systems adjust the type of information they surface based on these signals. They favor sources that match the implied goal, not just the words used. This is why some pages with fewer exact keyword matches can outperform highly optimized ones if they answer the underlying question more completely.
Queries Are Refined Before Answers Are Chosen
Another important shift is that the original query is rarely used as it is. It is internally clarified and expanded to better reflect what the searcher is likely trying to achieve. This refined version guides which sources are considered relevant. As a result, content that relies on narrow phrasing can be excluded, while content that covers the broader topic clearly and logically is included. This refinement process rewards structure, clarity, and context over repetition.
Why Context Matters More Than Frequency
Context now plays a central role in discovery. A page that explains a subject step by step, defines terms, and connects ideas signals a stronger understanding than a page that simply repeats phrases. Context helps search systems determine whether a source genuinely understands a topic or is merely trying to attract attention. This is also why long-form educational content often performs better than short promotional pages. It provides the surrounding detail needed to establish relevance and trust.
The Role of Language and Natural Expression
Natural language has become an advantage rather than a risk. Writing that mirrors how people actually speak and ask questions aligns better with intent-focused search. Overly mechanical phrasing or forced repetition can signal low value. Clear explanations, simple examples, and logical flow make it easier for systems to match content with real questions. This encourages writers to focus on communication rather than optimization tricks.
What This Means for Content Creators
Shifting from keywords to intent requires a change in mindset. Instead of asking which phrases to target, creators must ask which problems they are solving. Content should aim to answer questions fully, anticipate follow-up concerns, and provide clarity rather than persuasion alone. When intent is met, visibility follows naturally. In this new search environment, relevance is earned by usefulness, not by frequency of terms.
Inside the LLM Search Console: The Invisible Decision Layer
Dive into the mechanics of modern search and discover how large language model optimization influences the invisible decisions that determine which content is seen and trusted.
What Happens Before an Answer Appears
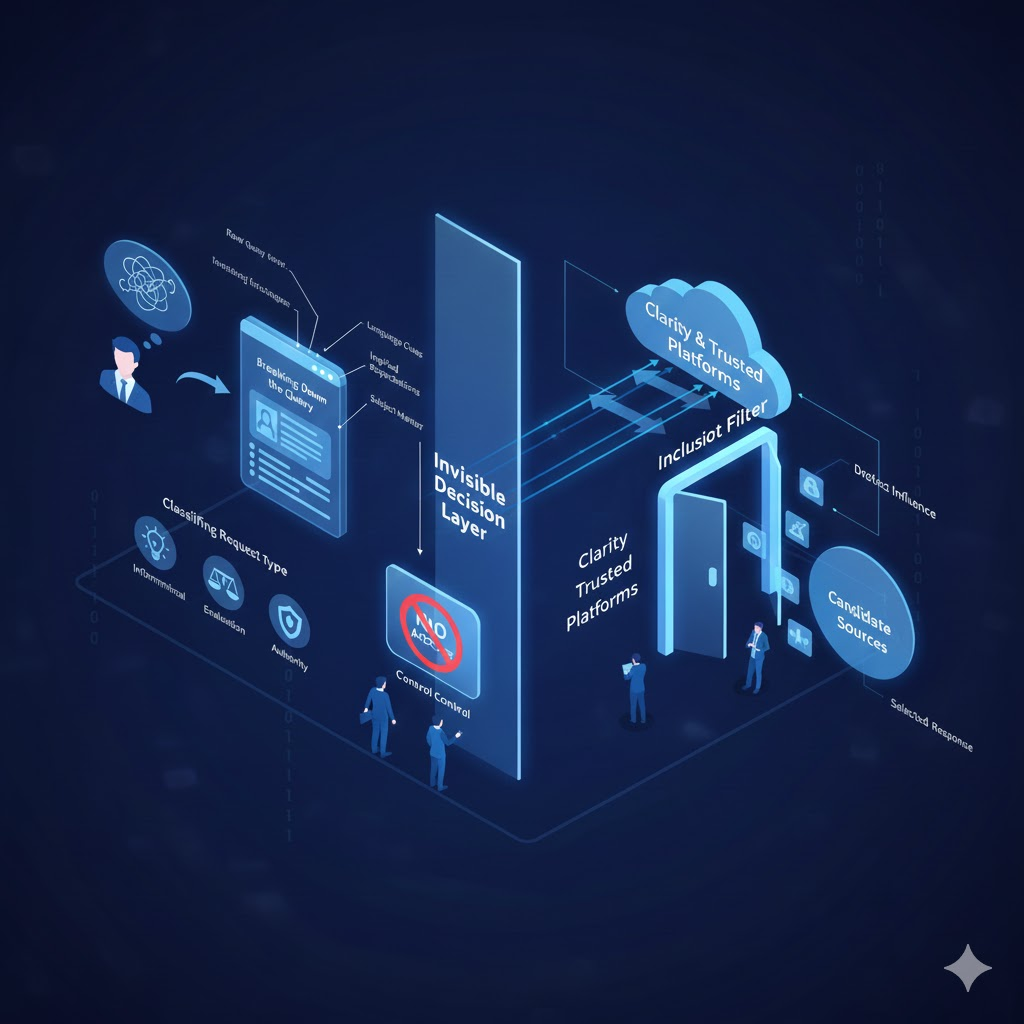
When a user submits a question, the response they see is the result of several decisions made long before any text is shown. There is an internal evaluation layer that examines the query and determines how it should be handled. This layer does not display results or rank pages. Its role is to decide what kind of response is appropriate and what sources should even be considered. Most users never see this process, yet it strongly influences which brands and explanations make it into the final answer.
Breaking Down the Query
The first task of this decision layer is to analyze the structure and meaning of the question. It looks at language cues, implied expectations, and subject matter. A short query may still contain signals that point to learning, comparison, or decision-making. This breakdown helps the system understand whether the user wants a definition, a recommendation, or a deeper explanation. Without this step, answers would be generic and often mismatched with intent.
Classifying the Type of Request
Once the query is understood, it is categorized based on its purpose. Some questions are informational and require clear explanations. Others involve evaluation and require balanced perspectives. There are also queries that demand authority, where accuracy and reliability matter more than speed. This classification determines how strict the system will be when selecting sources. Higher-stakes queries require stronger signals of credibility and consistency.
Why Brands Cannot Directly Control This Layer
This internal decision process cannot be influenced through direct optimization or formatting tricks. There is no setting to adjust and no keyword density to fine-tune. What influences this layer is the overall clarity of a brand’s public content, how often it appears in relevant contexts, and whether its explanations align with real-world understanding. Attempts to manipulate this process usually fail because the system prioritizes coherence over tactics.
Indirect Influence Through Clarity and Consistency
Although this layer cannot be controlled, it can be influenced over time. Brands that explain their domain clearly, publish consistent viewpoints, and maintain a stable presence across trusted platforms become easier to classify and trust. Their content fits naturally into the decision framework, making it more likely to be selected when relevant questions arise.
Why This Layer Matters More Than Rankings
Traditional rankings focus on position, but this invisible layer decides inclusion. If a source is not selected here, it never reaches the final response, regardless of how well it performs elsewhere. Understanding this shift helps explain why visibility today depends less on placement and more on being recognized as a reliable source of understanding.

Refined Questions: Why AI Never Uses the User’s Exact Query
Query Refinement Explained
When a user enters a search query, it is rarely treated as a final instruction. Instead, the system interprets it as a starting point. People often type quickly, omit context, or simplify what they are really trying to understand. To bridge this gap, the query is internally clarified before any information is selected. This clarification process focuses on meaning rather than wording. It attempts to identify what the user is actually trying to achieve, not just what they typed. A short phrase might represent a complex need, while a long question might still lack specificity. Refinement helps translate human language into a clearer request that can be matched with reliable explanations. Effective LLM Optimization ensures this refinement process translates human language into a clearer request that can be accurately matched with reliable explanations.
Semantic Expansion vs Keyword Matching
Traditional search relied heavily on matching exact phrases. If a page repeated the same words, it was considered relevant. Refined questioning works differently. Instead of looking for identical terms, it expands the topic into related concepts, definitions, and relationships. For example, a query about “best project management tools” may be expanded to include concepts like team collaboration, task tracking, reporting, and scalability. This approach allows the system to consider content that explains the topic well, even if it does not repeat the exact phrase. Keyword matching focuses on surface similarity, while semantic expansion focuses on shared meaning. This is why well-written educational content often appears in responses even when it is not optimized for specific terms.
How Refined Questions Shape the Candidate Pool
Once a refined version of the question is formed, it acts as a filter. Only sources that meaningfully address the expanded topic are considered. This stage determines which brands are even eligible to appear in the final response. If a brand’s content focuses narrowly on selling or promotion without explaining the broader subject, it may never enter this pool. On the other hand, brands that consistently publish clear explanations, comparisons, and contextual insights align naturally with refined questions. They become easier to match with a wide range of related queries, increasing their chances of inclusion.
