SUPERCHARGE YOUR ONLINE VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
SEO audit is a vital step for making any SEO campaign a successful one. Let’s discover some crucial SEO elements in terms of performing an in-depth SEO audit for any kind of website.

Chapter 1:
Initial Search Console Analysis
Overview:
Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor, maintain, and troubleshoot your site’s presence in Google Search results.

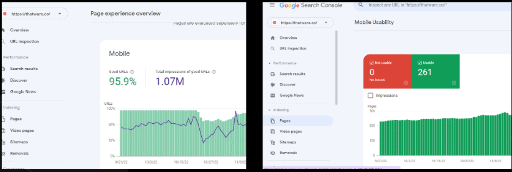
Mobile Usability:
All the mobile version pages are properly optimized for the website.
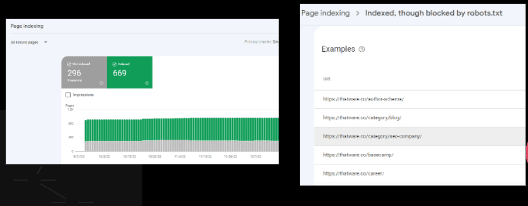
Observation:
There are 5 pages, which are blocked by robots.txt
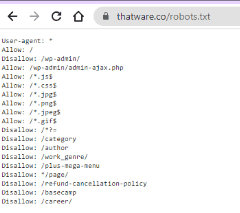
Recommendation and Solutions
If you do want to block this page from Google Search, robots.txt is not the correct mechanism to avoid being indexed. To avoid being indexed, remove the robots.txt block and use
‘noindex’.
If you do not want to block this page, update your robots.txt file to unblock your page. You can use the robots.txt tester to determine which rule is blocking this page.
Chapter 2:
Search Console Segmented Query Analysis
Overview:
Google search console provides data necessary to monitor website performance in search and improve search rankings, information that is exclusively available through Search Console.
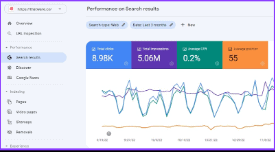
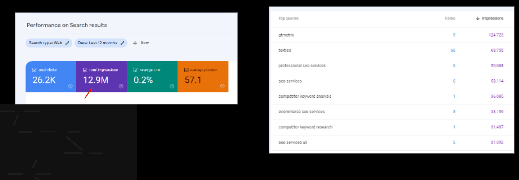
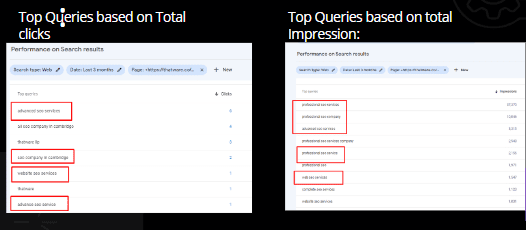
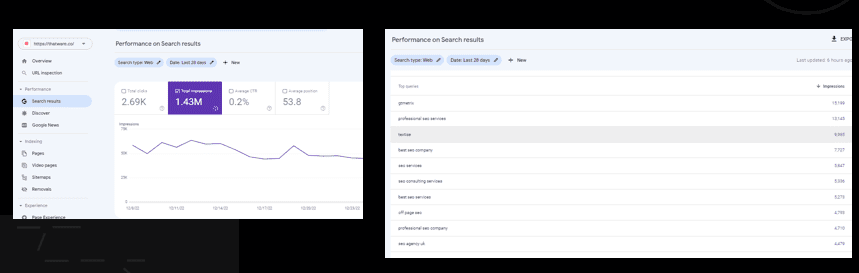
Total Clicks:
There are 26.2K clicks for the website, below mentioned
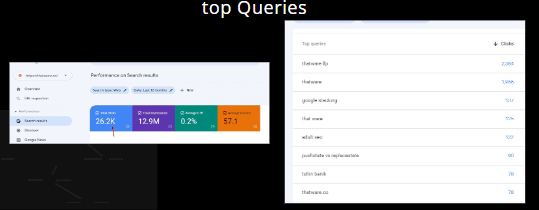
Total Impressions:
There are 12.9M impressions for the website, below mentioned top Queries
Chapter 3:
Search Console Device-Based Non Brand Query/Impression Analysis
Overview:
Here, we are analysing the clicks, and impression data based on the User device.
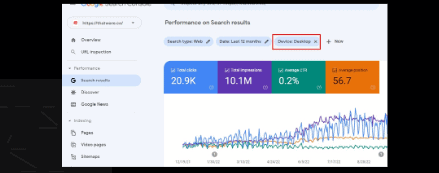
Performance based on Desktop:
Total Clicks: 20.9 K Total impressions: 10.1M Average CTR: 0.2%
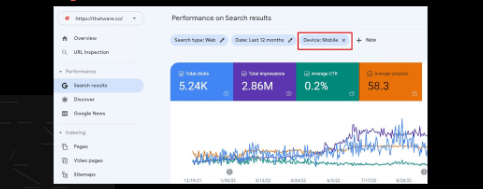
Performance based on Mobile:
Total Clicks: 5.24K
Total impressions: 2.86M Average CTR: 0.2%
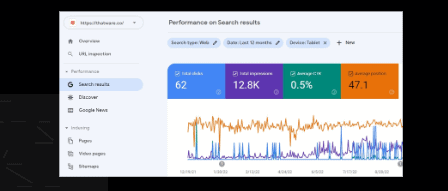
Performance based on Tablet:
Total Clicks: 62
Total impressions: 12.8K Average CTR: 0.2%
Chapter 4:
Keyword/Query Trajectory Analysis
Overview:
Keyword/query trajectory analysis is the process of tracking and analyzing the performance of specific keywords or search queries over time. This can be useful for understanding how well a particular keyword or query is performing, and can help you identify trends or changes in search behavior.
Observation:
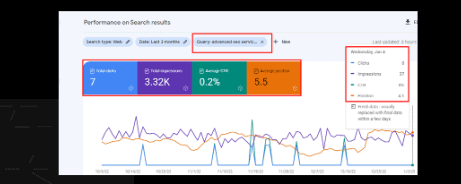
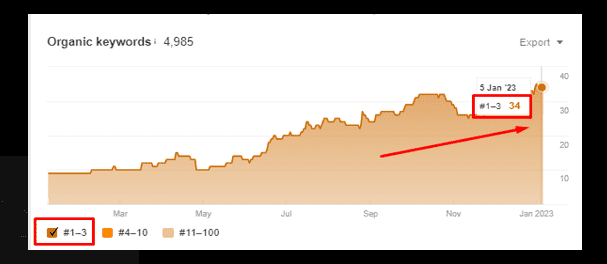
In the below mentioned screenshot, the query is Advance SEO service and this is the 3 month performance graph:
Observation:
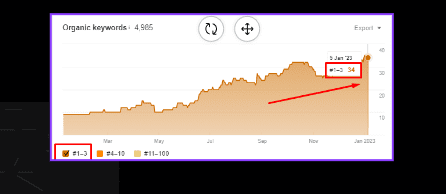
In the below-mentioned screenshot, there are 34 keywords within 1-3ʳᵈ position:
Observation:
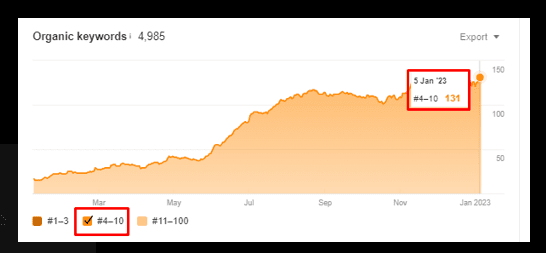
In the below-mentioned screenshot, there are 131 keywords within 4-10ᵗʰ position:
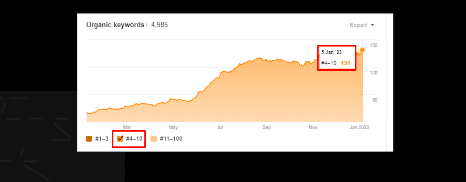
Observation:
In the below-mentioned screenshot, there are 4818 keywords within 11-100ᵗʰ position:
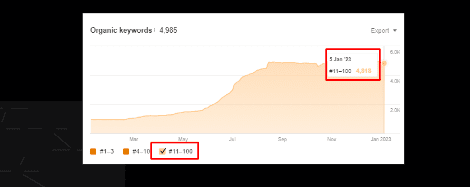
Chapter 5:
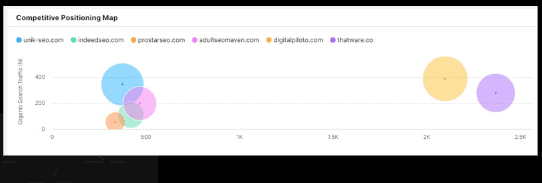
Competitor SERP Performance Over Time
Competitive positioning Map:
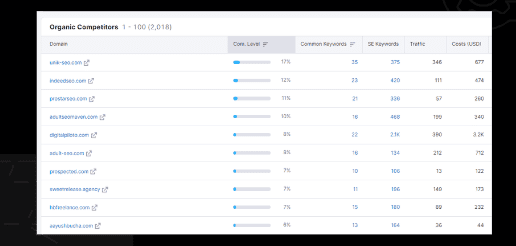
Organic Competitors:
Chapter 6:
Website Index Analysis
Overview:
Website indexation is the process where the search engine bot adds information about a certain resource to the search system database. The page indexation check is necessary to show the webmaster how robots scan the website.
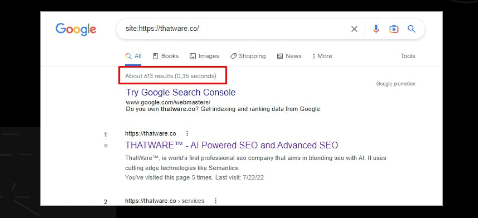
Index pages according to Google:
There are 613 pages are indexed on Google SERP.
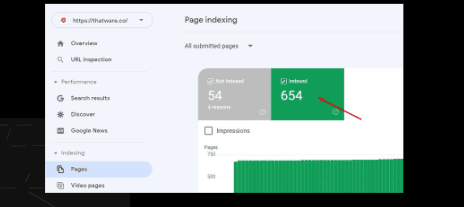
Index pages according to GSC:
There are 654 pages are indexed according to Google Search Console.
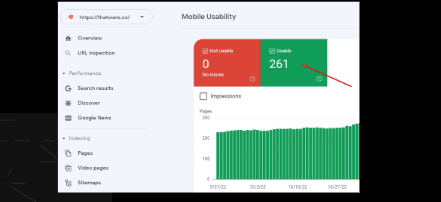
Index pages according to GSC Mobile:
There are 261 pages are indexed in the mobile version according to Google Search Console.
