SUPERCHARGE YOUR ONLINE VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
You are not a newcomer to SEO. You know the drill: discover the correct long-tail keywords, establish links, and so on. However, your concentration has been on consumers who search in your language. Now is the time to broaden your horizons and consider multilingual SEO.
The Advantages Of Multilingual SEO
All of us who live worldwide and buy online have undoubtedly made purchases from foreign firms. This has been a simple procedure because they have a webpage in the appropriate language, and we can pay in the appropriate currency. And if we enjoy the things, we’ll come back for more.

We are frequently ignorant that we are purchasing from a firm halfway around the world from us. So, why not do the same with your website — the advantages are obvious:
- Increased traffic when customers search in their local language. Only roughly one-fifth of Internet traffic originates in the United States. A firm in the United States with popular items at home is missing out on traffic by not turning multilingual.
- Improved user experience = more time spent on a site = higher conversion rate = higher SERP ranking
- Excellent SEO. SEO ranks on localized search engines will improve if your site is optimized for key search phrases in the target languages, engaging, and providing value to those audiences.
- Multilingual SEO for Empowering Businesses to Expand Globally
- Businesses flourish in today’s globalized environment by connecting with customers in several nations. This expansion is easy thanks to multilingual SEO. You may establish direct connections with various consumers by making your website multilingual, which promotes engagement and trust.
- Businesses aiming for international markets face a key challenge: language barriers. Multilingual SEO overcomes this hurdle by tailoring content effectively. This strategy ensures your message resonates with users in their native languages, enhancing user experience and driving conversions.
- Breaking Language Barriers
- Languages create natural divides among global audiences. Multilingual SEO bridges these gaps, enabling businesses to communicate effectively in different languages.
- Expanding Market Reach
- With multilingual SEO, your website ranks higher on search engines in specific regions, attracting more local customers.
- Enhancing Brand Credibility
- Localized content shows customers you value their culture and preferences, building trust and a stronger brand reputation internationally.
- How Does Multilingual SEO Work?
- Multilingual SEO involves optimizing your website for multiple languages, incorporating localized keywords, and ensuring accurate translations. This process enhances visibility across diverse search engines and markets.
- Conducting Keyword Research in Target Languages
- Understand search intent in each region by researching relevant keywords. Use localized terms to align with the preferences of local users.
- Optimizing Meta Tags and Content
- Ensure all meta tags, titles, and descriptions are localized. Translate content while keeping cultural nuances in mind.
- Leveraging Hreflang Tags
- Hreflang tags inform search engines about language versions of your site. They guide users to the appropriate content, improving rankings.
- Technical SEO Considerations
- Ensure fast loading speeds and mobile-friendliness across languages. Technical optimization boosts usability, regardless of your audience’s location.
- Benefits of Multilingual SEO for Businesses
- Implementing multilingual SEO delivers measurable advantages. Increased traffic, improved user engagement, and better ROI are just a few benefits businesses enjoy.
- Improved Customer Retention: Customers appreciate content in their native language, increasing loyalty and the likelihood of repeat purchases.
- Higher Search Engine Rankings: Localized SEO strategies help businesses rank higher in regional searches, boosting visibility and credibility in new markets.
- Competitive Edge: Businesses utilizing multilingual SEO stand out from competitors, positioning themselves as leaders in international markets.
- Hence, we can say that, multilingual SEO is more than just a marketing strategy; it’s a gateway to global success. Therefore, by embracing this approach, businesses unlock new opportunities, connect with diverse audiences, and drive growth across borders.
- So, begin your multilingual SEO journey today to achieve unparalleled global reach.
Multilingual SEO Best Practices
There are multiple phases to this process, and you should proceed with caution and consideration.
Step 1: Create a strategy.
- Determine whether you require international SEO. If there isn’t a lot of traffic from other nations or areas, you might wish to wait. On the other hand, international SEO should be considered if you have done your research and know that you have a market for your product/service in another country or area.
- Determine the nations from which portions of your clients originate that are not your own. You may have sold on Amazon and obtained that information there.
Alternatively, if you don’t have Google Analytics, go to the “audience” link on the main dashboard, then select “Geo” from the drop-down option. This will provide you with the languages spoken by your target audience, as well as the nations and areas they come from.
- Determine whether you require international SEO. If there isn’t a lot of traffic from other nations or areas, you might wish to wait. On the other hand, international SEO should be considered if you have done your research and know that you have a market for your product/service in another country or area.
Step 2: Determine if you want to target nations, languages, or both.
Understand that you can’t genuinely target places like Southeast Asia or Europe. Simply said, there are too many languages involved. It might be nations, languages, or both.
1) Countries to be targeted
Some businesses target certain nations for a variety of reasons. Consider a hotel chain such as Marriott or a travel website like Expedia. Because they have so many consumers with distinct demands in each of these nations, it makes sense to establish worldwide locations in various countries. It also makes sense for businesses to provide several languages on their primary websites.