Why This Matters More Than Rankings
This refinement step happens before any ranking or selection is visible. If a brand does not fit the refined question, its position elsewhere becomes irrelevant. This explains why some well-ranked pages fail to appear in modern answers while lesser-known sources are included. Inclusion depends on relevance to the refined intent, not on popularity signals alone. Being understood is now more important than being optimized.
Content Implications for Marketers and Founders
For marketers and founders, this shift requires a change in how content is planned. Writing should begin with understanding the real questions people ask and the problems they are trying to solve. Pages should cover topics broadly and clearly, using natural language and logical structure. Explaining how things work, why choices matter, and what trade-offs exist helps content align with refined questions. Narrow pages built around a single phrase often struggle, while comprehensive resources gain visibility across many related searches. The goal is not to predict exact queries, but to become a reliable source for a topic as a whole.
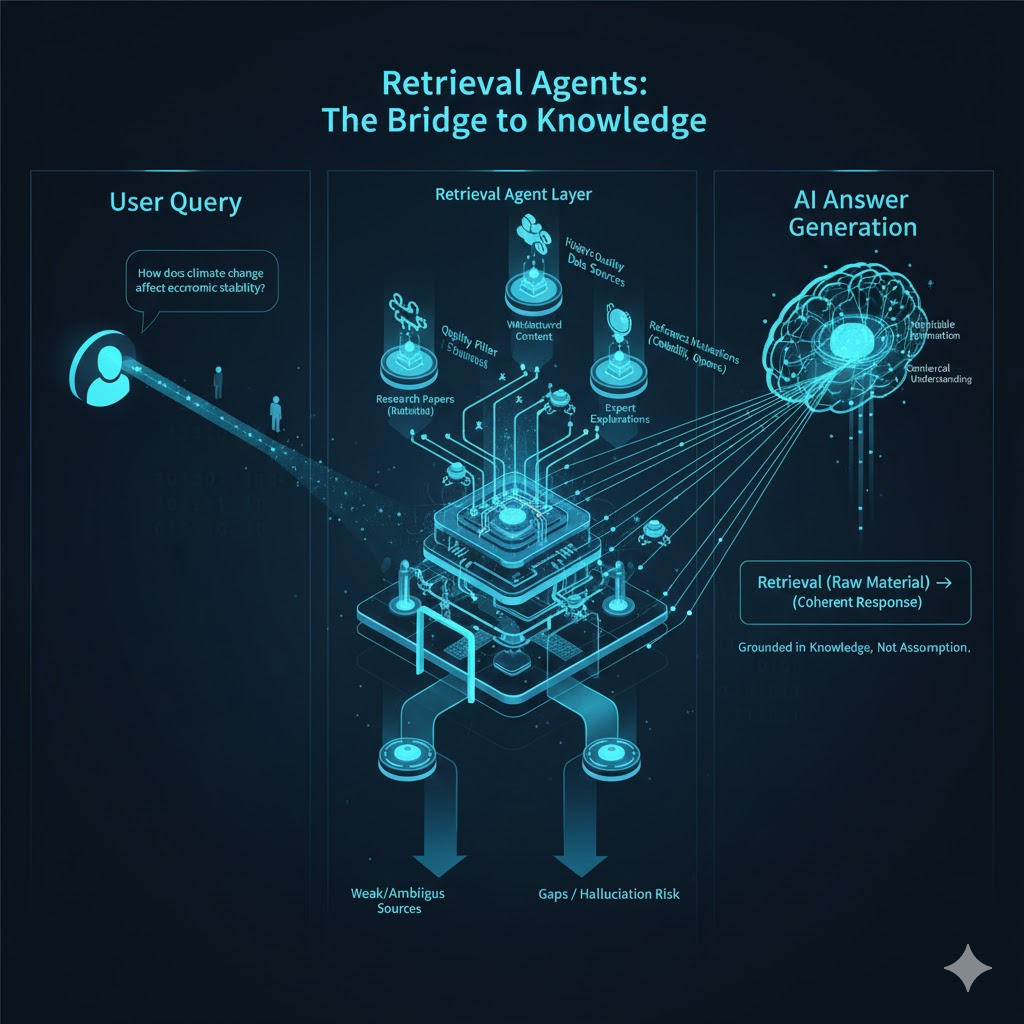
Retrieval Agents Explained: How AI Finds Information
What Retrieval Agents Are
Retrieval agents are systems designed to locate relevant information from external sources before an answer is formed. They do not create explanations on their own. Instead, they search across public content such as articles, discussions, and reference materials to find information that matches the refined question. Their role is to gather evidence, viewpoints, and context so that the final response is grounded in existing knowledge rather than assumption.
Retrieval Versus Generation
A common misunderstanding is that answers are produced purely through generation. In reality, retrieval plays a critical role. Generation is the process of forming a coherent response, while retrieval supplies the raw material. Without retrieval, responses would rely only on internal patterns and could quickly become outdated or incomplete. By pulling information from current and diverse sources, retrieval ensures that explanations reflect real-world understanding and recent discussions.
Why External Data Is Essential
Relying solely on memory would limit accuracy and relevance. Knowledge changes, best practices evolve, and new perspectives emerge constantly. External data allows systems to adapt to these changes without requiring constant retraining. It also helps ground responses in verifiable information. This approach reduces the risk of outdated advice and improves alignment with how topics are discussed publicly. Brands that publish clear and accessible content benefit because their explanations become part of this external knowledge pool.
Addressing the Myth of Hallucination
The term hallucination is often used to describe incorrect or fabricated responses. While errors can occur, many issues arise from weak or ambiguous source material rather than random invention. When retrieval agents fail to find strong references, the resulting explanation may lack precision. This highlights the importance of high-quality public content. Clear explanations, definitions, and examples reduce ambiguity and help ensure accurate responses. The problem is not imagination, but gaps in available information.
How Source Quality Influences Outcomes
Retrieval agents do not treat all sources equally. Content that is well-structured, explanatory, and consistent is easier to interpret and trust. Scattered mentions or shallow summaries carry less weight. This is why detailed guides, thoughtful analysis, and educational articles are more likely to be referenced than promotional copy. Quality signals help determine which information is included and which is ignored.
What This Means for Brand Visibility
Understanding retrieval changes how brands approach visibility. Success is not about appearing everywhere, but about appearing clearly in the right places. Publishing content that explains concepts, addresses common questions, and reflects real expertise increases the likelihood of being retrieved. Over time, this builds recognition and trust, making a brand a natural candidate when relevant questions arise.
The Bigger Picture
Retrieval agents form the bridge between public knowledge and user questions. They ensure that answers are informed, contextual, and grounded. For creators and businesses, this reinforces a simple principle. Visibility today comes from contribution, not manipulation. Those who focus on sharing understanding rather than chasing tactics are better positioned to be discovered and trusted in modern search environments.
Public Web Sources: Why Visibility Matters More Than Virality
The Role of Blogs, Articles, and Editorial Content
Public web content forms the foundation of modern search discovery. Blogs, long-form articles, and editorial pieces provide structured explanations that can be interpreted, compared, and referenced. Unlike short social posts or promotional pages, editorial content offers context. It explains how things work, why they matter, and where trade-offs exist. This depth allows systems to understand a topic rather than just recognize a name. Brands that invest in educational writing tend to appear more often because their content answers questions instead of advertising solutions.
Why Crawlability and Indexability Matter
For content to be discovered, it must be accessible. Pages blocked by scripts, login walls, or restrictive settings cannot be reliably processed. Crawlability ensures that content can be read, while indexability ensures that it can be stored and recalled. Many brands unintentionally hide their most valuable insights behind design choices that favor exclusivity over reach. When content is inaccessible, it may as well not exist in a discovery-driven environment.
The Power of Plain Language
Clarity is more valuable than cleverness. Content written in plain language communicates ideas without forcing interpretation. It defines terms, avoids unnecessary jargon, and explains concepts in a linear way. This makes it easier to understand and easier to reference. Plain language also reduces ambiguity, which improves accuracy when information is reused or summarized. Brands that prioritize explanation over sophistication tend to gain more consistent visibility.
Why Gated Content Is Invisible
Private reports, locked case studies, and gated guides may generate leads, but they do not contribute to public understanding. If content cannot be accessed freely, it cannot be evaluated or referenced. This creates a gap where expertise exists but remains unseen. While gated assets have a role in conversion, relying on them exclusively limits discoverability. Public-facing explanations are essential for recognition.
Content Formats That Are Preferred
Certain formats perform better because they are easier to interpret. Structured guides, step-by-step explanations, comparisons, and conceptual breakdowns provide clarity. Lists with context, well-labeled sections, and logical progression help systems identify relevance. Thin pages, fragmented thoughts, or purely promotional copy struggle because they lack substance.
Search Engines as Data Suppliers, Not Answer Engines
How Major Platforms Feed Discovery Systems
Search engines and community platforms now act as sources rather than destinations. Google and Bing supply indexed content. Reddit and Quora provide real conversations and lived experiences. LinkedIn offers professional perspectives and industry commentary. Together, these platforms create a diverse pool of information that reflects both expertise and public opinion.