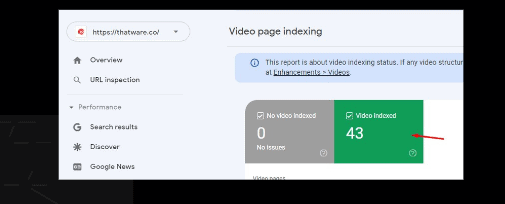
Index video pages according to GSC:
There are 43 video pages are indexed according to Google Search Console.
Chapter 7:
Supplemental / Omitted Result Analysis
Overview:
In the context of search engine optimization (SEO), omitted result analysis can be used to identify the factors that are most important in ranking a website in search engine results. SEO is the practice of optimizing a website in order to improve its ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs). There are many factors that can influence a website’s ranking, including the quality and relevance of the content, the structure and organization of the website, and the number and quality of external links pointing to the website.
Duplicate Page Title:
There is no page with a duplicate page title for the website.
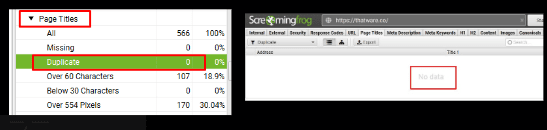
Duplicate Page Description:
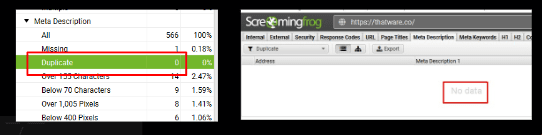
There is no page with a duplicate page description for the website.
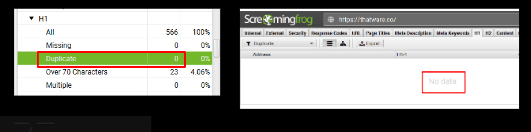
Duplicate H1 Tag:
There is no page with duplicate H1 Tag for the website.
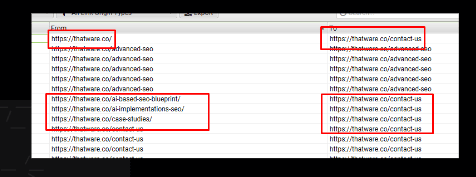
Canonicalised:
There are 3 pages with canonicalised issue for the website.
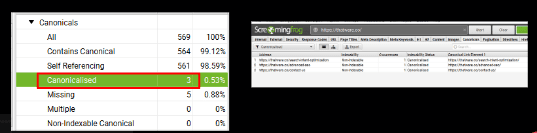
Recommendation and Solutions
Need to modify the hyperlink and put the relevant URLs on the red-marked pages.
Chapter 8:
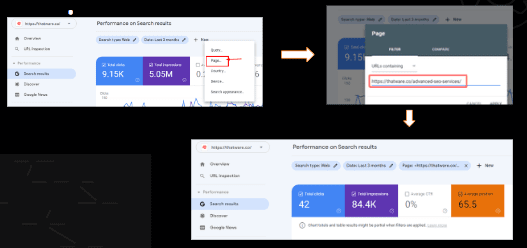
Page Level Query Performance Analysis
Page-level query performance analysis is a technique used in search engine optimization (SEO) to assess how well individual pages on a website are ranking for specific keywords or phrases. This type of analysis is important because it can help identify which pages on a website are performing well in search results and which pages may need additional optimization in order to improve their rankings.
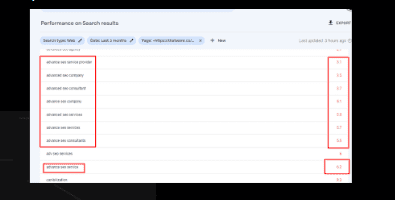
Top Queries based on Avg. position:
Chapter 9:
Cannibalisation Audit
A cannibalization audit is a process used in search engine optimization (SEO) to identify and resolve situations where multiple pages on a website are competing for the same keywords or phrases, resulting in a dilution of ranking and traffic for those keywords.
This type of audit is often performed when a website has a large number of pages that cover similar or overlapping topics, as this can lead to confusion for search engines and a reduction in the overall effectiveness of the website.
Observation:
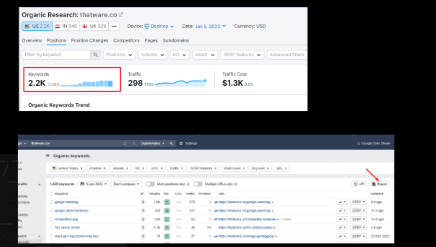
There are 2 keywords with Cannibalisation issue:

Recommendation:
Need to merge those two pages and create a beauty niche page:
Chapter 10:
Low Quality Content Audit
A low-quality content audit is a process used in search engine optimization (SEO) to identify and address pages on a website that are of poor quality or that do not provide value to users. This type of audit is often performed as part of a larger SEO strategy, as low-quality content can have a negative impact on a website’s ranking in search results.
To perform a low-quality content audit, a researcher typically begins by identifying the pages on a website that are of low quality or that do not provide value to users.
This can be done using a variety of methods, such as analyzing the traffic and engagement metrics of individual pages, reviewing the content of the pages, or identifying pages that have been flagged by search engines as low quality.
Observation:
There are 9 pages with Low content:
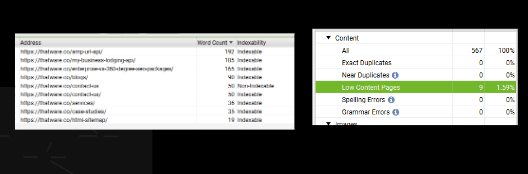
There are several ways you can improve low content pages on your website:
Add more content: If a page has very little content, consider adding more relevant and useful information.
Expand existing content: If a page has some content, but it is thin, you can expand on the existing content to make it more comprehensive.
Update outdated content: If a page contains outdated information, consider updating it with fresh and accurate content.
Improve formatting: Poor formatting can make a page look cluttered and unprofessional. Consider using headings, bullet points, and white space to improve the formatting of your content.
Chapter 11:
Initial Site Content Audit
An initial site content audit is a process used in search engine optimization (SEO) to assess the current state of a website’s content and identify opportunities for improvement. This type of audit is often performed when a website is being redesigned or when a new SEO strategy is being developed.
To perform an initial site content audit, a researcher typically begins by reviewing the current state of the website’s content, including the structure, organization, and quality of the content. The researcher may use a variety of tools and techniques to gather data on the website’s content, such as site audit tools, analytics data, and manual reviews of the content.
Observation:
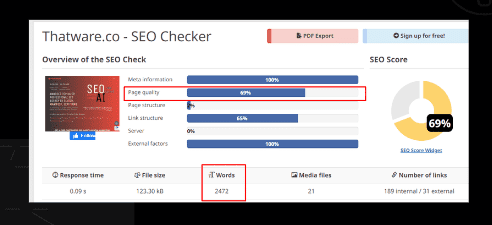
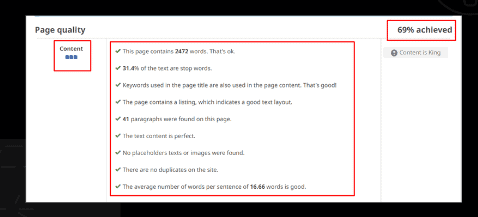
Chapter 12:
Duplicate & Cannibalising Content Evaluation
Duplicate and cannibalizing content are both issues that can impact the effectiveness of a website in search engine results. Duplicate content refers to content that is identical or very similar to content found on other websites or pages on the same website. Cannibalizing content refers to situations where multiple pages on a website are competing for the same keywords or phrases, resulting in a dilution of ranking and traffic for those keywords.
Duplicate and cannibalizing content evaluations are an important part of SEO, as they can help to ensure that a website is effectively targeting its desired keywords and that its pages are not competing against each other for ranking in search results.
Observation:
There are 21 pages with duplicate content for the website.
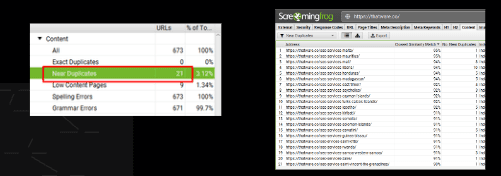
Recommendation:
Consolidate the content:
If you have multiple pages with very similar content, consider consolidating the content onto a single page. This will help prevent confusion for users and search engines, and may also help improve the overall quality of your content.
Use a 301 redirect:
If you have multiple pages with duplicate content that you cannot consolidate, you can use a 301 redirect to send users and search engines from the duplicate pages to the original page. This will help prevent any negative effects on your search engine rankings.
Use the rel=canonical tag:
If you have multiple pages with similar content that you want to keep separate, you can use the rel=canonical tag to indicate to search engines which page is the original and should be indexed.
Chapter 13:
Query to Landing Page Relevancy Alignment
Query to landing page relevancy alignment refers to the process of ensuring that the content of a landing page is closely aligned with the keywords or phrases that a user is searching for. This is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because it can help to improve the relevancy and quality of a website’s search results, which can lead to higher ranking and more traffic for the website.
Chapter 14:
Site URL Architecture Analysis
Site URL architecture analysis is the process of evaluating the structure and organization of the URLs (uniform resource locators) on a website. This is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because it can impact the usability and accessibility of a website, as well as its ranking in search results.
Site URL architecture analysis is an important aspect of SEO, as it can help to ensure that a website’s URLs are well-organized, easily accessible, and optimized for search engines.
Observation:
There is 1 page URL in uppercase and the rest of the URL structures are proper for the website.
Chapter 15:
URL Consistency Evaluation
URL consistency evaluation is the process of reviewing and ensuring that the URLs (uniform resource locators) on a website are consistent and adhere to best practices. This is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because it can impact the usability and accessibility of a website, as well as its ranking in search results.
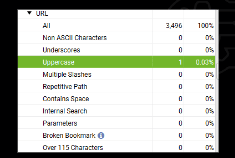
Observation:
There is 1 page URL with uppercase and the rest of the URL structures are proper for the website.
Chapter 16:
Full Tag Evaluation (Canonicals, HREFLANG et.c)
A full tag evaluation is a process of reviewing and evaluating the use of tags on a website. Tags are pieces of code that provide additional information about the content of a webpage and how it should be displayed or processed by search engines and other web browsers. Some common tags that may be included in a full tag evaluation include:
Canonical tags: Canonical tags are used to indicate the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple URLs that display the same content. This can be useful for avoiding duplication issues in search results.
Hreflang tags: Hreflang tags are used to indicate the language and targeted geographic region of a webpage. This can be useful for improving the relevancy of a website’s search results for users in different regions and languages.
Title tags: Title tags are used to specify the title of a webpage and are often displayed in the search results as the main link to the webpage. Title tags should be unique, relevant, and descriptive in order to improve the website’s ranking in search results.
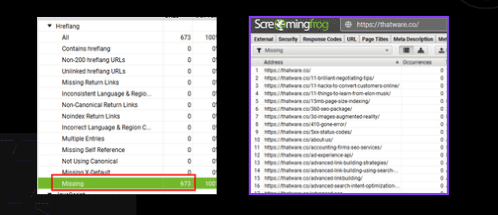
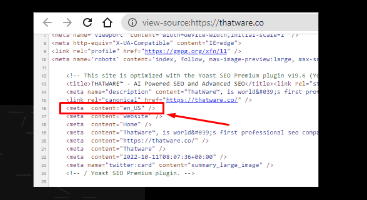
Hreflang:
All pages don’t have hreflang tag for the website.