2) Languages to be targeted
However, for most businesses whose products or services are the same regardless of location, the language option alone is a definitive decision. Consider how Facebook, which provides the same services to people worldwide, provides languages rather than specific sites for each nation.
3) Targeting both
It is advantageous for a corporation to target both nations and languages. Stripe, an online payment platform, needs to target both because it only serves a few countries yet wants to service all languages in those countries. As a result, a user can pick a nation and subsequently a language. In the United States, for example, where numerous languages are spoken, one can choose the nation and then various language selections.
This works well for Stripe and online banking companies expanding their footprint into developing nations where a burgeoning middle class remains unbanked. As a result, users may access their nation’s website in their native language.
Step 3: Decide On A Domain And URL Structure.
At first, this may appear to be a straightforward task, but it is not, and you have options.
- If you want to target nations rather than languages, you may use Country Code Top Domains (ccTLDs) like.ca or.co.uk, or subdirectories like XXX.com/de.
- If you wish to target languages, you should use SubDirectories like XXX.com/de or SubDomains like de/XXX.com/.
Again, if your site is huge and your services vary by nation, you’ll want to target certain countries with ccTLDs. If, on the other hand, your goals are customers based on their languages, wherever they may be, then SubDirectories, as illustrated above, are the way to go.
Step 4: Configure languages for SEO
This is vital in SEO; if the translations and localizations are poor, you will confuse and potentially anger your audience.
- Only use human translators. Suppose you can locate a native speaker of your target language who can advise you on cultural factors. If you want to translate into more than one language, go to a credible, major translation firm like The Word Point, which will offer native-speaking translators in practically any language you pick. Individual translators can be found on freelancing websites such as Upwork.
Google Translate is another free alternative; however, you will receive literal translations with no localization. Your target viewers will be reading a bad translation, not to mention that your graphics may be objectionable. Your keywords may be meaningless in those languages.
- Consider developing a sitemap for the translated website in the target language. It makes people happier by assisting them in navigating. Happy users Equal greater time spent on your site, good for SEO. It also aids search engines in accurately indexing your sites.
More Stats
- Make use of hreflang. This property informs search engines that you have the same text, graphics, and so on in many languages so that they do not treat this as duplicate content on the same page. Hreflang tags inform search engines that you have developed many copies of the same material in various languages. It will assist the search engine in serving up the appropriate language for searches while also recognizing that you are not simply offering duplicate information. You can simply accomplish this with Yoast if you have a WordPress site.
- Make language menus available on your website. Use nations as a last resort. In India, for example, there are 41 official languages; in China, there are just four. Also, when providing language options, utilize the language’s accepted spelling. Instead of “Spanish,” for example, use “Espanol.”
- A note on keywords: when translating to target languages, use the proper keywords/phrases popular for searches in those languages. Otherwise, you will be forced to conduct extensive research, the findings of which may be flawed. Again, a real native translator may be quite useful in this situation.
Step 5: Keep Housekeeping In Mind.
- It is not difficult to set up different currencies for whoever you use as a payment processor. However, you must choose the appropriate currencies for an audience viewing your site from various nations. For example, customers from Canada, France, or Algiers may visit your site in French. They should be able to choose their currency.
- The same is true for shipment. Choose an international shipper who will deliver to all countries/regions where the target language is spoken.
- Choose your photos with care. You will not utilize women in barely dressed bikinis to represent languages prevalent in Muslim nations. You may also want to avoid using images of white individuals in China because it is a hue associated with sadness rather than brides and purity. This is where a localization professional may help.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
This article will teach you the fundamentals of creating multilingual sites to improve your SEO for foreign language searches. Keep in mind that missteps can derail all of your efforts as you go through this process:
- Before targeting a language widespread in specific nations and areas, ensure that you are not infringing on local laws or regulations. New legislation in European nations, for example, mandates notice of cookie use. If your target language is French, you must follow this rule because many customers live in France.
- Don’t make any assumptions about linguistic nuances, cultural values, keywords, and so forth. Request that a native expert evaluates everything.
- Don’t trick search engines into thinking you’re repeating material. Use hreflang tags to tell them that your pages are divided into languages.
- Don’t focus on nations when you should focus on languages. Unless you sell different products/services to customers in different nations, you should focus on languages.
- Do your research on keywords/phrases. Seek expert assistance or be ready to conduct your study. It is a tremendous error to translate keywords from your local site.
Why do we need a multilingual strategy to take our Website global?
Expanding your Target Market
Only 25% of Internet users are native English speakers. 75% aren’t. Hindi is the dominant language in India, and Spanish is the second most spoken language in the US.