Why Discussion Matters More Than Links
Links were once the primary signal of importance. Today, discussion plays a growing role. When a brand or concept appears repeatedly in conversations, explanations, and comparisons, it gains relevance. Mentions across forums, articles, and commentary show that a topic is being actively engaged with. This form of visibility reflects trust built through participation rather than authority imposed through links.
Community Trust Versus Algorithmic Trust
Community trust is earned when people reference a brand naturally while explaining a topic. Algorithmic trust was earned through technical signals. The former is harder to fake and easier to sustain. Real conversations reveal how people perceive value, reliability, and usefulness. Brands that contribute meaningfully to discussions gain credibility that cannot be replicated through optimization alone.
The Importance of Human Conversations
Forums and discussion platforms capture nuance. They show how problems are described in real language and how solutions are evaluated. This information provides context that polished marketing pages often lack. Brands that engage in or are referenced within these conversations benefit from exposure that feels authentic and grounded.

Authority Signals: How LLMs Decide What to Trust
Defining Authority in Modern Search
Authority is no longer about size or dominance. It is about understanding. A source is considered authoritative when it explains a topic clearly, consistently, and accurately across multiple contexts. Authority is built through repetition of insight, not repetition of keywords.
Signals That Influence Trust
Consistency matters. When a brand explains the same concepts in similar ways across different platforms, it becomes easier to recognize. Depth of explanation shows understanding beyond surface-level claims. Cross-platform mentions reinforce presence and relevance. Topic ownership emerges when a brand is repeatedly associated with a specific problem space or framework.
Why Keyword Density Is Irrelevant
Repeating phrases does not demonstrate understanding. It often signals the opposite. Content that relies on repetition without explanation lacks substance. Trust is built through clarity and completeness, not frequency. This is why keyword-heavy pages are often ignored in favor of thoughtful explanations.
Authority Versus Optimized Fluff
Optimized fluff looks polished but says little. Authority content may be less flashy but offers real insight. One explains what to buy. The other explains how to think. The latter builds lasting trust.
Reasoning Models: Where Brand Selection Actually Happens
What Reasoning Models Do
After information is gathered, it must be evaluated. This evaluation process determines which sources align best with the question. It assesses whether the information is accurate, relevant, safe to present, and easy to understand.
Evaluation Criteria
Accuracy ensures that explanations reflect accepted knowledge. Relevance ensures that the information matches the refined intent. Safety ensures that claims are responsible and appropriate. Clarity ensures that the explanation can be communicated without distortion.
Why Only a Few Brands Are Mentioned
Responses are designed to be helpful, not exhaustive. Including too many sources reduces clarity. Only brands that meet all evaluation criteria are included. This makes selection competitive but meaningful.
Understanding Answer Confidence
Answer confidence reflects how complete and reliable a response feels. Sources that contribute to this confidence are favored. Ambiguous or partial explanations weaken confidence and are excluded.
Memory in AI Search: Short-Term vs Long-Term Brand Recall
What Memory Means and What It Does Not
Memory does not imply awareness or preference. It refers to recognition built through repeated exposure. When a brand appears consistently in relevant contexts, it becomes easier to recall.
The Role of Repetition
Repetition reinforces association. Seeing a brand explained clearly across different topics strengthens recall. This does not happen overnight. It is the result of sustained contribution.
Why Virality Fades Quickly
A single popular post creates temporary visibility but rarely builds understanding. Without follow-up and consistency, recall fades. Durable recognition requires ongoing explanation.
Building Lasting Associations
Associations form when a brand becomes linked to a specific idea or solution. This requires focus. Trying to cover everything weakens recall. Specialization strengthens it.
Why Ranking #1 Is No Longer the Goal
Ranking Versus Inclusion
Ranking measures position. Inclusion determines presence. Being ranked does not guarantee being referenced. Inclusion depends on relevance to the refined question.
Collapsing Multiple Sources
Modern responses combine insights from multiple sources into one explanation. This reduces the value of individual rankings and increases the value of contribution.
The New Competition Model
The real competition is not for position but for participation. Sources are either included or excluded. There is little middle ground.
LLM-SEO vs Traditional SEO: A Side-by-Side Comparison
Traditional SEO was built around the idea that search engines needed clear signals to match pages with queries. Success depended on identifying target terms, placing them strategically, and supporting them with links from other sites. The goal was visibility on a results page, and performance was measured by rankings and traffic volume. This approach worked well in an environment where users were willing to browse multiple links and evaluate information on their own. Structure, technical setup, and repetition played a central role in determining which pages appeared first.
Modern discoveries like LLMO services operate on a different principle. Instead of matching words, it evaluates intent. The question is no longer whether a page contains the right terms, but whether it genuinely addresses the reason behind a search. Visibility now depends on how well a source explains a topic, clarifies confusion, and aligns with real user needs. Rather than relying on links as a proxy for authority, modern systems look at citations, references, and contextual mentions across public platforms. These signals reflect understanding and relevance, not just popularity.
The shift in outcomes is equally important. Traditional SEO aimed to drive clicks. Modern discovery aims to build trust. A source may be referenced without generating direct traffic, yet still influence decisions and perception. This changes how success is measured. Instead of focusing solely on page performance, brands must consider whether they are being recognized as a reliable voice within their field. Education replaces optimization as the primary driver of visibility, and long-term credibility becomes more valuable than short-term ranking gains.

LLM Optimization Techniques for Business ApplicatioAdvanced Techniques for LLM Performance and Efficiency
As enterprises scale LLM deployments, performance and efficiency become critical factors. Large language models can require massive computational resources, resulting in high costs, slower response times, and infrastructure challenges. Advanced techniques now allow businesses to optimize LLM performance, reduce resource consumption, and deliver real-time, enterprise-grade AI experiences without compromising output quality. Implementing these strategies ensures that models remain scalable, responsive, and cost-efficient while maintaining accuracy and reliability.
1. Quantization and Pruning for Faster Inference
Quantization and pruning are two of the most effective techniques for reducing model size and improving inference speed. Both approaches aim to make LLMs more computationally efficient while retaining accuracy.
Quantization:
- Reduces the precision of model weights and activations, e.g., from 32-bit floating-point to 16-bit or 8-bit.
- Leads to smaller memory footprint and faster computation, particularly on GPUs and specialized AI accelerators.
- Enables deployment on edge devices or limited-resource environments without sacrificing too much accuracy.
Pruning:
- Removes redundant or less important parameters in the model.
- Can be structured (removing entire neurons or attention heads) or unstructured (removing individual weights).
- Reduces memory usage and computational load while maintaining comparable performance for most tasks.
When applied carefully, quantization and pruning together allow enterprises to achieve significant speedups in inference, enabling real-time or near-real-time applications without excessive cloud costs.
2. Knowledge Distillation for Lighter Models
Knowledge distillation is a technique where a smaller “student” model learns from a larger “teacher” model, effectively capturing most of the teacher’s capabilities while being more efficient to run.
Benefits of knowledge distillation:
- Resource efficiency: Smaller models require less memory and compute.
- Faster inference: Reduced model size allows quicker responses in real-time applications.
- Customizable performance: Student models can be tailored to specific enterprise use cases while retaining essential domain knowledge.
This approach is particularly useful for enterprise-grade LLMs, where deploying a full-scale model may be prohibitively expensive or slow. Knowledge distillation ensures that critical capabilities are preserved while optimizing for operational efficiency.
3. Optimizing Memory and Compute Resources
Large LLMs demand high memory bandwidth and computational power, which can lead to inefficiencies if not managed properly. Enterprises can implement several strategies to optimize memory and compute utilization:
- Model parallelism: Splitting a model across multiple GPUs or nodes to handle larger architectures without exceeding memory limits.
- Pipeline parallelism: Dividing the model into stages that can run concurrently, reducing idle compute cycles.
- Mixed-precision training/inference: Combining lower-precision computations with higher-precision accumulations to reduce memory usage and improve throughput.
- Batching and micro-batching: Grouping requests efficiently to maximize hardware utilization while minimizing latency.
- Memory caching and reuse: Storing intermediate activations and reusing them strategically during inference to reduce redundant computations.
These optimizations allow enterprises to scale LLM deployments effectively without exponentially increasing hardware costs or latency.
4. Latency Reduction Strategies for Real-Time Applications
In enterprise contexts, many applications demand near-instantaneous LLM responses, such as chatbots, recommendation engines, or dynamic decision-making systems. Reducing latency is therefore crucial.
Key strategies include:
- Serving optimized model variants: Use pruned, quantized, or distilled versions for latency-sensitive applications.
- Asynchronous processing: Handle multiple requests concurrently to avoid blocking and improve response times.
- Edge deployment: Run smaller LLMs locally or on edge devices to reduce network-induced delays.
- Caching frequent queries: Precompute responses for common queries to deliver instant answers.