Recommendation:
The website is only based on the English language and the below-mentioned tag in present for all the pages.
So, no need to add hreflang code on the website:
Chapter 17:
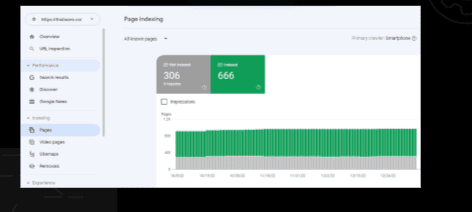
Search Console Coverage Evaluation
Overview:
A Search Console coverage evaluation is a process of reviewing the coverage of a website in Google Search Console, a tool provided by Google that allows website owners to monitor the performance of their website in Google search results. This type of evaluation can be useful for identifying issues with a website’s indexing and for improving its ranking in search results.
To perform a Search Console coverage evaluation, a researcher typically begins by accessing the Search Console and reviewing the data provided by the tool. This may include data on the number of pages that have been indexed by Google, the number of pages with errors or warnings, and the search queries that are driving traffic to the website.
Observation:
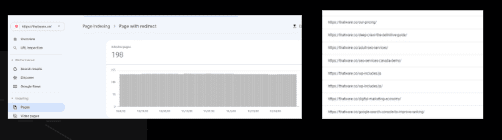
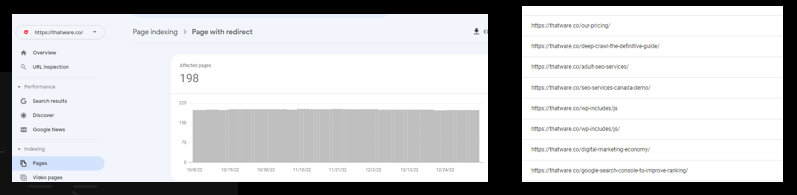
Page with redirect:
The URL redirects to another URL and therefore was not indexed. The final target URL might be indexed, and should appear in this report. If you test this URL in the URL Inspection report, the indexed test will show the redirect; the live test will follow and test the redirected page, though it won’t show the URL of the redirected and tested page.
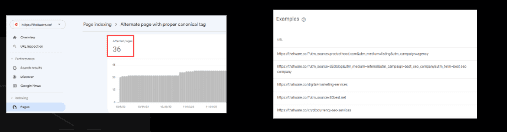
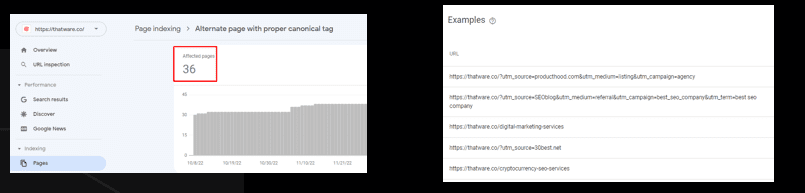
Alternate page with proper canonical tag:
This page is marked as an alternate of another page (that is, an AMP page with a desktop canonical, or a mobile version of a desktop canonical, or the desktop version of a mobile canonical). This page correctly points to the canonical page, which is indexed, so there is nothing you need to do. Alternate language pages are not detected by Search Console.
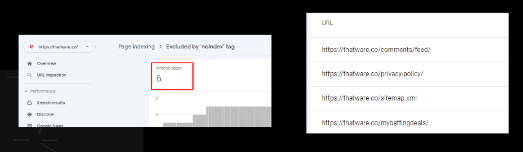
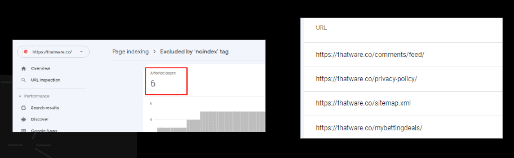
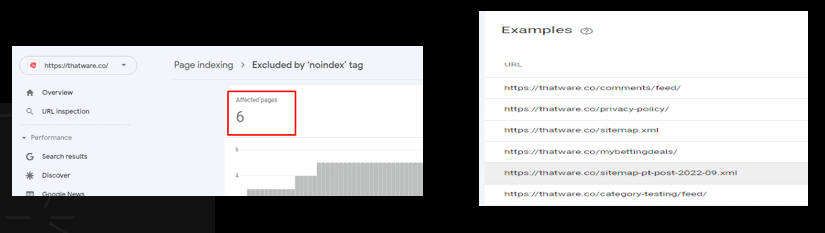
Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag:
When Google tried to index the page it encountered a ‘noindex’ directive and therefore did not index it. If you do not want this page indexed, so, the tag is ok for the page.
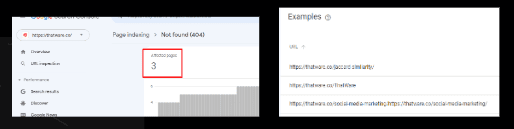
Not found (404)
This page returned a 404 error when requested. Google discovered this URL without any explicit request or sitemap. Google might have discovered the URL as a link from another page, or possibly the page existed before and was deleted.
Need to redirect those pages with the relevant page:
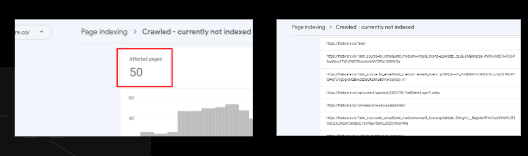
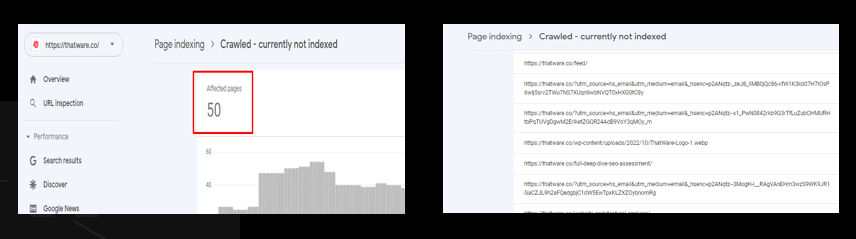
Crawled – currently not indexed:
The page was crawled by Google but not indexed. It may or may not be indexed in the future; no need to resubmit this URL for crawling.
Chapter 18:
Landing Page Construction (Template Evaluation)
Landing page construction, or template evaluation, is the process of reviewing and evaluating the design and structure of a website’s landing pages. Landing pages are the pages on a website that users are directed to after clicking on a link in search results or from another website. They are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can impact the website’s ranking in search results and the user experience of visitors to the website.
The Page URLs follow the proper structure and the URL structure is sorted and exact to the services:
Chapter 19:
Title performance, or CTR (click-through rate), refers to the percentage of users who click on a link in search results after seeing the title of the link. The title of a link is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because it can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the number of clicks that the link receives.
Title performance is an important aspect of SEO, as it can impact the ranking and traffic of a website. It is important to regularly review and optimize the titles of a website’s links in order to improve their performance in search results.
Over 60 char Title:
There are 110 pages that have Page title with over 60 characters:
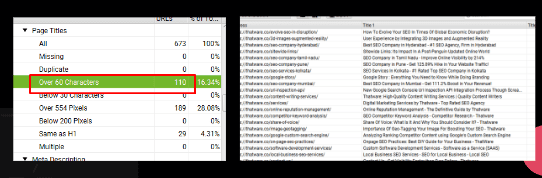
Recommendation:
To fix a title that is over 60 characters, you can try the following options:
Edit the title:
Review the title and see if there are any words or phrases that can be removed without changing the meaning of the title. This can help you get the title within the recommended length while still accurately describing the content.
Use a title tag plugin:
If you are using a content management system like WordPress, you can install a plugin that automatically adjusts the title tag to meet the recommended length.
Title same as H1 Tag:
There are 29 pages have Page title same as H1 tag:
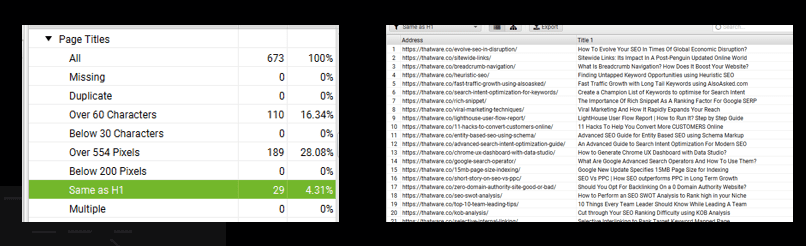
Recommendation:
If the title of your page is the same as the H1 tag, you can fix this by either changing the title or the H1 tag so that they are different.
Here are some options for fixing this issue:
Change the title:
If the title and H1 tag are the same, consider changing the title to be more descriptive or compelling. Make sure to keep the title within the recommended length of 60 characters or less.
Change the H1 tag:
If the title is fine but the H1 tag is the same as the title, consider changing the H1 tag to a more specific or descriptive heading. You can use subheadings (H2, H3, etc.) to provide more information about the content of the page.
It’s important to have unique and descriptive titles and H1 tags for each page on your website. This helps search engines understand the content of your page and can improve its ranking in the search results. It also helps users understand what the page is about and can make them more likely to click on the page in the search results.
Chapter 20:
MetaDescriptionEvaluation
A meta description evaluation is the process of reviewing and evaluating the meta descriptions of a website’s pages. Meta descriptions are short summaries of the content of a webpage that are displayed in the search results beneath the title of the page. They are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the number of clicks that the page receives.
Meta description evaluation is an important aspect of SEO, as it can impact the ranking and traffic of a website. It is important to regularly review and optimize the meta descriptions of a website’s pages in order to improve their performance in search results.
Missing Description:
There is 1 page with missing Description:
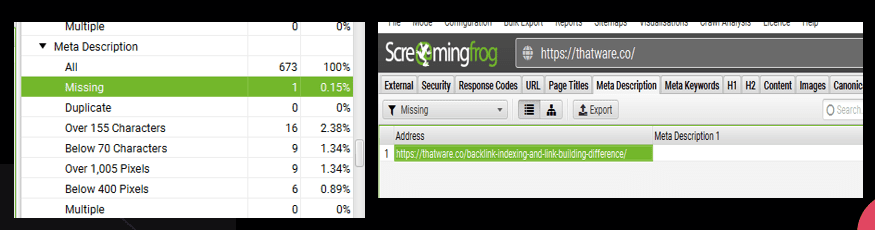
Recommendation:
To fix a missing description on your website, you can do the following:
Add a meta description:
A meta description is a brief summary of the content of a web page that appears in the search results. To add a meta description to your page, you will need to edit the source code of the page and include a meta description tag.
Make sure to include relevant keywords and phrases and make the description compelling to users. Aim for a description that is around 155 characters or less.
A well-written meta description can help improve the click-through rate (CTR) of your page in the search results, as it gives users a better idea of what the page is about and can make them more likely to click on the page.
