SUPERCHARGE YOUR Online VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
What is the concept of the customer journey?

A customer journey is a pattern of thought or a series of stages that a potential buyer goes through before ultimately buying a product or availing of a service. To understand this more clearly try to understand the last time you bought something for yourself. An expensive gadget like a mobile phone will be a great example.
Remember the steps you had taken before you finally committed to buying. First, you might have not known what model you should buy, so you must have made a note of the list of things you want to do with your new smartphone.
Namely, Gaming, watching movies, Social Media, or maybe even using it for recording videos or making content.
- After having a fair idea of the specifications, from Google required to perform these tasks, you might have searched in google about the phones that support those specifications in Google.
- After jotting a list of models you may have searched how they compare again each other. Again to come back to Google for the answer.
- While you are comparing the specifications you might have got a fair idea about the pricing.
- By now, you are quite aware of the specific model or models that you might want and you must be out for blood for some cheap deals. Again Google is your go-to place for finding offers and deciding on which brand to go for.
- Ultimately the decision of you wanting to buy online or from an offline store rests upon you but we already know ecommerce sales account for 30% – 40% of all smartphone sales in India alone.
Customer Journey and the AIDA Model
Seeing where I am getting with this? Throughout the entire journey, you followed through with some steps. Let me map them out for you
- First, you became aware of a need or a problem. In this case, the need was the ability to perform certain activities a smartphone can fulfil.
- Then you became interested in the solutions. In this case, you might have searched for “Best smartphones for Gaming in 2022” or “Smartphones with the best camera”.
- After you have understood the specific models you want, you now start calculating your budget and finding the best deal within that. Your “interest” has grown into a “desire” for that product.
- Finally, after deciding on the model you took action by purchasing your desired smartphone at the best deal possible.
- Another interesting thing to note, throughout your journey Google was your Go-to platform for research.
Your Journey outlined certain stages in the Customer Journey, namely Awareness, Interest, Desire and Action or AIDA.
Takeaway
“Customer Journey is a pattern of thought or a series of stages that a potential buyer goes through before ultimately buying a product or availing of a service.
“It generally has four stages: Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action that marketers should adher to also referred to as AIDA.”
How is the Customer Journey important for Businesses? Importance of Retention
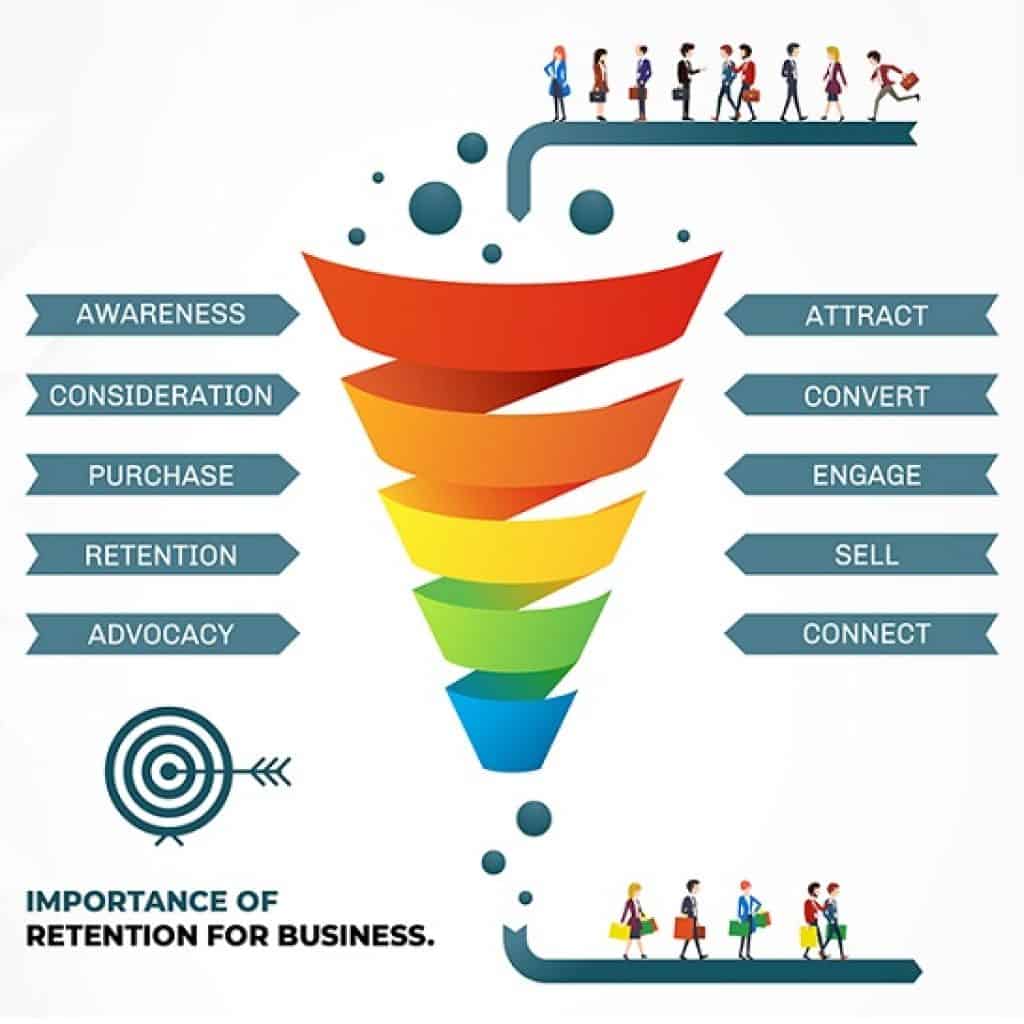
By now you must have understood that the above example is not just a case for a singular journey of a smartphone buyer, but the same stages can be generalised to the buying process of practically any product or service.