- Adaptive inference: Dynamically adjust the number of computation layers or attention heads based on input complexity.
These techniques ensure that enterprise LLMs remain responsive and efficient, even under high-load or mission-critical conditions.
5. Balancing Accuracy and Efficiency for Large-Scale LLM Tasks
A key challenge in large-scale enterprise LLM deployment is finding the right balance between model accuracy and computational efficiency. High-performing models often require significant resources, while lightweight models risk underperforming.
Approaches to balance accuracy and efficiency:
- Hybrid models: Use smaller models for most tasks and larger models only for complex queries.
- Progressive inference: Start with a lightweight model and escalate to a larger model only when confidence thresholds are low.
- Task-specific fine-tuning: Optimize a smaller model for a high-value domain rather than deploying a general-purpose large model.
- Dynamic resource allocation: Adjust compute allocation based on query complexity, priority, or SLA requirements.
By carefully balancing these factors, enterprises can deploy LLMs that are both performant and cost-effective, enabling scalable solutions across multiple departments and business functions.
6. Monitoring and Continuous Optimization
Even with advanced performance techniques, LLM efficiency requires continuous monitoring and iterative improvement.
Key monitoring strategies include:
- Latency and throughput metrics: Track real-time inference speed and system utilization.
- Accuracy metrics: Measure model output quality, confidence levels, and error rates.
- Resource utilization: Monitor GPU/CPU usage, memory consumption, and energy efficiency.
- Anomaly detection: Identify unusual behavior, hallucinations, or slowdowns to trigger automated mitigation.
- Model lifecycle management: Regularly update, fine-tune, and retrain models to maintain optimal performance as data and use cases evolve.
A feedback loop combining monitoring and optimization ensures that enterprise LLMs remain efficient, accurate, and scalable over time.
7. Integrating Multi-Layer Efficiency Techniques
For the most demanding enterprise use cases, combining multiple performance techniques delivers the best results. For example:
- Use quantization + knowledge distillation for lightweight, high-accuracy models.
- Apply pruning and adaptive inference for latency-sensitive real-time applications.
- Implement memory optimizations alongside batching strategies to maximize throughput while minimizing hardware costs.
Layering these techniques ensures that enterprises can support large-scale LLM deployments across diverse applications while controlling costs and maintaining reliability.
8. Preparing for 2026: Emerging Performance Strategies
As LLM technology continues to evolve, enterprises should prepare for upcoming trends in performance optimization:
- Sparse models: Architectures that dynamically activate only necessary parts of the model to save computation.
- Mixture-of-experts (MoE) approaches: Models that route inputs through specialized sub-models for efficiency.
- Hardware-aware model design: Optimizing models specifically for next-generation AI accelerators and cloud environments.
- Energy-efficient AI: Techniques that reduce power consumption while maintaining high performance, critical for sustainable enterprise deployments.
Staying ahead of these trends ensures that enterprise LLMs remain competitive, sustainable, and ready for large-scale applications in 2026 and beyond.
Advanced techniques for LLM performance and efficiency are essential for enterprises looking to scale AI responsibly and cost-effectively. By combining quantization, pruning, knowledge distillation, memory optimization, latency reduction, and continuous monitoring, businesses can deliver high-performing models that meet enterprise demands. Striking the right balance between efficiency and accuracy allows organizations to deploy LLMs for real-time, high-impact applications without overwhelming resources.
Enterprises that adopt these strategies are better positioned to leverage LLM performance scaling techniques, reduce infrastructure costs, and maintain a competitive edge in AI-driven business environments. Efficiency is no longer optional—it is a prerequisite for sustainable LLM adoption at scale.
Scaling Large Language Models for Enterprise Use Cases
As enterprises increasingly integrate large language models (LLMs) into core operations, the challenge shifts from deployment to scaling. Optimized LLMs that perform well in isolated experiments can struggle when handling thousands of concurrent queries, real-time decision-making, or enterprise-level data volumes. Scaling LLMs effectively requires both technical expertise and strategic planning. Implementing LLM performance scaling techniques ensures models remain fast, reliable, and cost-efficient while meeting the complex demands of enterprise workflows.
1. Horizontal vs. Vertical Scaling of LLM Infrastructure
Scaling LLMs can be approached in two primary ways: horizontal and vertical scaling. Both methods have unique benefits and limitations:
Horizontal scaling (scaling out):
- Distributes model workloads across multiple servers or nodes.
- Improves concurrency, enabling thousands of simultaneous requests.
- Allows redundancy, ensuring fault tolerance and minimal downtime.
- Ideal for enterprises with global operations and multi-department AI usage.
Vertical scaling (scaling up):
- Increases the capacity of a single server by adding more GPUs, memory, or processing power.
- Supports larger models that require high memory bandwidth and faster compute.
- Reduces latency for batch processing or high-throughput tasks.
Enterprises often implement a hybrid approach, combining horizontal and vertical strategies to balance speed, reliability, and cost-efficiency. Understanding the right mix depends on query patterns, peak loads, and the size of the LLM.
2. Cost Optimization for Large-Scale LLM Deployments
Scaling LLMs can be expensive, but strategic optimization can significantly reduce costs without compromising performance.
Key cost-saving strategies include:
- Dynamic resource allocation: Scale GPU clusters up or down based on demand to avoid over-provisioning.
- Mixed precision training and inference: Use lower-precision computation (FP16 or BF16) to reduce memory usage and increase throughput.
- Model pruning and distillation: Compress models while maintaining accuracy to reduce computational overhead.
- Serverless deployment: Leverage pay-per-use cloud resources for non-continuous workloads.
- Monitoring and auto-scaling: Track utilization metrics and adjust resources automatically for cost-effective operation.
Adopting these practices ensures enterprises can deploy LLMs at scale without incurring unsustainable infrastructure costs.
3. Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Strategies for Enterprise AI
Enterprises often require multi-cloud or hybrid infrastructure for redundancy, regulatory compliance, and flexibility.
Multi-cloud strategy:
- Distributes workloads across multiple cloud providers.
- Mitigates vendor lock-in and ensures high availability.
- Supports regional compliance requirements for data sovereignty.
Hybrid infrastructure:
- Combines on-premises and cloud-based resources.
- Keeps sensitive data on-prem while leveraging cloud for compute-heavy tasks.
- Optimizes cost by using local resources for continuous workloads and cloud bursts for peak demand.
Implementation tips:
- Use containerization and orchestration tools like Kubernetes to deploy models consistently across environments.
- Adopt unified monitoring tools to track performance and costs across platforms.
- Implement failover and backup strategies to maintain uptime and reliability.
By adopting multi-cloud and hybrid strategies, enterprises can scale LLMs without compromising control or compliance.
4. Real-Time Inference vs. Batch Processing in Business Contexts
Choosing the right inference strategy is critical for enterprise LLM applications.
Real-time inference:
- Processes queries immediately for instant responses.
- Essential for customer-facing applications, chatbots, recommendation engines, and support systems.
- Requires high-performance hardware and optimized LLM performance scaling techniques to handle low-latency requirements.
Batch processing:
- Handles multiple requests at once, processing them in a single pass.
- Ideal for analytics, report generation, content summarization, and knowledge extraction.
- More resource-efficient for non-urgent, high-volume tasks.
Many enterprises adopt hybrid inference strategies, using real-time inference for critical queries and batch processing for large-scale background tasks. Balancing these approaches ensures optimal performance, reduced latency, and cost-efficiency.
5. Advanced LLM Performance Scaling Techniques
Beyond infrastructure and inference strategies, there are advanced techniques enterprises can implement to maximize performance:
Model parallelism:
- Splits large models across multiple GPUs or nodes to handle models that exceed a single GPU’s memory capacity.
Pipeline parallelism:
- Breaks the model into stages where each stage runs on a different GPU, improving throughput for sequential operations.
Sharding and load balancing:
- Divides large datasets and requests across multiple compute nodes to prevent bottlenecks.
- Ensures that peak loads do not degrade performance.
Caching and precomputation:
- Store common embeddings, frequent responses, or intermediate results to reduce repeated computation.
- Significantly improves latency for high-traffic operations.
Asynchronous processing:
- Decouple input requests from output generation to allow non-blocking operation.
- Supports multi-threaded or distributed workflows in enterprise applications.
Adopting these strategies enables enterprises to deploy LLMs at scale while maintaining responsiveness and reliability across departments.
6. Monitoring and Observability for Scaled LLMs
Scaling LLMs successfully requires robust monitoring to detect issues, maintain quality, and ensure compliance.
Monitoring metrics include:
- Latency: Average and tail latency per query to measure responsiveness.
- Throughput: Requests processed per second or per node.
- Resource utilization: GPU, CPU, memory, and network usage.
- Error rates: Frequency of failed queries, hallucinations, or invalid responses.
- User feedback loops: Qualitative evaluations from employees or customers to identify improvement areas.
Observability best practices:
- Use distributed tracing to identify bottlenecks.
- Implement dashboards for real-time infrastructure and model monitoring.