Description over 155 char:
There are 16 pages have meta description over 155 characters:
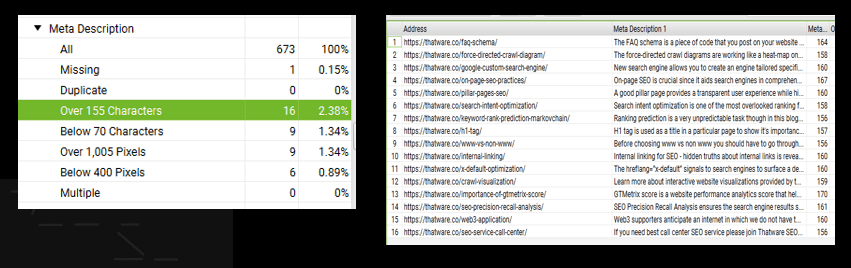
Recommendation:
If your meta description is over 155 characters, you can fix this by shortening the description to meet the recommended length. Here are some tips for doing this:
Remove unnecessary words or phrases:
Review the description and see if there are any words or phrases that can be removed without changing the meaning of the description. This can help you get the description within the recommended length.
Use abbreviations:
If the description is still too long after removing unnecessary words, consider using abbreviations to save space. Just make sure to use commonly accepted abbreviations and avoid using abbreviations that may not be familiar to users.
Description below 70 char:
There are 9 pages that have meta descriptions below 70 characters:
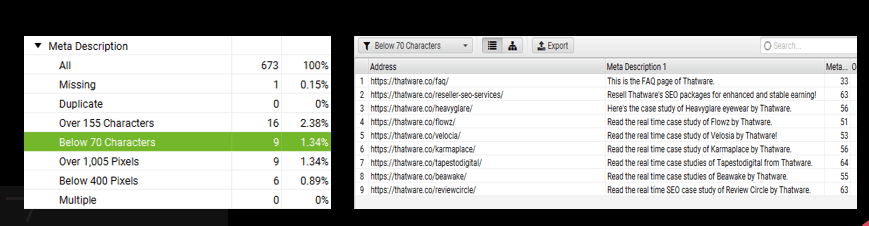
Recommendation:
If your meta description is below 70 characters, you can fix this by lengthening the description to meet the recommended length. Here are some tips for doing this:
Add more detail:
Consider adding more detail to the description to give users a better understanding of the content of the page. You can include information about the main topic of the page, any unique features or benefits, or any other relevant details.
Include relevant keywords and phrases:
Make sure to include relevant keywords and phrases in the description to help search engines understand the content of the page. This can also help the page rank higher in the search results for those keywords.
Chapter 21:
Site Crawl & Reported Header Codes
A site crawl is a process of reviewing and analyzing the structure, content, and other characteristics of a website by reviewing and analyzing the code and data associated with the website. Header codes are a type of code that can be included in the header of a webpage and provide additional information about the page, such as its content type or its server location.
Site crawls and reported header code evaluations are important aspects of search engine optimization (SEO) as they can help to ensure that a website is optimized for search engines and provides a high-quality user experience. It is important to regularly review and analyze the code and data associated with a website in order to identify and address any issues or opportunities for improvement.
How to prevent:
Need to index all the pages properly on Google SERP.
Google index value is 847
Daily crawl rate: 341
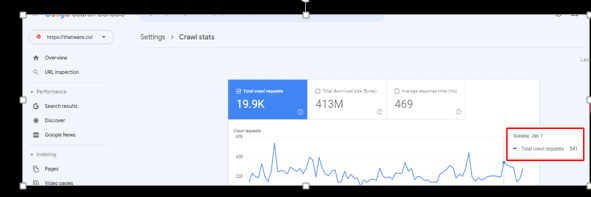
How to prevent:
Crawl budget = (Site Index value) / (Single day crawl stat)
The ideal score are as follows:
1. If the Crawl budget is between 1 – 3 is Good
2. If the Crawl budget is 4 – 10 is bad and needs fix
3. If the crawl budget is 10+ then its worst and needs immediate technical fixes
As per the calculation,
Crawl budget for https://thatware.co = 847/341 = 2.48
Crawl Budget Comparison:
The score for https://thatware.co is 2.48 which is in ideal zone of 1 – 3.
Summary:
Hence, the campaign https://thatware.co is optimized by crawl budget, but need to increase daily crawl pages.
Chapter 22:
Re-Direction & Re-Direct Chains
Redirection and redirect chains refer to the use of techniques to redirect users or search engines from one URL (uniform resource locator) to another. Redirection is often used to ensure that users and search engines are directed to the most appropriate or up-to-date version of a webpage.
Redirection and redirect chain evaluations are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO), as they can impact the performance and ranking of a website in search results. It is important to regularly review and optimize the use of redirects on a website in order to ensure that they are being used effectively and efficiently.
Observation:
There are 6 redirect chains for the website.
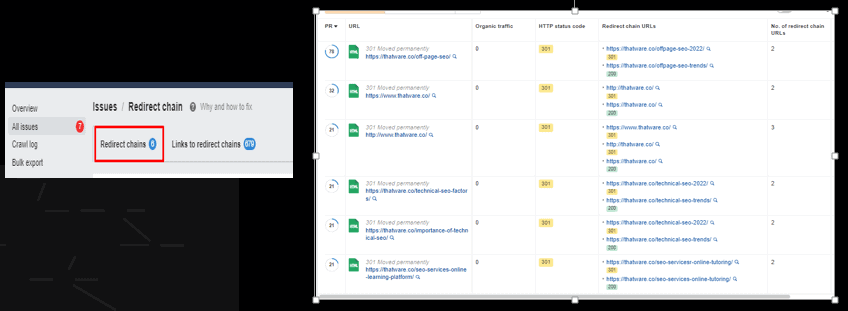
Observation:
There are 175 redirection pages for the website.
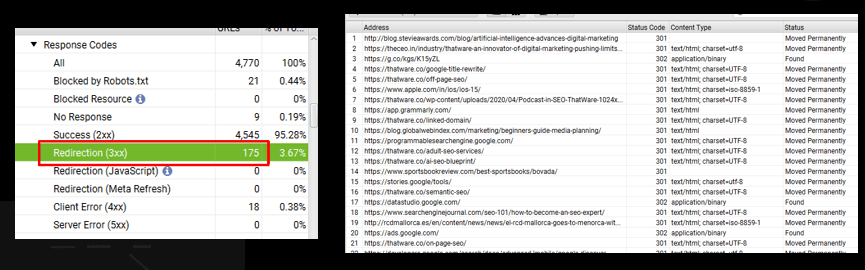
To fix a redirect chain, you can use a tool like Screaming Frog to identify the redirect chain, and then update the redirects to point directly to the final destination URL. You can also try to consolidate the redirects by using a single redirect from the initial URL to the final destination URL.
It’s generally a good idea to keep the number of redirects to a minimum, so if you have a long redirect chain, it’s worth taking the time to clean it up. This can help improve the speed and performance of your website, as well as help ensure that your pages have maximum authority and ranking power.
Chapter 23:
Internal Linking Audit
An internal linking audit is a process of reviewing and evaluating the internal links on a website. Internal links are links that point to other pages within the same website.
They are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can help to improve the accessibility and usability of a website, as well as its ranking in search results.
An internal linking audit is an important aspect of SEO, as it can help to ensure that a website’s internal links are being used effectively and efficiently. It is important to regularly review and optimize the internal linking on a website in order to improve its performance in search results.
Observation:
Chapter 24:
Use of Headings & Content Relation Evaluation
The use of headings and content relation evaluation refers to the process of reviewing and evaluating the use of headings and the relationship between the headings and the content on a website. Headings are used to structuring and organize the content of a webpage, and they can impact the accessibility and usability of a website, as well as its ranking in search results.
Evaluating the use of headings and the content relation is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO), as it can impact the accessibility, usability, and ranking of a website. It is important to regularly review and optimize the use of headings and the content relation on a website in order to improve its performance in search results.
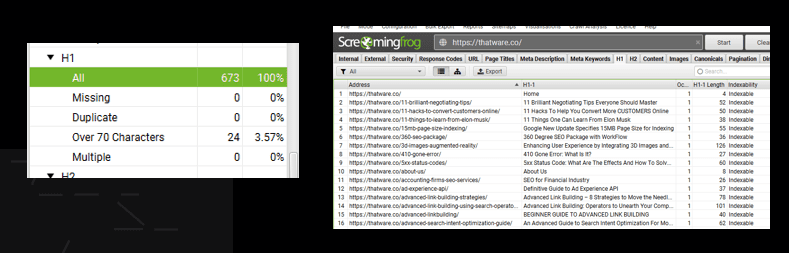
Overview:
There is no issue with the H1 tag for the website, all the H1 tags are properly optimized.
Chapter 25:
Page Accessibility Element Review
Based on the review of the accessibility of the website’s pages, the researcher can identify any issues or opportunities for improvement and make recommendations for optimizing the accessibility of the pages. This may involve adding or updating elements on the pages to improve their accessibility, reorganizing the content of the pages to make it easier for users with disabilities to access and understand, or implementing other accessibility-related changes as needed.
Page accessibility element review is an important aspect of website design and development, as it can help to ensure that a website is accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities. It is important to regularly review and optimize the accessibility of a website’s pages in order to provide a high-quality user experience for all visitors.
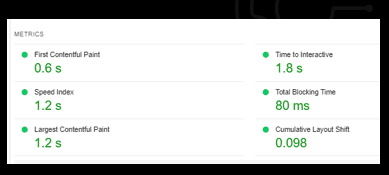
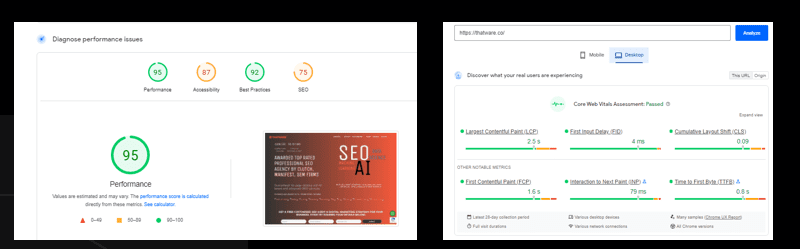
Overview:
The overall performance score is 95, which is better than the leading competitors.
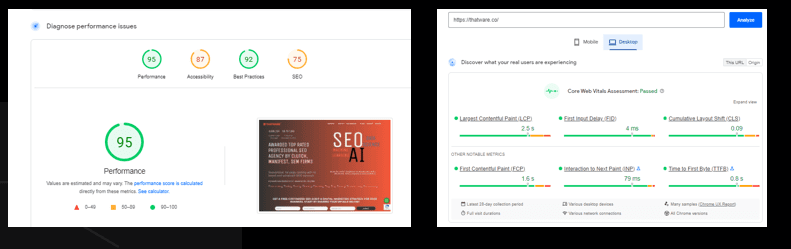
Overview:
Chapter 26:
Site Navigation & Footer Evaluation
Site navigation and footer evaluation is the process of reviewing and evaluating the navigation and footer elements of a website. The navigation of a website refers to the structure and organization of the links and menus that allow users to move around the website and access its content. The footer of a website is the bottom section of the website that typically contains links to additional content or information.