This signifies the changing behaviour of today’s educated audience, who have a tendency of researching any product before making a purchase. Since Google is the go-to tool for research, I think it goes without saying the importance of having a Digital Presence for any company or brand.
Notice the different kinds of content that you consume in each stage. The type of content you consume in the interest stage is vastly different then what you are consuming in the desire or the action stage. This holds significance from an SEO Standpoint, the importance of creating different types of content optimised to satisfy each stage in the buying journey.
This way you are not only targeting customers.
who are currently in-market actively trying to purchase, but also you are reaching out to a broader range of prospects educating them in their buying journey and facilitating their eventual conversion.
Takeaway
“A content marketing strategy mapped according to the customer’s buying journey simply tips the odds of the customer going with your brand, in your favor. A significant point that can impact future ROI.”
Importance of Retention | AIDAR Model

There is a fifth component to the User journey that is often overlooked and that is Retention. The customer had availed service or bought a product like a smartphone. Now comes the hard part of making sure the customer returns to the same brand the next time he makes a similar purchase.
At this stage, the customer continues to ask service-related questions, and issues regarding usage and also continues to compare benefits with competitors.
Creating content that answers these questions goes a long way in ensuring a delightful customer service experience.
Also rewarding the customer for loyalty and other related offers often do move the needle enough to make them stay.
Takeaway
“There are 5 stages in a Customer Journey: Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action and Retention. Hence the AIDAR Model”.
How is Customer Journey Mapping important for SEO?
There are essentially three arguments to support this:
- With RankBrain, PaLM and LAMda Update, Google is shifting its focus from relying on Keywords to Identifying Search Intent
Understanding User Intent has been the long-standing objective of Google and with the advent of recent algorithm updates like BERT and Rankbrain, Google understands searches better than ever.
Also, Google has taken Natural Language Processing to the next level with PaLM and LAMda updates adding to its sophistication in identifying search intent.
All this means we SEOs need to adapt from not only creating articles for Keywords but also creating content that satisfies every reliable aspect of particular search intent.
This is where mapping specific content marketing efforts with each stage of the customer journey comes into place.
After identifying all the relevant Topics in each stage of the buying journey, it simply boils down to creating relevant and helpful content that will satisfy each stage and eventually ranking for all these topics thus capturing the entire spectrum of your target market,… at least in Google.
- Coordinate with Marketing Teams
Your marketing team might have an upcoming campaign that might increase the search volume of a particular product or service. It might be wise to leverage, maybe create a Page around that Keywords and build backlinks that naturally. This way we can blend SEO with brother Marketing tactics.