- Set automated alerts for performance degradation, anomalous outputs, or resource spikes.
This continuous observability ensures that scaled LLMs remain performant, reliable, and aligned with business needs.
7. Security, Privacy, and Compliance at Scale
Scaling LLMs in enterprises introduces additional risks that must be addressed:
- Data encryption: Encrypt data in transit and at rest to maintain confidentiality.
- Access control: Implement role-based permissions to ensure only authorized users can query sensitive models.
- Regulatory compliance: Ensure model deployment aligns with GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards.
- Auditability: Maintain logs of prompts, model outputs, and infrastructure changes for accountability.
Security and compliance considerations become increasingly critical as LLM workloads grow in size and complexity.
8. Automation and Orchestration
Automation reduces human intervention, ensures consistency, and simplifies scaling:
- Auto-scaling clusters: Automatically add or remove compute nodes based on demand.
- Automated deployment pipelines: Use CI/CD for model updates, versioning, and rollbacks.
- Job scheduling: Optimize batch processing and off-peak resource utilization.
These automation strategies allow enterprises to scale LLMs efficiently while minimizing operational overhead.
9. Continuous Improvement and Future-Proofing
Scaling LLMs is an ongoing process. Enterprises must continuously evaluate model performance, infrastructure efficiency, and user satisfaction:
- Regularly retrain or fine-tune models with new data.
- Adopt emerging LLM architectures designed for efficiency and multi-modal capabilities.
- Evaluate next-generation hardware accelerators and AI chips for cost-effective scaling.
- Leverage advanced LLM performance scaling techniques to stay competitive and maintain enterprise-grade performance.
This iterative approach ensures that LLM deployments remain future-proof and continue to deliver value as business needs evolve.
Scaling large language models for enterprise use cases is a multi-faceted challenge that involves infrastructure, cost management, inference strategies, advanced technical techniques, monitoring, security, and continuous improvement. Enterprises that adopt structured LLM performance scaling techniques can achieve high throughput, low latency, and reliable outputs while maintaining compliance and cost efficiency.
By combining horizontal and vertical scaling, multi-cloud strategies, batch and real-time inference, advanced parallelism, and rigorous monitoring, businesses can fully leverage the potential of LLMs at scale. These practices turn large language models into enterprise-grade assets capable of supporting critical business decisions, enhancing productivity, and providing competitive advantage in the AI-driven economy of 2026.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in LLM Optimization
As enterprises increasingly rely on large language models (LLMs) to drive decision-making, customer interactions, and content generation, ethical and regulatory concerns have become central to responsible deployment. Businesses cannot afford to treat LLMs as black boxes; misaligned outputs, biased responses, or regulatory non-compliance can result in reputational damage, legal penalties, and loss of user trust. Addressing these concerns proactively ensures that LLM deployments are not only effective but also trustworthy and compliant.
1. Bias Detection and Mitigation in Enterprise Models
Bias in LLMs can emerge from training data, model architecture, or deployment practices. Left unchecked, biased outputs can harm decision-making, misrepresent groups, or generate discriminatory content.
Key practices for detecting and mitigating bias include:
- Data auditing: Evaluate training datasets for underrepresented groups, skewed distributions, and historical biases.
- Bias testing: Use quantitative metrics like demographic parity, equalized odds, or calibration tests to measure output fairness.
- Prompt evaluation: Ensure that prompts do not reinforce stereotypes or favor certain perspectives inadvertently.
- Post-processing corrections: Apply techniques such as debiasing layers, re-ranking, or filtering to adjust outputs in sensitive contexts.
- Diverse evaluation teams: Incorporate input from a variety of stakeholders to identify biases that automated testing may miss.
Implementing these measures helps enterprises align LLM outputs with ethical standards and avoid unintended harm. Bias mitigation should be a continuous process, especially as models are fine-tuned or updated with new data.
2. Ensuring Compliance with Privacy Regulations
Enterprises deploying LLMs must navigate a complex landscape of privacy regulations, including GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and evolving data protection laws worldwide. Non-compliance can result in substantial fines and legal exposure.
Best practices for regulatory compliance include:
- Data minimization: Use only the necessary personal data for training and inference. Avoid storing sensitive information unnecessarily.
- Anonymization and pseudonymization: Ensure that training data and query logs do not contain personally identifiable information (PII).
- Audit trails: Maintain records of data usage, model training, and user interactions for regulatory reporting.
- Right to be forgotten: Implement mechanisms to remove user data upon request.
- Cross-border compliance: If data is processed internationally, ensure adherence to regional laws regarding data transfer and storage.
By integrating privacy-conscious practices into LLM workflows, businesses protect user rights and maintain regulatory trust.
3. Transparency and Explainability in LLM-Generated Content
LLMs often produce outputs that appear authoritative but can obscure how conclusions are reached. Transparency and explainability are crucial for fostering trust and meeting regulatory scrutiny.
Key strategies include:
- Explainable AI (XAI) techniques: Use attention visualization, feature attribution, or simplified surrogate models to clarify why the model made a particular prediction or output.
- Output provenance tracking: Maintain metadata about the source of information used for generating responses. This is especially important in research, financial, or legal applications.
- Clear labeling: Indicate when content is AI-generated versus human-authored, particularly in customer-facing communication.
- Confidence scoring: Provide an estimate of reliability for generated outputs to help users gauge trustworthiness.
Transparent LLMs allow decision-makers and end-users to understand, verify, and challenge outputs, reducing the risk of misuse or misinterpretation.
4. Accountability for LLM Errors in Customer-Facing Applications
Even well-optimized models can produce errors. Enterprises must establish accountability frameworks to manage risk, protect customers, and ensure legal compliance.
Key accountability measures include:
- Human-in-the-loop (HITL) oversight: Ensure that high-risk outputs are reviewed or validated by humans before deployment.
- Error tracking and reporting: Log mispredictions, hallucinations, or misleading responses for ongoing improvement and audit purposes.
- Response protocols: Define how the organization will address errors, including automated rollback, user notifications, and internal escalation procedures.
- Liability assessment: Identify which teams, departments, or stakeholders are responsible for specific LLM applications and outputs.
By establishing accountability, enterprises reduce reputational risk and foster user trust even when errors occur.
5. Building Trust While Scaling LLM Solutions Ethically
Scaling LLMs across multiple departments or applications amplifies the ethical and regulatory stakes. Enterprises must balance efficiency with responsibility to maintain stakeholder confidence.
Key practices for ethical scaling include:
- Ethics-by-design: Incorporate ethical considerations into every stage of the LLM lifecycle, from data collection to deployment.
- Regular audits: Conduct internal reviews of model outputs, decision-making processes, and alignment with organizational values.
- Stakeholder engagement: Gather input from employees, customers, and external experts to guide responsible deployment.
- Continuous monitoring: Implement automated alerts for anomalous outputs, potentially harmful responses, or biased trends.
- Education and training: Equip teams with knowledge of ethical AI principles, regulatory requirements, and best practices for responsible LLM usage.
Ethical scaling ensures that LLM solutions generate value while respecting user rights, promoting fairness, and maintaining trust across the enterprise ecosystem.
6. Risk Mitigation Framework for LLM Deployment
Enterprises should develop structured risk frameworks to anticipate, monitor, and respond to ethical and regulatory challenges:
Components of a robust framework:
- Risk identification: Map potential ethical, legal, and operational risks for each LLM application.
- Impact assessment: Evaluate potential harm to users, customers, or the organization.
- Mitigation strategies: Define proactive measures such as data anonymization, bias detection, and HITL interventions.
- Ongoing review: Periodically reassess risk as models evolve, new regulations emerge, or applications expand.
- Incident response: Establish procedures for addressing ethical breaches, compliance violations, or major errors promptly.
A formal risk framework reduces liability, ensures governance, and fosters long-term enterprise confidence in LLM adoption.
7. Emerging Regulatory Trends to Watch
By 2026, regulatory oversight for AI and LLMs is expected to grow in scope and complexity. Enterprises should anticipate the following trends:
- Global AI regulations: Beyond GDPR and CCPA, new laws may mandate model transparency, impact assessments, and ethical audits.
- AI certification standards: Governments or industry bodies may introduce certification frameworks for safe, ethical LLM deployment.
- Explainability mandates: Certain industries may require clear reasoning behind automated outputs, particularly in finance, healthcare, and legal sectors.
- Cross-border data compliance: Increased scrutiny on data sharing and AI model training across jurisdictions.
- Bias and fairness audits: External audits may become standard for high-risk applications, requiring documented mitigation strategies.
Proactively adapting to emerging regulations ensures enterprises remain compliant while leveraging LLM capabilities.
8. Ethical Guidelines for Enterprise LLM Use
Establishing internal guidelines provides a foundation for consistent, responsible LLM deployment:
Key guidelines:
- Fairness: Ensure outputs do not perpetuate discrimination or bias.
- Transparency: Clearly communicate AI involvement and reasoning where appropriate.