Overview
The copyright section and Social media links are properly present in the Footer section.
All the important pages and proper addresses are present in the Footer section.
Chapter 27:
Domain Trust Factors Review
Domain trust factors refer to the elements of a website that can impact the level of trust that users and search engines have in the website. These elements can include the age of the website, the quality and relevance of the content on the website, the website’s reputation, and the security and privacy of the website.
Domain trust factors are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) and online reputation management, as they can impact the ranking and traffic of a website in search results. It is important to regularly review and optimize the domain trust factors of a website in order to improve its performance in search results and its reputation online.
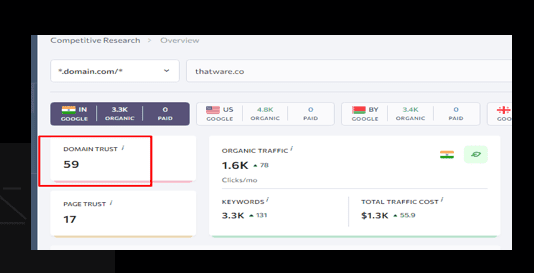
Overview:
The domain trust of the website is 59, which is quite good for the website.
Chapter 28:
Sub Domain Evaluation
A subdomain evaluation is the process of reviewing and evaluating the use of subdomains on a website. A subdomain is a section of a website that is hosted on a separate domain but is still part of the main website. Subdomains can be used to organize and structure the content of a website, and they can also be used to create separate websites or web applications that are related to the main website.
To perform a subdomain evaluation, a researcher typically begins by reviewing the use of subdomains on a website and identifying any issues or opportunities for improvement. This may involve examining the structure and organization of the subdomains, the relevance and quality of the content on the subdomains, and the relationship between the subdomains and the main domain.
Overview:
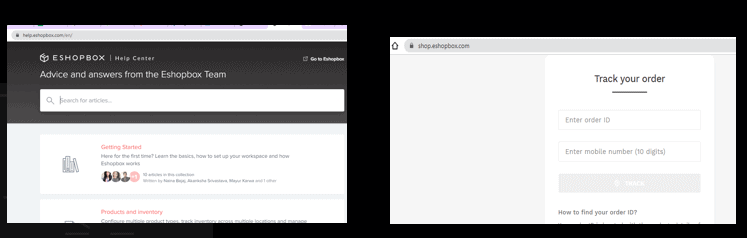
Here the main website is https://www.eshopbox.com/, where they provide fast, affordable and reliable fulfilment for all of your eCommerce sales channels.

Overview:
On the other hand, there are 2 subdomains:
- help.eshopbox.com: For any type of advice and answer on fulfilment service.
- Shop.eshopbox.com: For tracking the order data.
Chapter 29:
Link Audit (Full Referring Domain Review)
A link audit, or full referring domain review, is the process of reviewing and evaluating the links that point to a website. Links are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the traffic that the website receives.
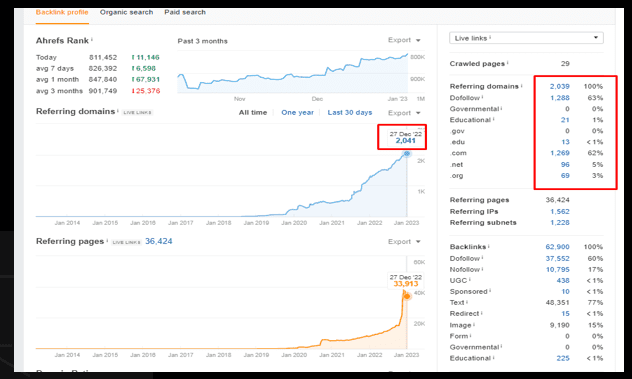
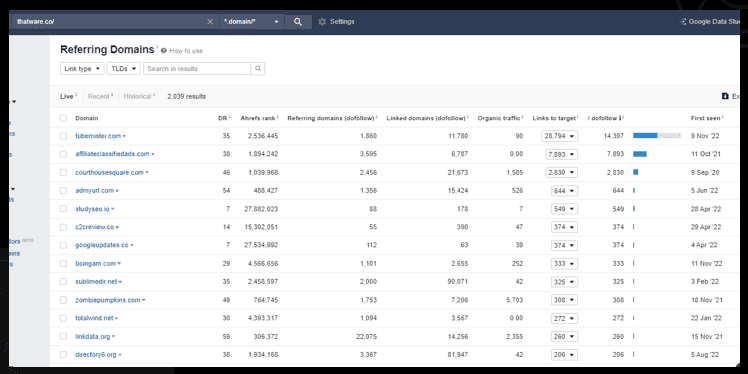
To perform a link audit, a researcher typically begins by reviewing the links that point to a website and identifying any issues or opportunities for improvement.
This may involve examining the quantity and quality of the links, the relevance and authority of the websites that are linking to the website, and the use of anchor text and other link attributes.
Observation:
Chapter 30:
Link Performance Over Time & Distribution
Link performance over time and distribution refers to the analysis of the performance of a website’s links over time and the distribution of the links across different sources and platforms. Links are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the traffic that the website receives.
Evaluating link performance over time and distribution is an important aspect of SEO, as it can help to identify trends and patterns in the performance of a website’s links and identify opportunities for improvement. It is important to regularly review and analyze the link performance and distribution of a website in order to optimize its performance in search results.
Observation:
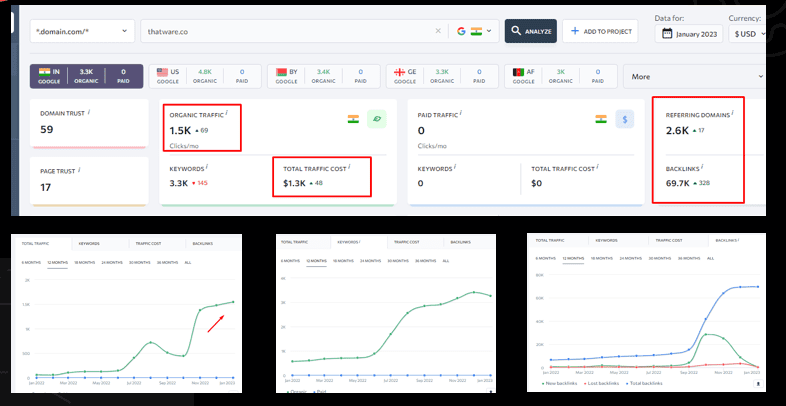
Chapter 31:
Anchor Text Audit
An anchor text audit is the process of reviewing and evaluating the anchor text of the links that point to a website. Anchor text is the visible, clickable text in a hyperlink. It is an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because it can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the traffic that the website receives.
An anchor text audit is an important aspect of SEO, as it can help to ensure that the anchor text of the links to a website is being used effectively and efficiently. It is important to regularly review and optimize the anchor text of the links to a website in order to improve its performance in search results.
Overview:
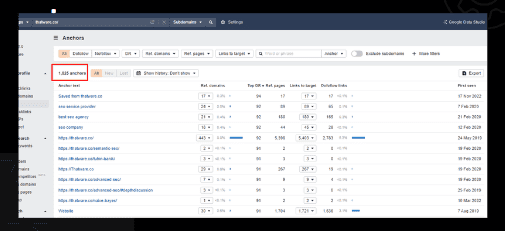
Chapter 32:
Competitor Link Performance Evaluation
Competitor link performance evaluation is the process of reviewing and evaluating the link performance of a website’s competitors. Links are an important aspect of search engine optimization (SEO) because they can impact the ranking of a website in search results and the traffic that the website receives.
Competitor link performance evaluation is an important aspect of SEO, as it can help to identify trends and patterns in the link performance of a website’s competitors and identify opportunities for improvement. It is important to regularly review and analyze the link performance of a website’s competitors in order to optimize the performance of the website in search results.
Overview:
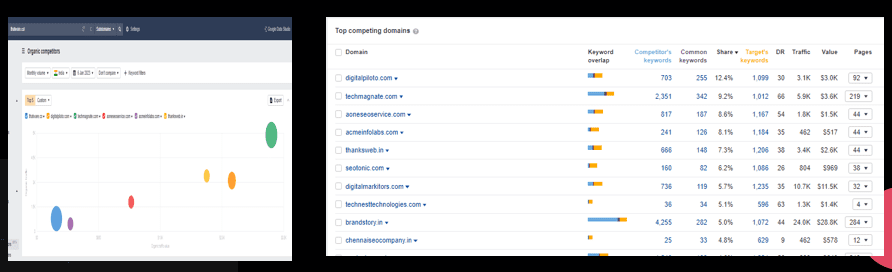
Chapter 33:
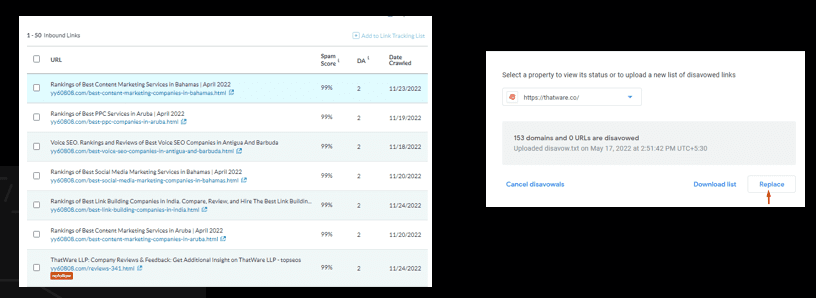
Link Spam Review
Link spam is a type of spamming technique that involves the use of low-quality or unrelated links to manipulate search engine rankings.
Link spamming is generally considered to be a negative practice by search engines and is actively discouraged. Search engines have implemented various measures to detect and penalize websites that engage in link spamming, as it can have a detrimental effect on the overall quality and integrity of search engine results. If you suspect that a website is engaging in link spamming, it is advisable to report it to the relevant search engine or to a reputable website that monitors and reports on spamming activities.
Link spam is a type of spamming technique that involves the use of low-quality or unrelated links to manipulate search engine rankings.