- Its not the Same as a Pillar Cluster Structure
A pillar cluster structure is usually designed to address all aspects of a particular topic. It generally has a single pillar page with several smaller posts addressing related topics.
The difference is a Pillar Cluster structure is usually optimised for 1-2 Search Intents, mostly Interest and Desire. Here we define the full spectrum of Search Intent in the buying journey. Hence several pillar cluster structures might have to be employed to cover each buying stage separately.
How to conduct Customer Journey mapping with Google
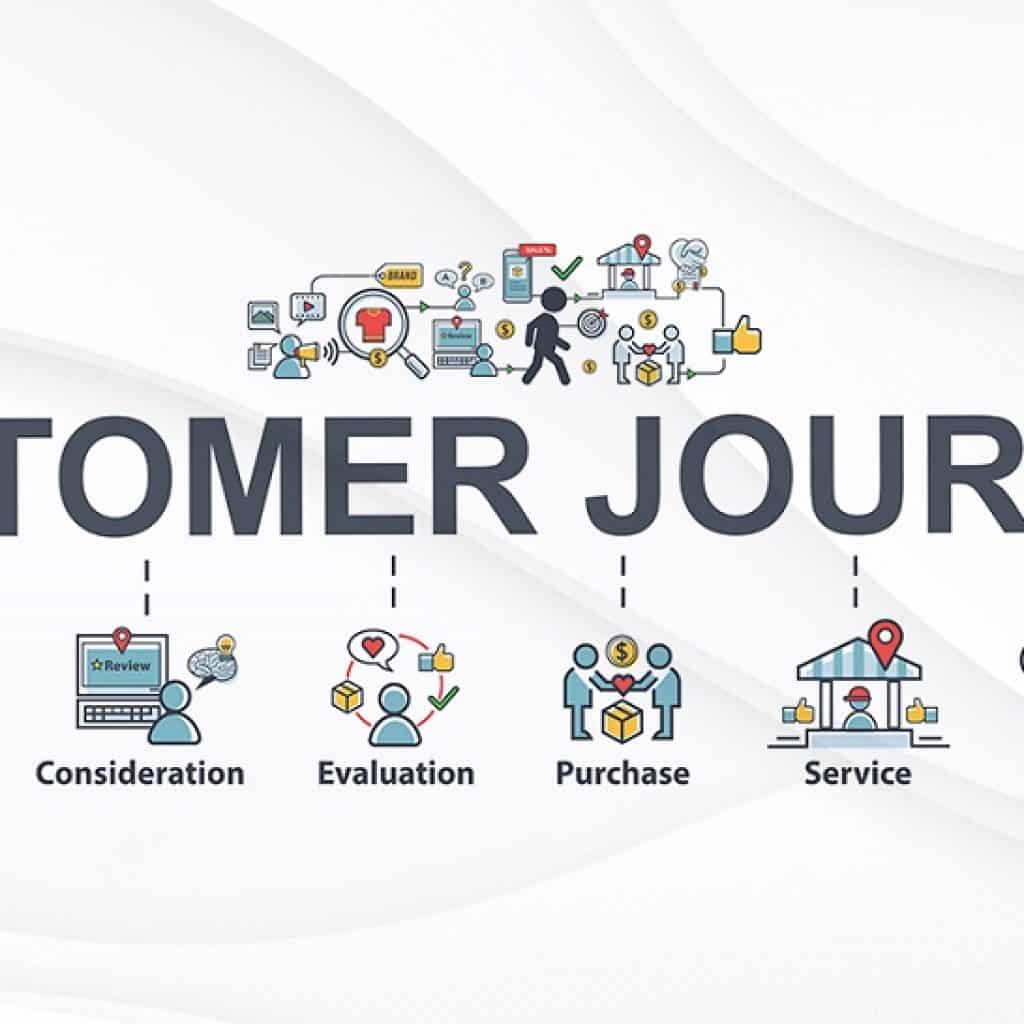
Step 1. Define the User Persona and User Journey Stages
In order to even begin carving a customer journey, we have to determine the kind of audience we are targeting. Hence creating a Buyer Persona can help.
There an excellent article in Hubspot where you can learn to create elaborate User Personas.
After that we can define each stage of the User Journey and determine the probable search intents.