- Safety: Prevent the generation of harmful or misleading content.
- Privacy: Protect sensitive data and comply with regulations.
- Accountability: Assign ownership for outputs and governance of LLM applications.
These principles should be embedded in policies, workflows, and performance metrics to reinforce ethical operations at scale.
9. Benefits of Ethical and Compliant LLM Deployment
Focusing on ethical and regulatory compliance is not just about avoiding risks—it also creates strategic advantages:
- Builds trust with customers, employees, and stakeholders.
- Enhances brand reputation by demonstrating responsible AI use.
- Reduces legal and financial liability associated with misaligned outputs.
- Facilitates long-term adoption and scaling, as compliance frameworks streamline approvals and deployment.
- Encourages innovation by setting clear boundaries for safe experimentation.
Enterprises that prioritize ethics and compliance are better positioned to leverage LLMs effectively and sustainably in 2026.
Ethical and regulatory considerations are no longer optional in enterprise LLM deployment—they are a critical component of sustainable AI strategy. From bias detection and mitigation to compliance with global privacy laws, from transparent and explainable outputs to accountability for errors, enterprises must approach LLM optimization with foresight and responsibility. Building trust, implementing robust risk frameworks, and preparing for evolving regulations ensures that LLM solutions generate value while upholding ethical principles.
By embedding these practices, businesses can scale LLMs responsibly, protect stakeholders, and maintain competitive advantage in an AI-driven enterprise landscape. Ethical and compliant LLM optimization is both a risk management necessity and a strategic differentiator in the modern digital economy.
Practical LLM-SEO Strategy for Brands
Here in this section of this article we will talk about the finest large language model deployment strategies with a brief note.
Creating Readable Content
Content should explain concepts clearly, define terms, and follow logical progression. Structure matters, but clarity matters more. This is the first and most important criteria for large language models optimization.
Explainers Over Landing Pages
Landing pages sell. Explainers teach. Teaching builds recognition and trust.
Presence Across Trusted Platforms
Visibility grows when explanations appear in multiple places. This reinforces understanding and recall.
Consistency in Messaging
Contradictory messaging weakens trust. Consistency strengthens recognition.
Best Practices for LLM Optimization in Enterprise Environments
As large language models become integral to enterprise operations, simply deploying them is no longer sufficient. Success depends on structured strategies that ensure LLMs deliver accurate, reliable, and aligned outputs. Implementing best practices for LLM optimization can elevate the impact of these models, turning them from experimental tools into robust assets that enhance efficiency, insight, and decision-making across your organization.
1. Establish Clear Objectives for LLM Deployment
Before integrating an LLM into enterprise workflows, clarity about goals is essential. LLMs are versatile—they can generate content, summarize documents, provide research support, or assist with customer interactions—but without defined objectives, outputs may be inconsistent or misaligned.
Key considerations:
- Define the purpose: Identify whether the LLM will assist in internal knowledge management, customer support, content generation, or decision support.
- Measureable outcomes: Establish KPIs such as accuracy of responses, response time, user satisfaction, or content consistency.
- Scope boundaries: Specify areas where the model can operate autonomously versus tasks requiring human review.
By anchoring LLM deployment in clear objectives, enterprises reduce risks, avoid model misuse, and focus optimization efforts where they deliver maximum value.
2. Governance and Quality Control of AI Outputs
Even advanced LLMs can generate incorrect, biased, or incomplete information if left unchecked. A robust governance framework ensures the outputs meet organizational standards and regulatory requirements.
Best practices include:
- Content review protocols: Implement checkpoints to verify model outputs before external use.
- Bias detection: Regularly audit model outputs for fairness and neutrality.
- Error logging: Track inconsistencies and incorrect outputs to inform retraining or refinement.
- Version tracking: Maintain clear documentation of model updates and modifications to monitor performance changes over time.
Strong governance ensures LLM outputs remain trustworthy, actionable, and aligned with enterprise expectations.
3. Aligning LLM Responses with Brand Tone and Compliance Standards
Every output of large language model optimization for enterprise reflects on the brand. Misalignment with tone, messaging, or regulatory compliance can damage credibility.
Approaches to alignment:
- Brand voice embedding: Train models with content reflecting your company’s preferred style, tone, and vocabulary.
- Compliance frameworks: Integrate rules for sensitive topics, legal disclaimers, or sector-specific regulations.
- Consistency checks: Ensure outputs are consistent across multiple platforms, channels, and touchpoints.
By embedding brand and compliance considerations directly into LLM behavior, enterprises can confidently deploy AI at scale without compromising corporate integrity.
4. Versioning and Continuous Monitoring for Model Improvements
Large language model optimization for enterprise is not “set and forget” technologies. Continuous iteration and monitoring are crucial for maintaining relevance, accuracy, and performance over time.
Key strategies:
- Model versioning: Maintain separate versions of models for testing, production, and experimental features. This allows controlled rollout and rollback in case of errors.
- Performance metrics: Track metrics such as answer relevance, response time, and user engagement to evaluate effectiveness.
- Feedback loops: Collect feedback from internal teams or users to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Periodic retraining: Update the model periodically with new data, ensuring it reflects current trends, policies, and enterprise knowledge.
This systematic approach ensures your LLM continues to improve while minimizing risks associated with model drift or outdated knowledge.
5. Integrating Human-in-the-Loop for Oversight and Trust
While LLMs are powerful, human oversight remains essential, especially for high-stakes or complex decisions. A human-in-the-loop (HITL) system allows enterprises to balance automation with accountability.
Implementation strategies:
- Approval workflows: Route sensitive or critical outputs to human reviewers before external publication.
- Guided refinement: Humans can correct, enhance, or reframe outputs, feeding improvements back into the model.
- Trust-building: HITL systems enhance confidence among internal teams and external users by ensuring accountability.
- Training reinforcement: Human corrections can be used to reinforce model learning, improving future responses.
By embedding human oversight into the LLM workflow, enterprises achieve both efficiency and reliability, turning AI into a trusted partner rather than a black-box tool.
6. Data Management and Privacy Considerations
Enterprise LLM optimization must account for data sensitivity, privacy, and security. Mismanaged data can lead to regulatory issues or compromised results.
Best practices include:
- Data anonymization: Remove personal identifiers from training and evaluation datasets.
- Access controls: Limit model inputs and outputs to authorized personnel.
- Audit trails: Maintain logs of queries and responses for accountability.
- Compliance alignment: Ensure adherence to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific standards.
Proper data handling safeguards both your organization and your users while improving the quality and relevance of LLM outputs.
7. Iterative Testing and Scenario-Based Training
LLMs perform best when trained and tested in real-world contexts. Scenario-based testing ensures the model can handle diverse situations without producing unreliable results.
Methods include:
- Simulated use cases: Test the model with potential customer queries, internal tasks, or reporting scenarios.
- Edge-case analysis: Identify unusual queries that may produce errors or unexpected outputs.
- Continuous refinement: Update training data to cover newly discovered gaps or trends.
This proactive approach strengthens model reliability and reduces the likelihood of errors when the LLM is deployed broadly.
8. Scaling and Resource Optimization
In enterprise environments, LLM optimization isn’t just about outputs—it’s also about resource efficiency. Large models can be resource-intensive, so scaling strategies are essential.
Approaches include:
- Selective inference: Use smaller models for routine tasks and reserve full-scale models for complex queries.
- Caching common responses: Store frequently requested answers to reduce repeated computation.
- Distributed processing: Leverage cloud or on-premise resources efficiently to balance latency and throughput.
- Model compression techniques: Use pruning or quantization to reduce model size without sacrificing accuracy.
Optimizing resources ensures the enterprise can scale LLM capabilities sustainably while maintaining high performance.
Implementing best practices for LLM optimization in enterprise environments requires a multi-layered approach: clear objectives, governance, brand alignment, versioning, human oversight, data security, iterative testing, and efficient scaling. Enterprises that systematically follow these guidelines gain models that are not only powerful but also reliable, trustworthy, and aligned with organizational goals.
By embedding these practices into LLM workflows, businesses can maximize ROI, enhance decision-making, and ensure that AI-generated insights consistently support both operational efficiency and strategic objectives.
Remember, best practices for LLM optimization are not a one-time checklist—they are an evolving framework that grows as models, enterprise needs, and AI capabilities advance. Enterprises that prioritize structured, responsible, and transparent LLM practices will be the ones leading the next generation of AI-driven insights.
ns
Deploying large language models in business environments offers significant advantages—but only if they are optimized properly. Simply integrating an LLM into workflows is not enough; enterprises must adopt structured strategies to ensure outputs are accurate, actionable, and aligned with business objectives. Implementing LLM optimization techniques for businesses transforms models from experimental tools into strategic assets capable of driving measurable value.
1. Prompt Engineering Strategies for Consistent Output
Prompt engineering is the foundation of controlling LLM behavior. Crafting effective prompts ensures the model understands context, intent, and desired output format.