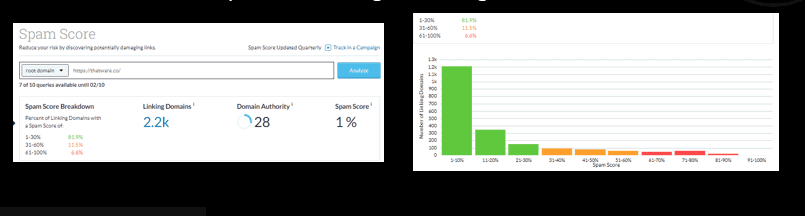
Chapter 34:
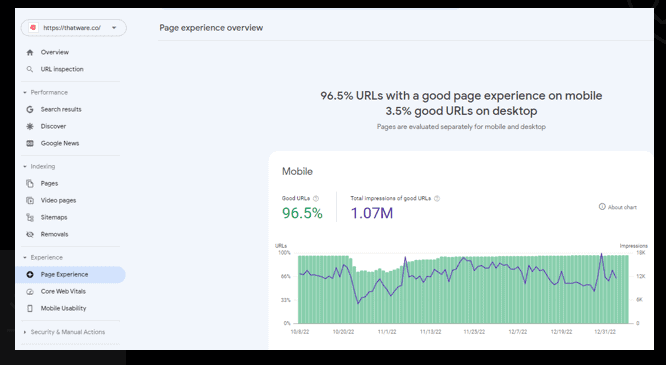
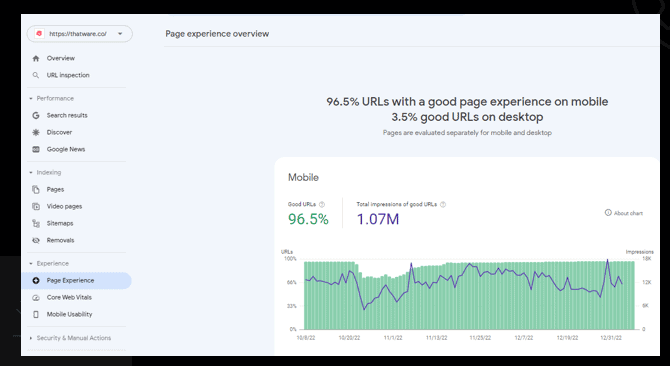
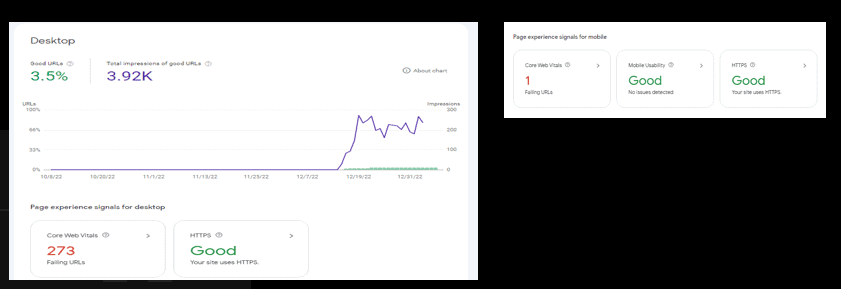
Page Experience/Core Web Vitals Review
Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics that measure the performance, accessibility, and user experience of a website. They were introduced by Google in May 2021 as part of the Page Experience update to its search ranking algorithm. The three Core Web Vitals are:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures the loading speed of a page and reflects the time it takes for the largest content element. A good LCP score is under 2.5 seconds.
First Input Delay (FID): This measures the interactivity of a page and reflects the time it takes for a page to become responsive to user input (such as a click or tap). A good FID score is under 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): This measures the visual stability of a page and reflects the amount of unexpected layout shifts (such as an element moving or resizing unexpectedly) that occur while the page is loading. A good CLS score is under 0.1.
Overview:
The overall performance score is 95, which is better than the leading competitors.
Chapter 35:
Google Tag Checks
Google Tag Manager is a free tool that allows you to easily add and manage marketing and analytics tags on your website without requiring code changes. It works by allowing you to add small snippets of code (called “tags”) to your website that can track and send data to various marketing and analytics platforms (such as Google Analytics or Google Ads).
There are several checks that you can perform to ensure that your Google Tag Manager implementation is correct and functioning properly:
Verify that the Google Tag Manager container snippet has been properly added to your website. This snippet should be added to every page of your website, and it should be placed immediately after the opening <body> tag.
By performing these checks, you can ensure that your Google Tag Manager implementation is correct and that your tags are functioning properly. This will help you to accurately track and measure the performance of your website and marketing efforts.
Google Analytics and Google Search Console codes are properly present on the website.
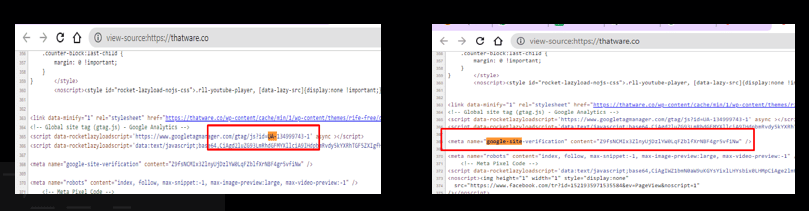
Chapter 36:
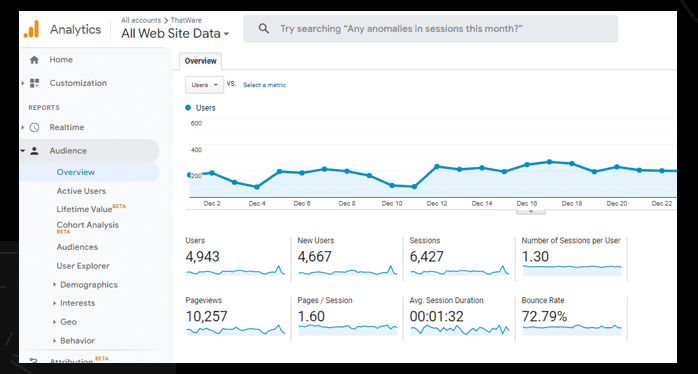
Google Analytics Initial Audit
An initial audit of your Google Analytics implementation can help you to ensure that your tracking is set up correctly and that you are accurately measuring the performance of your website. Here are some steps you can take to conduct an initial audit of your Google Analytics implementation:
Verify that the Google Analytics tracking code is installed correctly on your website. The tracking code should be added to every page of your website, and it should be placed immediately after the opening <head> tag.
Check that the Google Analytics tracking code is only added once to each page. If the tracking code is added multiple times, it could cause errors or duplication of data.
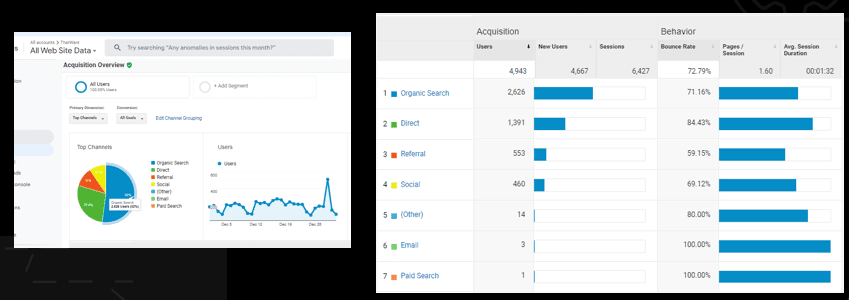
Chapter 37:
Overall SEO Performance Summary
Here are some key metrics and areas that you should consider when evaluating your overall SEO performance:
Organic traffic: This is the number of visitors who arrive at your website through search engine results pages. You can check your organic traffic in Google Analytics or a specialized SEO tool.
Keyword rankings: This is the position that your website appears in search engine results for specific keywords. You can check your keyword rankings using a specialized SEO tool or by manually searching for your keywords in a search engine.
On-page SEO: This refers to the optimization of individual web pages on your website to improve their ranking in search engine results. On-page SEO factors include the page title, meta description, header tags, and content quality.
Technical SEO: This refers to the optimization of the underlying technical infrastructure of your website to improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results. Technical SEO factors include the website’s loading speed, mobile-friendliness, and security.
Backlinks: These are links from other websites to your website. Backlinks are an important factor in SEO because they help to show search engines that your website is authoritative and trustworthy.
By analyzing these metrics and areas, you can get a summary of your overall SEO performance and identify areas for improvement. This will help you to optimize your website and improve its visibility and ranking in search engine results.
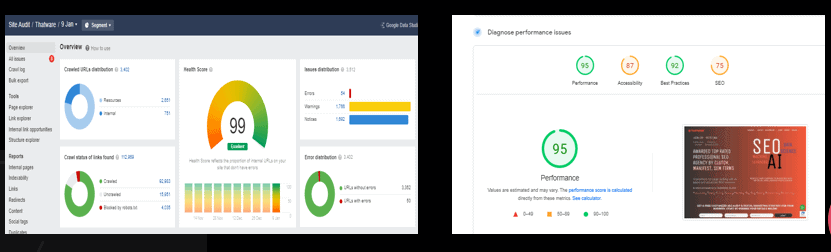
Overview:
Here the On-page score of the website is 99% and the technical score of the website is 95%.
Chapter 38:
Aggregated Query / Click to Query Vol Analysis
Aggregated query data refers to data that has been grouped or summarized in some way. For example, you might aggregate query data by grouping it by date, or by grouping it by the search terms that were used.
Click-to-query (CTQ) volume analysis is a way of analyzing the relationship between the number of searches for a specific query (the query volume) and the number of clicks on the search results for that query (the click volume). CTQ volume analysis can help you to understand how users are interacting with search results and can provide insights into the effectiveness of your website’s ranking in search results.
To perform CTQ volume analysis, you can use tools such as Google Search Console or a specialized SEO tool such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz. These tools will allow you to view the query volume and click volume for specific keywords or groups of keywords over a given time period. You can then use this information to identify trends and patterns in user behavior and to optimize your website’s ranking in search results.
For example, you might use CTQ volume analysis to identify which keywords have a high query volume but a low click volume. This could indicate that users are not finding the search results relevant or that your website’s ranking is not high enough. In this case, you might consider optimizing your website’s content or improving your website’s technical SEO to improve its ranking for these keywords.
Chapter 39:
Primary & Secondary Impression Audit
To perform a primary and secondary impression audit, you can use tools such as Google Analytics or a specialized SEO tool such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz. These tools will allow you to view data on user behavior, including the time that users spend on a page, the pages that users visit most frequently, and the pages that users exit from. You can also use tools such as Hotjar or Crazy Egg to view heatmaps and scroll maps, which can help you to understand how users are interacting with the content on your webpage.
In addition to using tools, you can also perform a manual audit of your webpage’s primary and secondary impressions by reviewing the content and design elements of your webpage and considering how they might impact user behavior. For example, you might consider the following factors:
Is the page title and meta description clear and concise?
Is the content above the fold engaging and relevant to the user’s needs?
Is the navigation clear and easy to use?
Is the design of the page visually appealing and consistent with the brand?
Is the content below the fold relevant and useful to the user?
By performing a primary and secondary impression audit, you can identify areas for improvement and optimize your website to better meet the needs and expectations of your users. This can help you to improve the user experience of your website and to drive more qualified traffic to your website.
Chapter 40:
Competitor Site Content Evaluation
Competitor site content evaluation is the process of reviewing and analyzing the content on a competitor’s website to understand their marketing and SEO strategy and to identify areas for improvement on your own website.
To perform a competitor site content evaluation, you can follow these steps:
Identify your main competitors: Start by identifying the websites that are competing with you for the same keywords and audience. You can use tools such as Google Search Console or a specialized SEO tool such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to identify your main competitors.