The image below reflects the various stages of a basic User Journey:
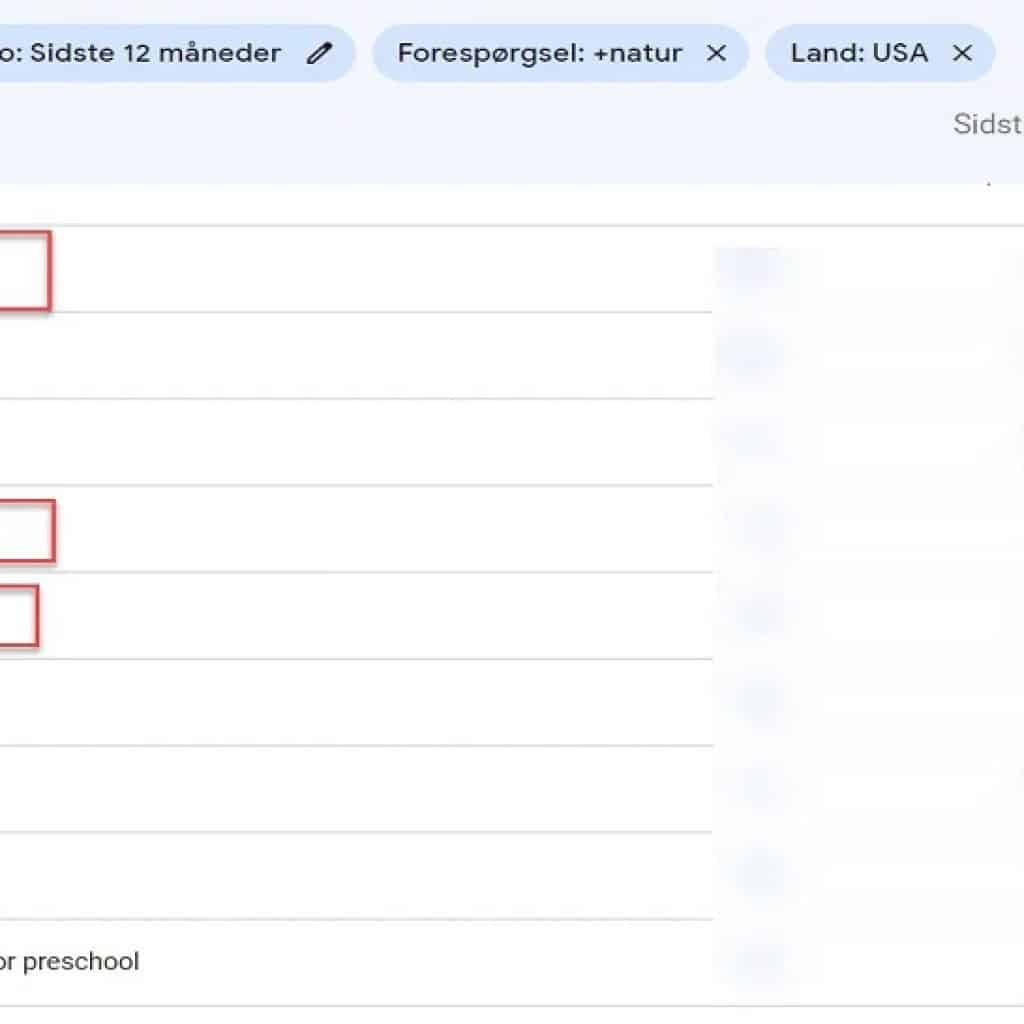
Step 2: Data Collection
We will use the client’s search console data to find keywords with different intent related to the topic. I will filter 12 months of data for a specific keyword. I will then go through my keyword list.
In this example, I am doing a map for “Natural playgrounds”. One intent is “natural playground equipment”. I have marked three queries below, which have the same intent: Natural playground equipment, Nature playground equipment and Nature play equipment.
After we have exhausted all search queries from the Google search console, we can move on to other Keyword research tools like Keyword Planner and SERanking for finding more keyword prospects with different intents.
Step 3: Search intent Mapping
Once all possible keywords for various intents have been identified we will move on to map each keyword to the specific journey stage that may seem suitable. We will do it in a presentation slide as below to be shown to the client.