Key approaches:
- Structured prompts: Use step-by-step instructions, bullet-point guides, or formatted queries to reduce ambiguity.
- Context inclusion: Provide relevant background information to improve the specificity of responses.
- Temperature and max-token adjustments: Fine-tune generation settings to balance creativity and factual consistency.
- Iterative refinement: Test prompts repeatedly to identify phrasing that consistently produces reliable results.
By mastering prompt engineering, businesses can achieve predictable and uniform outputs, which is critical for enterprise applications like reporting, customer support, or internal knowledge management.
2. Fine-Tuning vs. Instruction Tuning for Domain-Specific Knowledge
Not all LLMs perform equally well across industries or tasks. Customizing models for domain-specific applications improves relevance and reduces errors.
Techniques include:
- Fine-tuning: Adjusts a pre-trained LLM on domain-specific datasets. Ideal for highly specialized tasks, such as legal, financial, or technical content.
- Instruction tuning: Focuses on teaching the model how to follow specific instructions rather than retraining its underlying knowledge. Useful when consistent output formats or style adherence is required.
- Hybrid approaches: Combine instruction tuning with selective fine-tuning for complex applications.
Selecting the right approach ensures the model understands specialized terminology and workflows, enhancing reliability for business-critical operations.
3. Using Embeddings and Semantic Search for Better LLM Retrieval
Embedding vectors and semantic search are essential for leveraging LLMs in knowledge retrieval, research, and decision-making.
Best practices:
- Vector embeddings: Convert documents, queries, and user inputs into semantic vectors to capture meaning rather than literal keyword matches.
- Semantic similarity searches: Retrieve the most relevant context or references for the LLM to consider during generation.
- Hybrid search techniques: Combine traditional keyword-based search with embeddings for precision and recall.
- Knowledge augmentation: Feed retrieved documents into the LLM prompt to improve answer accuracy and completeness.
This approach reduces the chance of irrelevant outputs and ensures LLMs are aligned with enterprise knowledge bases, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiency.
4. Techniques for Reducing Hallucination in Business-Critical Contexts
LLMs are powerful, but they can occasionally produce confident yet inaccurate or fabricated outputs, known as hallucinations. Mitigating these risks is crucial in high-stakes business applications.
Methods to reduce hallucination:
- Grounding in trusted data: Use retrieval-augmented generation to base responses on verified, enterprise-approved sources.
- Prompt constraints: Instruct the model to provide references, disclaimers, or only answer when confident.
- Answer verification layers: Implement automated checks to flag improbable or unsupported outputs.
- Human-in-the-loop oversight: For sensitive outputs, include human review before deployment.
Enterprises that actively reduce hallucination strengthen trust in LLM outputs and avoid costly errors in operations, reporting, or customer-facing scenarios.
5. Performance Monitoring and Evaluation Metrics for LLMs
Continuous evaluation is essential to maintain LLM reliability. Businesses must track performance to detect drift, degradation, or misalignment over time.
Recommended metrics and techniques:
- Accuracy: Compare outputs against a verified knowledge set or benchmark.
- Relevance: Assess whether responses meet user intent and provide actionable insight.
- Consistency: Track variability across repeated queries or prompts.
- Latency and efficiency: Measure response times to ensure models meet enterprise operational requirements.
- User feedback: Collect qualitative input from internal teams or end-users to refine prompts, models, and workflows.
Regular monitoring and structured metrics allow enterprises to iterate on models effectively, ensuring long-term performance and alignment with business goals.
6. Advanced Strategies for Enterprise-Level LLM Deployment
Beyond basic tuning and prompts, businesses can implement advanced techniques to optimize performance and scalability:
- Context window management: Maximize model understanding by managing input length and relevance. Include only high-priority context to improve response quality.
- Multi-turn dialogue optimization: For chatbots or internal assistants, structure prompts to retain state across multiple interactions.
- Dynamic knowledge injection: Update the model with the latest data or policy changes without full retraining.
- Modular model design: Deploy specialized models for discrete tasks (e.g., summarization, recommendation, Q&A) to improve efficiency and reduce error rates.
These techniques provide a scalable framework for applying LLM optimization techniques for businesses in complex, enterprise-scale environments.
7. Security and Compliance Considerations
LLM optimization isn’t only about performance—it’s also about ensuring outputs are secure and compliant:
- Data privacy safeguards: Anonymize inputs and outputs, restrict access, and encrypt sensitive data.
- Regulatory alignment: Configure the model to respect industry-specific regulations, ensuring outputs don’t violate compliance standards.
- Audit trails: Maintain detailed logs of prompts, outputs, and model versions for accountability and traceability.
Integrating security and compliance measures ensures LLM applications are trustworthy and legally safe for enterprise deployment.
8. Iterative Refinement and Continuous Learning
Optimization is not a one-time process. Enterprise LLMs improve with iterative updates and feedback:
- Regular dataset updates: Include new content, business rules, or evolving terminology to maintain relevance.
- Feedback loops: Use user corrections or ratings to guide model refinements.
- A/B testing: Evaluate different prompts, tuning methods, or retrieval strategies to identify optimal approaches.
This continuous learning loop ensures the model remains relevant, accurate, and aligned with evolving enterprise needs.
9. Integrating LLM Optimization into Business Workflows
Finally, successful implementation requires embedding LLM optimization into daily operations:
- Cross-functional adoption: Encourage departments to adopt LLMs for research, drafting, analysis, and internal communication.
- Standard operating procedures: Define clear protocols for when and how LLMs are used in different tasks.
- Training and education: Ensure employees understand model limitations, best practices, and how to provide meaningful feedback.
By integrating LLM optimization into business workflows, enterprises maximize value while maintaining control over quality and consistency.
LLMs are transforming how enterprises process information, generate insights, and interact with stakeholders. Implementing LLM optimization techniques for businesses ensures models are accurate, consistent, and aligned with strategic goals. From prompt engineering and fine-tuning to semantic search, hallucination mitigation, and rigorous performance monitoring, each step strengthens the model’s utility while reducing risk.
Enterprises that adopt these strategies create an environment where AI is not only a tool but a reliable collaborator, enhancing decision-making, productivity, and operational excellence. With proper optimization, large language models become scalable, trustworthy assets capable of powering the next generation of enterprise innovation.
Incorporating these techniques into day-to-day workflows, continuously refining models, and embedding governance and compliance ensures your LLM deployments remain robust, responsible, and highly effective.
By following these approaches, businesses stay ahead of competitors, deliver consistent value, and harness the full potential of LLM-driven intelligence.
Content Types That Win in Modern Search
Educational Guides That Build Understanding
Educational guides perform well because they focus on explanation rather than persuasion. They walk readers through a subject from the ground up, define important terms, and address common points of confusion. This type of content helps establish a clear mental model for the topic, which makes it easier to reference and reuse. Guides that answer how and why questions tend to remain relevant longer than trend-driven articles. Their value lies in clarity and completeness, not urgency. Brands that invest in teaching rather than selling are more likely to be recognized as dependable sources of knowledge.
Framework Explanations That Reveal How You Think
Framework-based content shows structure behind ideas. Instead of listing tips, it explains relationships, priorities, and decision paths. This reveals how a brand approaches a problem, not just what it recommends. Frameworks make complex subjects easier to understand by breaking them into logical components. They also make ideas memorable. When a framework is well explained and consistently referenced, it becomes associated with its creator. This association strengthens recognition and positions the brand as a source of original thinking.
Thought Leadership That Adds Perspective
Thought leadership succeeds when it contributes a point of view rather than repeating accepted wisdom. It interprets change, challenges assumptions, and connects ideas across disciplines. The goal is not to predict the future but to help readers think more clearly about the present. Effective thought leadership is grounded in experience and observation, not speculation. It earns attention by offering insight that cannot be found in generic advice. This type of content builds credibility by showing judgment, not just knowledge.
Case-Based Insights That Demonstrate Application
Case-based content works because it shows how ideas function in real situations. It moves beyond theory and illustrates decision-making, constraints, and outcomes. These narratives help readers understand not only what worked, but why certain choices were made. Practical detail adds weight to claims and reduces skepticism. Cases also humanize expertise by showing learning through action. When shared openly, they reinforce trust and provide concrete reference points for future discussions.
Why Thin Content Falls Short
Thin content often tries to cover too much with too little substance. It summarizes without explaining and promotes without teaching. While it may attract brief attention, it rarely contributes to understanding. Without depth, there is nothing to reference or remember. Over time, such content fades because it does not answer meaningful questions. Substance, not volume, determines long-term relevance.
Common Mistakes Brands Make
Focusing Only on Traditional Search
Many brands continue to design content solely for legacy ranking systems. They prioritize placement over understanding and visibility over usefulness. This narrow focus ignores how discovery now works across platforms and contexts. By optimizing only for one channel, brands miss opportunities to be recognized elsewhere.
Hiding Expertise Behind Sales Pages
Another common mistake is placing most expertise behind promotional pages. Sales pages are designed to convert, not explain. They assume understanding rather than build it. When expertise is locked inside persuasive language, it becomes harder to recognize and reference. Public explanations are necessary for discovery, even if conversion happens later.