Review the content on your competitors’ websites: Take a close look at the content on your competitors’ websites, including their blog posts, product pages, and landing pages. Pay attention to the types of content that they are publishing, the topics that they cover, and the tone and style of their content.
Analyze the keywords that your competitors are targeting: Use a specialized SEO tool to identify the keywords that your competitors are targeting in their content. This will give you an idea of the topics and phrases that are important to them and will help you to identify any gaps in your own keyword strategy.
Evaluate the quality and effectiveness of your competitors’ content: Consider the quality of your competitors’ content in terms of its relevance, value, and originality. Does their content provide valuable information or solutions to their audience? Is it well-written and easy to understand? Is it visually appealing and easy to navigate?
Identify areas for improvement: Use the insights you gain from your competitor site content evaluation to identify areas for improvement on your own website. For example, you might consider creating more detailed or in-depth content, targeting different keywords, or improving the quality and design of your content.
By performing a competitor site content evaluation, you can get a better understanding of your competitors’ marketing and SEO strategy and identify areas where you can differentiate your own website and improve your content. This can help you to drive more qualified traffic to your website and to better meet the needs and expectations of your audience.
Chapter 41:
Query Intent to Landing Page Evaluation
To evaluate the alignment between query intent and landing page, you can follow these steps:
Identify the main keywords and queries that are driving traffic to your website. You can use tools such as Google Search Console or a specialized SEO tool such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to identify the keywords and queries that are driving traffic to your website.
Review the content and purpose of your landing pages. Take a close look at the content and purpose of your landing pages, and consider how well they align with the intent of the search queries that are driving traffic to those pages.
Analyze user behavior on your landing pages. Use tools such as Google Analytics or Hotjar to view data on user behavior on your landing pages, including the time that users spend on the page, the pages that users visit after the landing page, and the actions that users take on the page (such as clicking on links or filling out forms).
Identify areas for improvement. Use the insights you gain from your query intent to landing page evaluation to identify areas for improvement. For example, you might consider creating more targeted landing pages for specific keywords or queries, optimizing the content and design of your landing pages to better meet the needs and expectations of your users, or redirecting traffic from low-performing landing pages to more relevant pages on your website.
By evaluating the alignment between query intent and landing page, you can improve the user experience of your website and increase the likelihood of users taking desired actions (such as making a purchase or filling out a form). This can help you to drive more qualified traffic and conversions on your website.
Chapter 42:
Topical Clustering Analysis
Topical clustering is a technique for organizing and grouping related content on a website. It involves creating clusters of content around specific topics or themes, with each cluster containing a range of related pages and articles.
Topical clustering analysis is the process of reviewing and analyzing the topical clusters on a website to understand the organization and structure of the website’s content and to identify areas for improvement.
To perform a topical clustering analysis, you can follow these steps:
Identify the main topics and themes of your website’s content. Take a close look at the content on your website and identify the main topics and themes that it covers.
Group related content into topical clusters. Organize your content into clusters based on the topics and themes that you identified in step 1. Each cluster should contain a range of related pages and articles.
Review the structure and organization of your topical clusters. Take a close look at the structure and organization of your topical clusters and consider how well they are organized and how easy they are to navigate.
Analyze user behavior on your website. Use tools such as Google Analytics or Hotjar to view data on user behavior on your website, including the pages that users visit most frequently and the actions that they take (such as clicking on links or filling out forms).
Identify areas for improvement. Use the insights you gain from your topical clustering analysis to identify areas for improvement. For example, you might consider reorganizing your topical clusters to make them more logical and easy to navigate, creating new clusters to cover underrepresented topics, or merging clusters that are too small or unrelated.
By performing a topical clustering analysis, you can improve the organization and structure of your website’s content and make it easier for users to find and engage with the content that they are interested in. This can help you to improve the user experience of your website and to drive more qualified traffic and conversions.
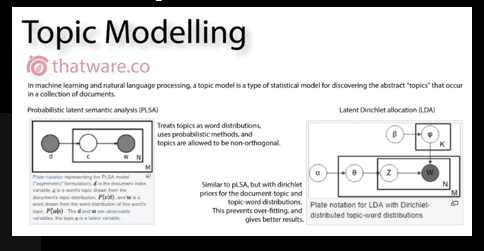
How to prevent:
This algorithm is basically used to discover topic clusters which occur within a collection of the corpus of a document set. This is a customized modeling set where the principal algorithm which is used are namely LDA and PLSA.
In the seo world, topic modeling is widely used for specifying the intent behind the content. This is very important, especially for the rank brain algorithm
Chapter 43:
Search Console Link Evaluation (Internal)
To perform a Search Console link evaluation, you can follow these steps:
Log in to your Google Search Console account and select your website.
In the left-hand menu, click on “Links.”
Click on the “Internal links” tab.
Review the data on the “Internal links” page. This page will show you the pages on your website that have the most internal links pointing to them, as well as the pages on your website that have the most internal links pointing away from them.
Use the data on the “Internal links” page to identify any issues or opportunities for improvement. For example, you might notice that some pages on your website have a high number of internal links pointing to them, while other pages have very few. This could indicate that some pages are more important or useful to your users than others. Alternatively, you might notice that some pages have a high number of internal links pointing away from them, which could indicate that these pages are not being used as effectively as they could be.
Use the insights you gain from your Search Console link evaluation to optimize your internal linking strategy. For example, you might consider adding more internal links to important or useful pages to help them rank higher in search results, or you might consider removing or consolidating internal links to pages that are not performing well.
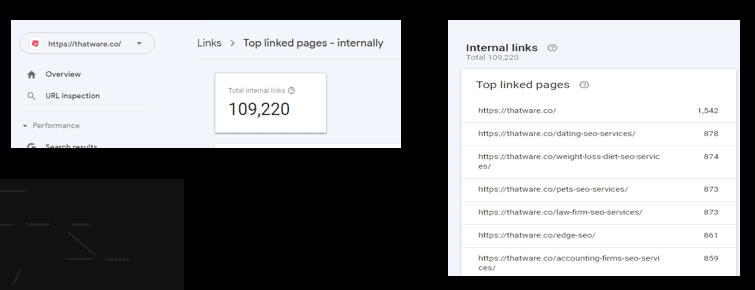
Overview:
There are 109220 internal links for the website:
Chapter 44:
Search Console Link Evaluation (External)
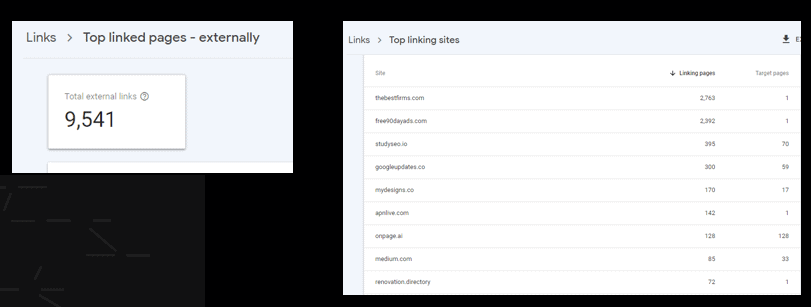
External links are links from your website to other websites. They can help to improve the credibility and authority of your website, and they can also help to improve the visibility of your website in search results.
To perform a Search Console link evaluation of external links, you can follow these steps:
Log in to your Google Search Console account and select your website.
In the left-hand menu, click on “Links.”
Click on the “External links” tab.
Review the data on the “External links” page. This page will show you the websites that have the most external links pointing to them, as well as the pages on your website that have the most external links pointing away from them.
Use the data on the “External links” page to identify any issues or opportunities for improvement. For example, you might notice that some pages on your website have a high number of external links pointing to them, while other pages have very few.
There are 9541 external links for the website:
Chapter 45:
Above the Fold vs Centre Fold vs Low Fold Content Evaluation
The term “above the fold” refers to the content that is visible on a webpage without scrolling. It is the part of the page that users see first, and it is an important factor in the user’s experience and engagement with a website.
The term “centre fold” refers to the content that is in the middle of the page and that becomes visible when the user scrolls down. It is the content that is below the initial “above the fold” content but above the content that is “below the fold.”
The term “below the fold” refers to the content that is below the initial “above the fold” content and that becomes visible when the user scrolls down.
An above the fold, centre fold, and below the fold content evaluation is the process of reviewing and analyzing the content on these different parts of a webpage to understand how users are interacting with the page and to identify areas for improvement.
Overview:
Centre Fold : The contact us form and some key points are present here.
Low Fold : The FAQ and client portfolio are present here.

Chapter 46:
Other Known Brand Based Domain Evaluation
Overview:
When evaluating other known brand-based domains, you can consider the following factors:
Domain authority: Domain authority is a measure of the strength and credibility of a website. It is determined by a range of factors, including the quality and quantity of links pointing to the website, the age of the domain, and the relevance and quality of the content on the website. You can use a tool such as Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Moz to check the domain authority of a website.
Content quality: Take a close look at the content on the website and consider its relevance, value, and originality. Is the content well-written and easy to understand? Does it provide valuable information or solutions to its audience?
Design and user experience: Consider the design and user experience of the website. Is the website visually appealing and easy to navigate? Does it provide a good user experience for mobile users?
Social media presence: Check the website’s social media presence to see how active and engaged they are with their followers. This can give you an idea of their level of brand awareness and their ability to connect with their audience.
Competition: Consider the competition in the market and how the brand-based domain compares to its competitors. Are they offering similar products or services? How does their pricing compare? Do they have a similar target audience?
Chapter 47:
Site Behaviour Flow Analysis
Site behaviour flow analysis is the process of reviewing and analyzing the paths that users take as they interact with a website. It can help you to understand how users are engaging with your website and to identify opportunities for improvement.
Identify areas for improvement. Use the insights you gain from your site behavior flow analysis to identify areas for improvement. For example, you might consider reorganizing the content and navigation of your website to create a more logical and seamless flow for users, or you might consider improving the design and user experience of your website to make it more engaging and enjoyable for users.
By performing a site behavior flow analysis, you can improve the user experience of your website and increase the likelihood of users taking desired actions (such as making a purchase or filling).
Chapter 48:
Segmented Site Behaviour Flow Analysis
Segmented site behaviour flow analysis is the process of reviewing and analyzing the paths that users take as they interact with a website, segmented by specific groups or characteristics. This can help you to understand how different groups of users are engaging with your website and to identify opportunities for improvement.
By performing a segmented site behavior flow analysis, you can get a more detailed understanding of how different groups of users are interacting with your website and identify opportunities for improvement. This can help you to optimize your website and improve the user experience for all of your users.
Chapter 49:
Guided Recommendations
There are many different types of guided recommendations that can be made in a variety of contexts, including business, marketing, technical, and more. Some examples of guided recommendations include:
Marketing recommendations:
Recommendations for improving the visibility and performance of a website in search results, such as optimizing the content, improving the user experience, or acquiring high-quality backlinks.