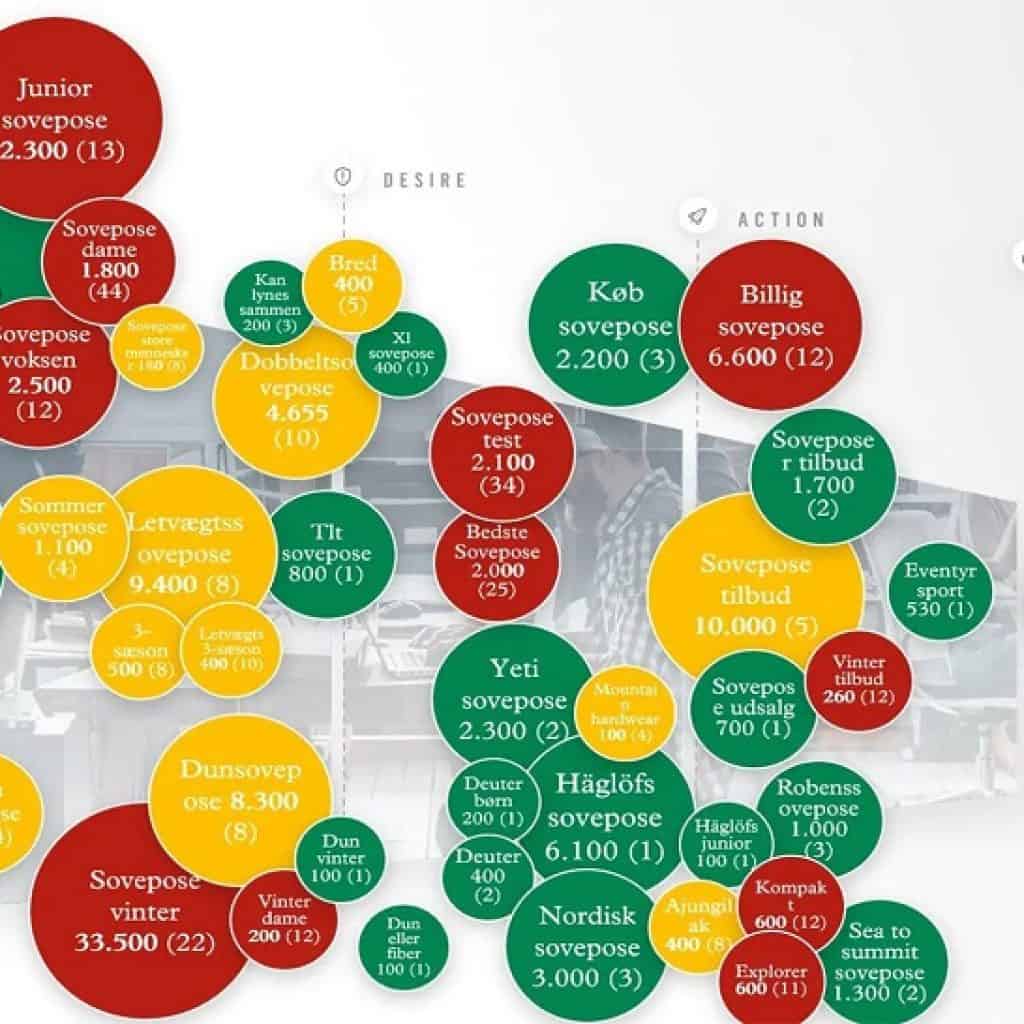
- Each bubble represents a search query.
- The size of the bubble represents its search volume.
- The Green bubbles represent the queries ranking on 1st Page.
- The Yellow bubbles represent the pages ranking somewhere from the 2nd page to the 100th Page.
- The Red Bubbles are keywords where the client’s website doesn’t rank at all.
When a map like this is presented, it will naturally kick-start a focus on how we can convert all the intents to green.
User Journey Mapping according to the Business Objective
So as you get accustomed to the above segment about the AIDAL model, we can segregate the user journey mapping in accordance with specified business objectives. The user journey mapping can be categorised as follows:
User Journey Mapping for Service-Oriented Business
First, we will discuss the service-oriented business to start. We are taking a keyword called “SEO agency in Kolkata” as an instance to understand the entire consumer journey as a basis of the AIDAL model.