Reduce Bounce Rates
72.1% of consumers spend most or all of their time on websites in their own language. – CSA
Slashing the competition
English is obviously the most competitive language. However, things may not be so rough in other languages.
Customer Centric Marketing
Being available in other languages is a modest gesture of personalization. What better way to improve a Brand’s image
Things to Do Before Implementing a MultiLingual Approach
- Research Audience
Develop your Customer avatar and identify their demographics, language preferences, where they
congregate mostly.
2. Language and Location
Multilingual SEO is a huge undertaking. Knowing the exact language and location of our target market can save time and improve efficiency.
3. Keyword Research
Since content needs to be personalized, it’s a good idea to have keywords ready in local languages to save time.
4. Choose the right search engines
Although Google is the dominant search engine, some countries have a preference. Make sure to include that in your research.
Steps to create a Multilingual site
Choose the right domain and URL Structure
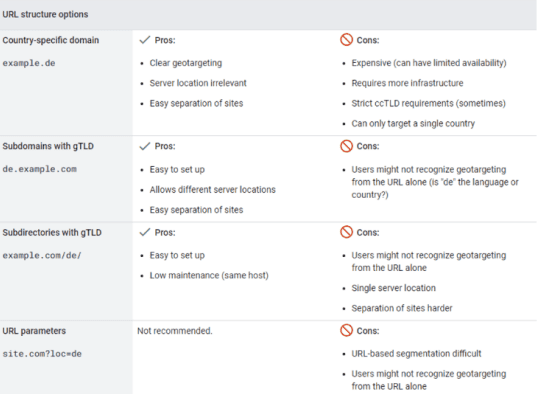
Whatever you do. Just do not go for URL Parameters. That’s the worst!
Create Multiple Language Versions Of Content
This is the hardest part… But Why Should you Do it?
A dedicated URL for your translated page can tell search engines that the page corresponds to a specific language so that it knows which one should be shown to speakers of different languages.
Common Mistakes
#Do not Set Up Automatic Redirects to language-specific pages. Instead, Google recommends giving internal links to different versions to let the user decide.
#Flag icons represent nations but not languages.
It is best to use links instead.
Translate and Create New content to make it Unique
It is unacceptable to use AI Content Writers or Google Translate. Why??
Google can detect automatically translated content and decrease its position and visibility in the search results.
Inaccurate grammar and language nuances can lead to irrelevant content leading to poor user experience and a higher bounce rate.
Recommendation:
Google can detect automatically translated content and decrease its position and visibility in the search results.
Take the help of professional copyrighting services.
It cheap Costs and gets the job done.
Use Hreflang Tags
Adding hreflang tags to your website is the best way to tell search engines how to distinguish which URLs are appropriate for each language on the website.
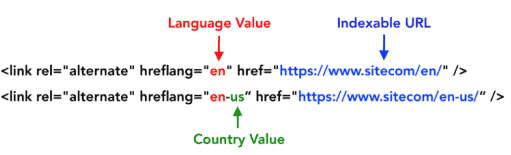
How to do it?
#Implement them in your language sitemap.
#Place them in the head section of the HTML Page.
#Place it in the HTTP header of non-HTML pages.
Using a Multilingual Sitemap
If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, you can use a plugin like Yoast SEO to automatically generate a sitemap.
A multilingual sitemap doesn’t differ much from a traditional one. However, it should include additional information about each <loc> entry.

Use Local Link Building Techniques
Why Should you Do it?
#Helps in Gaining Local Authority for
#Ranking in Local Indexes.
#Backlinks are more relevant.
#Reduces Spam
How To Do It
#Participate in Local Events.
#Get Listed in local citations.
#Influencer Marketing
#Guest Posting.
Final Conclusion
You have a lot of work ahead of you. But none of it is insurmountable if you make a strategy and take some rational actions.
- First and foremost, research to ensure a foreign audience.
- Second, decide if you want to target nations, languages, or both, and utilize the infographic above to organize your domain and URL.
- Third, as you design your localization techniques, get professional assistance from native speakers of those languages/countries.
- Fourth, be willing to study or discover specialists who can supply SEO-friendly keywords/phrases in the languages you are targeting.
- Fifth, get all of your housework in order.
This multilingual SEO guide should get you started. As you dip your toes into the multilingual SEO waters, you will learn from your mistakes, make adjustments and changes, and eventually become a master of this undertaking.

Thatware | Founder & CEO
Tuhin is recognized across the globe for his vision to revolutionize digital transformation industry with the help of cutting-edge technology. He won bronze for India at the Stevie Awards USA as well as winning the India Business Awards, India Technology Award, Top 100 influential tech leaders from Analytics Insights, Clutch Global Front runner in digital marketing, founder of the fastest growing company in Asia by The CEO Magazine and is a TEDx speaker and BrightonSEO speaker.