Ignoring Conversational Platforms
Discussions on forums and community sites reflect how people actually describe problems and evaluate solutions. Ignoring these spaces limits exposure to real language and real concerns. Brands that avoid conversation miss signals about relevance and perception. Participation or organic mention in these spaces strengthens credibility.
Treating Discovery Systems Like Simple Crawlers
Some still assume that visibility depends on technical access alone. While accessibility matters, interpretation matters more. Discovery systems evaluate meaning, not just presence. Treating them like basic crawlers leads to overemphasis on structure and underemphasis on clarity. This imbalance reduces impact.
Measuring Success in a New Search World
Why Traffic Is No Longer Enough
Traffic measures visits, not influence. A brand may shape understanding without generating direct clicks. This makes traditional analytics incomplete. Success must be viewed in terms of recognition and trust, not just volume.
Understanding Visibility Without Attribution
Modern discovery often lacks clear attribution. A brand may be referenced or its ideas used without a direct link. This makes impact harder to track but not less real. Influence now spreads through explanation rather than referral.
New Indicators of Success
More meaningful indicators include how often a brand is mentioned in relevant contexts, how consistently it appears across platforms, and what it is associated with. Quality of association matters more than frequency alone. Being linked to clear explanations and reliable guidance signals success.
The Value of Qualitative Signals
Qualitative feedback reveals perception. Are people citing a brand when explaining a concept? Are its ideas being repeated accurately? These signals indicate understanding and trust. While harder to measure, they reflect real progress in visibility.
Redefining Performance
Performance is no longer about winning a position. It is about being part of the explanation. Brands that adapt to this mindset focus on contribution, clarity, and consistency. Over time, these qualities create durable presence that outlasts any single metric.

Enterprise LLM-SEO Deliverables by ThatWare
What you Receive When Our LLM-SEO Framework Is Deployed
1. Strategic Intelligence & Discovery Deliverables
This phase establishes the foundation of AI visibility. Before optimization begins, ThatWare determines how AI systems currently interpret, classify, and include the brand. This prevents wasted execution and ensures every action aligns with real AI decision layers.
- LLM Visibility & Inclusion Audit
Determines whether the brand is eligible for AI answer inclusion, not just search rankings. - Intent Intelligence Mapping
Identifies real user intent clusters across informational, evaluative, and decision-making stages. - Semantic Authority Gap Report
Pinpoints missing explanations preventing AI trust and inclusion. - Refined Query Eligibility Matrix
Shows which AI-refined questions the brand qualifies for — and which require intervention.
Outcome:
Strategic clarity on why a brand is included or excluded from AI-generated answers.
2. Semantic Architecture & Intent Engineering
Once intelligence is established, ThatWare restructures the brand’s digital presence around how AI systems understand meaning, not how legacy search engines match keywords. This layer ensures the brand aligns with refined intent and contextual relevance.
- Entity & Concept Graph Development
Defines how AI systems understand the brand’s domain knowledge. - Intent-First Content Architecture
Rebuilds site structure around explanation depth, not keyword placement. - Context Expansion Framework
Adds surrounding intelligence AI models rely on for answer confidence. - Natural Language Optimization Layer
Aligns brand language with how humans actually ask and evaluate questions.
Outcome:
AI systems recognize the brand as a subject-matter explainer, not a promotional page.
3. LLM-Ready Content Engineering
Content is engineered to be retrievable, explainable, and trusted by AI systems. Rather than promotional copy, ThatWare builds educational and framework-driven assets that AI models can confidently reference and reuse.
- Explainer-First Content Assets
Educational content built for retrieval, reasoning, and long-term trust. - Proprietary Framework Documentation
Clearly articulated models that demonstrate how the brand thinks and decides. - Case-Based Authority Narratives
Real-world execution insights that reinforce credibility. - RAG-Optimized Content Structuring
Content formatted for retrieval-augmented generation systems. - Thin Content Identification & Upgrade Plan
Eliminates non-referencable content that weakens authority signals.
Outcome:
Content becomes retrievable, quotable, and reusable by AI systems.
4. Retrieval & AI Inclusion Optimization
This stage ensures the brand’s content is technically and contextually eligible for AI retrieval systems. Visibility here determines whether content ever reaches the reasoning layer.
- Retrieval Agent Compatibility Validation
Ensures AI systems can locate, parse, and reuse brand content. - Public Knowledge Surface Expansion
Strategic presence across editorial, expert, and knowledge-driven platforms. - Contextual Brand Mention Strategy
Builds semantic mentions instead of artificial link dependency. - Cross-Platform Explanation Consistency Control
Prevents conflicting signals that reduce AI trust.
Outcome:
Brand explanations consistently qualify for AI retrieval pipelines.
5. Authority, Trust & Brand Memory Engineering
Authority in AI search is built through consistent explanation, repetition, and clarity across environments. This phase focuses on embedding the brand into AI memory systems through durable association.
- Authority Signal Standardization
Consistency, depth, repetition, and explanation clarity alignment. - Brand Recall Conditioning Framework
Builds long-term AI memory through repeated concept ownership. - Conversation-Based Trust Visibility
Inclusion within real discussions, not surface-level promotion. - Answer Confidence Contribution Optimization
Ensures brand strengthens AI answers instead of diluting them.
Outcome:
The brand becomes remembered, not just discovered.
6. Enterprise Performance, Ethics & Governance
At enterprise scale, visibility must be efficient, compliant, and future-proof. This layer ensures LLM-SEO execution aligns with performance, regulatory, and governance standards.
- LLM Performance & Efficiency Advisory
Guidance on latency, scalability, and inference optimization. - Ethical & Regulatory Compliance Mapping
Bias mitigation, privacy, transparency, and accountability readiness. - Governance & Quality Control Systems
Human-in-the-loop oversight for AI-facing content. - Future-Readiness Roadmap (2026+)
Preparedness for evolving AI discovery ecosystems.
Outcome:
AI visibility at enterprise scale — without regulatory or reputational risk.
Strategic Business Impact for Clients
- Inclusion in AI-generated answers
- Authority without dependency on rankings
- Durable brand recall across platforms
- Reduced volatility from algorithm updates
- Visibility even when clicks do not occur
Monthly LLM-SEO Growth Report by ThatWare
Enterprise-Grade Visibility & Authority Measurement
1. Executive Intelligence Summary
- Net change in AI inclusion footprint
- Authority growth highlights
- Strategic wins and risks
- Next-phase focus areas
2. AI Visibility & Inclusion Metrics
- Number of AI responses referencing brand intelligence
- Growth in refined query eligibility
- Inclusion vs exclusion ratio
- Contribution to AI answer confidence
3. Intent Coverage Progress
- New intent clusters covered
- High-impact gaps closed
- Intent-content alignment score
- Reduction in intent mismatch signals
4. Retrieval Performance Analysis
- Pages successfully retrieved by AI systems
- High-impact content segments
- Retrieval blockers identified and resolved
- Optimization actions implemented
5. Authority & Trust Signals
- Cross-platform consistency index
- Topic ownership expansion metrics
- Editorial and community recognition growth
- Stability of authority signals
6. Content Impact Intelligence
- Explainers driving AI reuse
- Frameworks strengthening recall
- Case insights influencing trust
- Thin content eliminated or upgraded
7. Brand Memory & Recall Indicators
- Short-term recall improvements
- Long-term association growth
- Reduced reliance on viral spikes
- Stability across AI systems
8. Traditional SEO (Supportive Layer)
- Organic traffic trends (contextual)
- SERP presence correlation
- Branded demand lift
- AI-to-search influence patterns
9. Risk, Ethics & Governance Review
- Bias and compliance checks
- Content safety validation
- Output consistency monitoring
- Governance improvements applied
10. Strategic Action Roadmap
- Next-month intent priorities
- New explainer & authority assets
- Platform expansion targets
- Long-term visibility reinforcement plan
Enterprise Interpretation
Success is no longer defined by ranking positions.
Success is defined by inclusion, trust, and repeat recognition.
Wrapping Up
The shift from traditional SEO to LLM-driven discovery marks a fundamental change in how visibility, authority, and success are defined online. Search is no longer about winning positions on a results page, but about being understood, trusted, and repeatedly referenced across the public web. Modern discovery systems reward clarity over cleverness, depth over density, and education over optimization tricks. Brands that explain well, participate in real conversations, and contribute meaningful insight are more likely to be included in AI-generated answers than those relying solely on technical signals or short-term tactics. This evolution forces a rethink of content strategy, measurement, and intent. Traffic may fluctuate, attribution may blur, but influence persists where trust is established. As AI collapses multiple sources into singular responses, the real competition becomes inclusion versus exclusion, not rank versus rank. The brands that thrive will be those that invest in durable understanding, consistent narratives, and genuine value creation. In this new search landscape, visibility is earned by helping users think better, not by forcing systems to notice you.