In the Awareness stage, the consumer might have the query like “How to choose the best SEO agency in Kolkata? ”. So once consumers triggered the search on Google they stepped into the AIDAL model. This is how the user journey mapping started.
Then in the very next user journey, the respective consumer starts searching for simple solution queries to satisfy his/her intent. This stage is about the Interest of that particular consumer. The instance would be like “SEO agency in Kolkata”. In this stage, they will also look for substitutes (e.g. “SEO services company in Kolkata”).
So by gathering interest in the respective query, the prospect now became more knowledgeable and they entered into the Desire stage by refining their search in an optimal way. They start searching for something like segments (“Fully managed SEO firm in Kolkata”).
For service-based businesses, the keywords of both the Desire/Action stage queries can be similar and overlapping.
User Journey Mapping for Ecommerce-Oriented Business
Let’s say we have an ecommerce store selling various Body Oil, Hair Oil and other related products.
In the Awareness stage, the consumer might search for queries like “Benefits of Body Oil” or “How to prevent hair loss”
In the Interest/Desire level the consumer may search for specific products and their pros and cons and also compare between products of your brands and other brands.
The action Stage is the point when the customer has decided on the product. He may now look for queries like “Best Deals of Good Vives Hair Oil”, and “How to apply body Oil properly”. At this stage, the customer is confident with their research but needs some incentive to be pushed to purchase.
In the Retention stage, the Customer will continue to compare products. At this stage posts like “Pros and Cons” or Loyalty Benefits or offers might be a good idea to retain customers.
User Journey Mapping for Product-Oriented Business
It’s similar to an Ecommerce Business. In this case, only the product may be a physical product or a Digital Product like software.
Customer Touchpoints: Where Businesses Interact with Customers
Understanding customer touchpoints is crucial for businesses looking to create a seamless and engaging experience for their customers. Touchpoints are the moments when a customer interacts with a brand, whether it’s through a digital platform, a physical store, or a personal conversation with a company representative. These touchpoints play an essential role in shaping the customer’s perception of the brand and influencing their decisions at various stages of their journey.
In this article, we will explore the different types of customer touchpoints, why they matter, how to optimize them for a seamless experience, and the critical role of emotional engagement in building lasting customer relationships.
Understanding Customer Touchpoints
Definition: Touchpoints
Customer touchpoints are the interactions between a customer and a brand, from the moment they become aware of the product or service to post-purchase follow-ups. These touchpoints can happen at any stage of the customer journey, whether it’s before, during, or after the sale.
Touchpoints are significant because they directly impact the customer’s experience, perception, and emotional connection with the brand. Every interaction leaves an impression, and these impressions can either build trust and loyalty or lead to frustration and dissatisfaction. A positive experience at a touchpoint strengthens the relationship between the customer and the brand, while a negative experience can lead to customer churn or bad reviews.
Why Touchpoints Are Important
Touchpoints are crucial because they provide an opportunity for brands to engage with customers, shape perceptions, and influence decision-making. Customers interact with brands in multiple ways across various channels, and each touchpoint contributes to the overall customer experience. Whether it’s browsing a website, receiving a personalized email, or talking to customer service, these interactions collectively form the customer’s view of the brand.
A brand that can provide consistent, high-quality interactions at each touchpoint is more likely to earn customer trust, increase satisfaction, and, ultimately, build loyalty.
Types of Customer Touchpoints
1. Digital Touchpoints
In today’s digital-first world, most customer interactions with a brand happen online. Digital touchpoints are essential for driving customer engagement and creating an accessible brand experience. Some key digital touchpoints include:
- Website: The company’s website is often the first place customers visit to learn more about products or services. A user-friendly, responsive, and informative website can leave a positive impression and guide customers down the conversion funnel.
- Social Media: Brands use platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and others to connect with customers, provide updates, respond to inquiries, and build a community. Social media is a powerful touchpoint because it allows businesses to engage with customers in real-time.
- Email: Email marketing continues to be a highly effective touchpoint for building relationships with customers. Whether through newsletters, personalized offers, or transactional emails (e.g., order confirmations), email provides a direct line to the customer’s inbox.
- Online Ads: Display ads, Google search ads, and retargeting ads are forms of digital touchpoints that help businesses attract potential customers and keep their brand top-of-mind during the decision-making process.
- Chatbots: Increasingly popular for their ability to provide instant responses, chatbots are an essential tool for customer service and sales. They help guide customers, answer queries, and collect information, all while creating an efficient experience.
2. Physical Touchpoints
While digital touchpoints dominate, physical touchpoints remain an important part of the customer experience, especially for businesses with brick-and-mortar stores. These touchpoints can include:
- In-store Experiences: A well-designed store, helpful staff, and pleasant atmosphere create a memorable in-store experience. The tactile experience of touching and testing a product in person is something that digital channels cannot replicate.
- Events: Trade shows, product launches, and other in-person events are an excellent opportunity for brands to interact directly with customers. These events allow customers to experience the product firsthand, meet the brand’s representatives, and participate in exclusive offers or promotions.
- Trade Shows: These are specialized events where businesses showcase their products or services. Trade shows provide a valuable opportunity to interact with potential customers, generate leads, and build awareness.
3. Human Touchpoints
Human interactions remain one of the most influential touchpoints in the customer journey. Customers value personal service, especially when dealing with issues or making purchasing decisions. Key human touchpoints include:
- Customer Service Calls: Customers often turn to customer service when they need assistance or have concerns. The quality of the service they receive can significantly impact their overall perception of the brand.
- Sales Representatives: Sales teams play an essential role in guiding customers through the decision-making process. A knowledgeable, personable salesperson can have a positive influence on customers, turning interest into desire and ultimately a sale.
- Customer Support Teams: Post-purchase support, including returns, exchanges, troubleshooting, and inquiries, is another key human touchpoint. How businesses handle issues post-purchase determines whether the customer will remain loyal or move to a competitor.
Optimizing Touchpoints for a Seamless Experience
1. Consistency Across All Touchpoints
One of the most critical aspects of managing touchpoints is consistency. Whether customers interact with your brand online or in person, they should receive a consistent experience in terms of messaging, tone, and service quality. Inconsistent interactions create confusion and frustration, leading to a disjointed customer experience.
Businesses must ensure that their branding, customer service, and offerings are aligned across all channels. For example, if a customer reads about a promotion online, they should find the same information and promotion in the store. Inconsistent messaging can harm trust and damage the relationship with the customer.
2. Personalization
Personalizing customer touchpoints is a powerful way to enhance the customer experience and build deeper relationships. Personalization refers to tailoring the interaction based on the customer’s behavior, preferences, past interactions, and other relevant data. Personalization can be as simple as addressing the customer by name in an email or as complex as offering product recommendations based on browsing history.
Personalized content or offers make customers feel valued, improving satisfaction and increasing the likelihood of repeat business. For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine, which suggests products based on a user’s browsing and purchase history, is a prime example of personalized touchpoints driving engagement.
3. Omnichannel Marketing
Omnichannel marketing ensures a seamless experience across digital and physical touchpoints. Customers may start their journey online and complete a purchase in-store, or vice versa. Brands must deliver consistent, cohesive experiences across every channel and device.
For example, if a customer interacts with your brand via email but later visits your website or physical store, they should have the same experience—whether it’s in terms of promotions, messaging, or product availability. Omnichannel marketing bridges the gap between the digital and physical worlds, ensuring that the customer feels connected to the brand at all touchpoints.
The Role of Emotional Engagement in Touchpoints
Emotional Touchpoints
Beyond practical interactions, businesses must also consider emotional touchpoints. Emotional engagement occurs when a customer has a connection with the brand beyond functional benefits. These touchpoints elicit emotions such as joy, excitement, trust, or even nostalgia.
Creating emotional touchpoints involves connecting with customers on a deeper level. This could be through storytelling, aligning with customer values, or creating memorable moments during interactions. For example, brands like Coca-Cola and Nike leverage emotional advertising to make customers feel inspired or happy, fostering long-term loyalty.
How Emotional Engagement Leads to Loyalty
When customers feel emotionally connected to a brand, they are more likely to become loyal advocates. Emotional engagement leads to positive word-of-mouth, repeat purchases, and an increased lifetime value (LTV) of the customer. Brands that consistently evoke positive emotions during customer interactions are better positioned to retain customers and build a strong, loyal following.
The Challenges in Managing the Customer Journey
Managing the customer journey is a complex task that involves navigating multiple stages, touchpoints, and interactions. Despite its importance, many businesses face challenges when it comes to understanding and optimizing the journey for their customers. These challenges can hinder the ability to deliver a seamless, personalized experience and may ultimately affect customer satisfaction and retention. In this section, we’ll discuss the common obstacles businesses encounter in managing the customer journey and explore how these challenges can be overcome.
Common Obstacles Businesses Face
- Fragmented Customer Data
One of the most significant challenges in managing the customer journey is dealing with fragmented customer data. Businesses often have customer data spread across multiple platforms—CRM systems, social media accounts, email marketing software, website analytics, and offline channels. This fragmentation makes it difficult to get a comprehensive view of each customer’s journey and understand their preferences, behaviors, and interactions with the brand.
Impact: Without a unified view of the customer, it becomes challenging to deliver personalized experiences or accurately predict customer needs, which can lead to inefficiencies, missed opportunities, and suboptimal customer service. - Inconsistent Experiences Across Different Channels and Touchpoints
Customers today interact with brands across various channels—websites, mobile apps, physical stores, customer service calls, social media, and more. If the customer experience is inconsistent across these touchpoints, it can lead to confusion and frustration, damaging the customer’s perception of the brand.
Impact: Inconsistent experiences make it harder to build customer trust and can result in lost sales and diminished loyalty. For example, if a customer receives one type of messaging via email but encounters contradictory information on the website, they may feel unsure about making a purchase. - Difficulty in Tracking and Measuring the Customer Journey
Another obstacle businesses face is tracking and measuring the customer journey effectively. With customers interacting across various digital and offline touchpoints, it can be difficult to track each stage of their journey, attribute actions to specific channels, and measure the effectiveness of different marketing efforts.
Impact: Without proper tracking, businesses may miss key insights that could help optimize the journey. This also hinders the ability to calculate ROI accurately and make data-driven decisions for future campaigns.
How to Overcome These Challenges
Utilizing Omnichannel Strategies
An omnichannel approach ensures that customers receive a consistent and seamless experience across all channels. By integrating both online and offline touchpoints, businesses can create a unified customer experience. This includes ensuring that information such as product availability, promotions, and customer service is consistent across all platforms.
Example: A customer who starts browsing a product on a mobile app can seamlessly continue shopping on the website or pick up the product in-store without having to repeat information or encounter discrepancies.
Integrating Data Across Platforms
The first step in overcoming fragmented customer data is to integrate it across all platforms. By using customer relationship management (CRM) systems, businesses can consolidate data from social media, website analytics, email campaigns, and other channels into a single, unified platform. This enables a more complete view of the customer journey, making it easier to personalize experiences and improve interactions.
Example: Integrating a CRM with social media platforms and email marketing tools can help a business track customer behavior across touchpoints and provide relevant offers based on previous interactions.
Building a Customer-Centric Culture
To address inconsistent experiences, businesses must foster a customer-centric culture that prioritizes the customer journey at every stage. This means ensuring that all departments, from marketing and sales to customer service, are aligned in their approach to customer interactions. Creating a consistent brand message, tone, and experience across all channels is essential to delivering a cohesive customer experience.
Example: Companies can invest in training their employees to handle customer inquiries consistently, ensuring that the same level of service and messaging is maintained whether the customer contacts the business through social media, the website, or in person.
In summary
Google is by far the biggest touchpoint in most customer journeys across industries, so it is obvious that hard data from Google Search Console and third-party can help us understand user intent. Customer journey mapping on Google is a model to enable the data by visualizing it, ensuring we as marketers understand the prospects’ conversation and intent.
At the same time, it gives a clear overview of content prioritization, which is an important point, since most teams have limited resources.

Thatware | Founder & CEO
Tuhin is recognized across the globe for his vision to revolutionize digital transformation industry with the help of cutting-edge technology. He won bronze for India at the Stevie Awards USA as well as winning the India Business Awards, India Technology Award, Top 100 influential tech leaders from Analytics Insights, Clutch Global Front runner in digital marketing, founder of the fastest growing company in Asia by The CEO Magazine and is a TEDx speaker and BrightonSEO speaker..