Technical recommendations:
Recommendations for improving the technical performance and security of a website, such as optimizing the site’s loading speed, implementing security measures, or updating outdated software.
Business recommendations:
Recommendations for improving the operations and efficiency of a business, such as streamlining processes, implementing new technologies, or changing business practices.
Personal recommendations:
Recommendations for individuals to improve their personal or professional skills and knowledge, such as training or education programs, networking opportunities, or personal development strategies.
Chapter 50:
SEO Priority Resolution List
Here is a list of priorities that you may want to consider when optimizing your website for search engines:
On-page optimization: This includes optimizing the content and HTML source code of your web pages to make them more easily understood by search engines. This includes things like adding relevant keywords to your page titles and headers, optimizing images with descriptive file names and alt tags, and using header tags to break up the content into sections.
Content optimization: Creating high-quality, useful content that is relevant to your target audience is essential for SEO. This includes conducting keyword research to identify the terms and phrases that people are using to search for the products or services you offer, and then incorporating those keywords into your website’s content.
Technical optimization: This includes things like improving the website’s loading speed, making sure the website is mobile-friendly and responsive, and ensuring that the website is easy to navigate.
Off-page optimization: This refers to actions taken outside of your website to improve its visibility and ranking in search results. This includes things like building high-quality backlinks from other reputable websites, engaging with users on social media, and optimizing your Google My Business listing.
Local SEO: If your business has a physical location or serves a specific geographic area, it’s important to optimize your website for local search. This includes claiming and optimizing your Google My Business listing, getting listed in local directories, and incorporating location-specific keywords into your website’s content.
Remember, SEO is a long-term strategy and it’s important to be patient and consistent in your efforts. It’s also a good idea to regularly track your progress and make adjustments as needed.
Chapter 51:
SERP Analysis (SERP Changes Over Time)
Observation:
In the below mentioned screenshot, there are 34 keywords within 1-3ʳᵈ position:
In the below mentioned screenshot, there are 131 keywords within 4-10ᵗʰ position:
Chapter 52:
Wayback Analysis & Site Review
To conduct a Wayback analysis, you can use the Wayback Machine to access and review the archived versions of a website. You can then analyze the content, design, and functionality of the website at different points in time to understand how it has evolved over time.
Chapter 53:
Competitor wayback analysis is the process of reviewing and analyzing the archived versions of a competitor’s website that have been stored by the Wayback Machine. The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web that allows users to access and view archived versions of websites dating back to the early days of the internet.
Conducting a competitor wayback analysis can be a helpful way to understand the history and evolution of a competitor’s website over time and to identify trends and patterns in their content and design. This can provide valuable insights into the strategies and tactics that your competitor has used in the past and can help you stay ahead of the competition.
Chapter 54:
NLP Topical Analysis
Natural language processing (NLP) topical analysis is a technique used to analyze and understand the content and themes of text data. It involves using algorithms and software to extract and analyze the key topics and themes contained within a text, such as a document, article, or social media post.
By using NLP topical analysis, you can gain a better understanding of the content and themes contained within a text and use that information to make more informed decisions about how to engage with your audience or address their needs and concerns.
Chapter 55:
Search Console Reported Link Audit (vs Third Party)
A link audit is the process of reviewing and analyzing the links that are pointing to your website. This can be helpful for understanding the quality and relevance of the links to your website and identifying any issues or opportunities for improvement.
There are two main sources for conducting a link audit: Google Search Console and third-party tools.
Google Search Console is a free service offered by Google that allows website owners to monitor and maintain their website’s presence in Google search results. One of the features of Search Console is the ability to view and analyze the links pointing to your website. This can be helpful for identifying any potential issues with the links, such as spammy or low-quality links, or links from untrusted sources.
Third-party tools are standalone software or services that can be used to conduct a link audit. These tools often offer more advanced features and functionality, such as the ability to analyze the quality and relevance of the links, identify broken or dead links, and track the changes in the links over time.
Chapter 56:
Link Equity Distribution Evaluation (Internal vs. External)
Link equity is a measure of the value and authority that a link passes to a website. Link equity can be internal, meaning it is passed from one page on a website to another, or external, meaning it is passed from a page on one website to a page on another website.
Evaluating the distribution of link equity between internal and external links can be helpful for understanding the overall strength and authority of a website. A healthy balance of internal and external links can help improve the visibility and ranking of a website in search results.
Chapter 57:
Tiered Link Audit
A tiered link audit is a method of analyzing and evaluating the links pointing to a website in order to understand the overall quality and relevance of those links. In this type of audit, the links are organized into tiers or categories based on their relative importance and value to the website.
There are various approaches to organizing links into tiers, but a common method is to divide the links into three tiers:
Tier 1 links: These are the most valuable and important links pointing to a website. They are typically from high-authority and reputable sources and are considered to have the greatest impact on the website’s visibility and ranking in search results.
Tier 2 links: These are links that are considered to have some value, but are not as valuable as tier 1 links. They may come from less authoritative or reputable sources and are considered to have a lesser impact on the website’s visibility and ranking in search results.
Tier 3 links: These are the lowest-value links pointing to a website. They may come from low-authority or spammy sources and are generally considered to have little or no impact on the website’s visibility and ranking in search results.
Chapter 58:
SERP Aggregated Link Power Audit
A SERP (search engine results page) aggregated link power audit is a method of analyzing and evaluating the links pointing to a website in order to understand the overall strength and authority of the website in the eyes of search engines. This type of audit involves aggregating the link power of all the links pointing to a website and analyzing the results to identify any issues or opportunities for improvement.
Chapter 59:
Historic Penalty Checks / Reviews
Historic penalty checks or reviews are a way to identify any past penalties or issues that may have affected the visibility or ranking of a website in search results. Penalties can be applied by search engines if a website is found to be in violation of the search engine’s guidelines or is engaging in unethical or spammy practices.
To conduct a historic penalty check or review, you can use tools such as Google Search Console or third-party software to identify any past penalties or issues that may have affected the website. You can also review the website’s history and look for any changes in traffic or ranking that may be related to a penalty.
Chapter 60:
Google Update & Query Coverage Review
Google updates are changes to the algorithms that Google uses to crawl and index websites and determine their ranking in search results. Google makes updates to its algorithms on a regular basis, and these updates can have a significant impact on the visibility and ranking of websites in search results.
Observation:
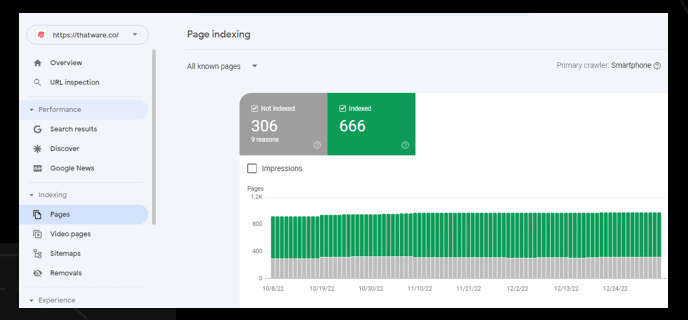
Observation:
Page with redirect:
The URL redirects to another URL and therefore was not indexed. The final target URL might be indexed, and should appear in this report. If you test this URL in the URL Inspection report, the indexed test will show the redirect; the live test will follow and test the redirected page, though it won’t show the URL of the redirected and tested page.
Alternate page with proper canonical tag:
This page is marked as an alternate of another page (that is, an AMP page with a desktop canonical, or a mobile version of a desktop canonical, or the desktop version of a mobile canonical). This page correctly points to the canonical page, which is indexed, so there is nothing you need to do. Alternate language pages are not detected by Search Console.
Excluded by ‘noindex’ tag:
When Google tried to index the page it encountered a ‘noindex’ directive and therefore did not index it. If you do not want this page indexed, so, the tag is ok for the page.
Not found (404)
This page returned a 404 error when requested. Google discovered this URL without any explicit request or sitemap. Google might have discovered the URL as a link from another page, or possibly the page existed before and was deleted.
Need to redirect those pages with the relevant page:
Crawled – currently not indexed:
The page was crawled by Google but not indexed. It may or may not be indexed in the future; no need to resubmit this URL for crawling.
Chapter 61:
Landing Page Engagement Factors (LPEF)
Landing page engagement factors (LPEFs) are elements or features of a landing page that can impact the engagement and conversion rates of the page. A landing page is the page on a website that a user is directed to after clicking on a search result or ad.
LPEFs can include a variety of elements, such as the layout and design of the page, the relevance and quality of the content, the effectiveness of the call-to-action (CTA), and the overall user experience of the page.
Chapter 62:
Content Strategy / Support Guidance
A content strategy is a plan for creating and distributing valuable and relevant content to a target audience. It typically includes goals and objectives for the content, a plan for creating and publishing the content, and a schedule for distributing and promoting the content.
Content strategy is an important part of any marketing or communication plan, as it helps to ensure that the content being created is aligned with the overall goals and objectives of the organization and is effective in reaching and engaging the target audience.
Chapter 63:
Link Building & Digital PR Recommendations
Link building is the process of acquiring links from other websites to your own. These links, also known as backlinks, can help to improve the visibility and ranking of your website in search results.
Digital PR is the practice of promoting a brand, product, or service through online channels, such as social media, blogs, and online news outlets. Digital PR can be an effective way to build links and improve the online visibility and reputation of a website.
Chapter 64:
Advanced Site Content Audit
An advanced site content audit is a comprehensive review and analysis of the content on a website. This type of audit is designed to identify any issues or opportunities for improvement with the content and provide recommendations for optimizing the content to better meet the needs of users and achieve the goals of the website.
To conduct an advanced site content audit, you will need to review and analyze all of the content on the website, including the text, images, videos, and other media. You can use tools such as a content audit template or spreadsheet to organize and track the content and identify any issues or opportunities for improvement.
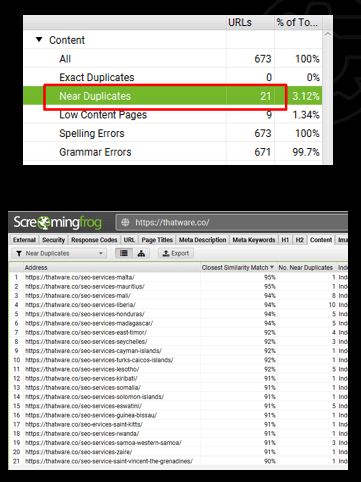
Observation:
There are 21 pages with duplicate content on the website.
Recommendation:
Consolidate the content:
If you have multiple pages with very similar content, consider consolidating the content onto a single page. This will help prevent confusion for users and search engines, and may also help improve the overall quality of your content.
Use a 301 redirect:
If you have multiple pages with duplicate content that you cannot consolidate, you can use a 301 redirect to send users and search engines from the duplicate pages to the original page. This will help prevent any negative effects on your search engine rankings.
Use the rel=canonical tag:
If you have multiple pages with similar content that you want to keep separate, you can use the rel=canonical tag to indicate to search engines which page is the original and should be indexed.
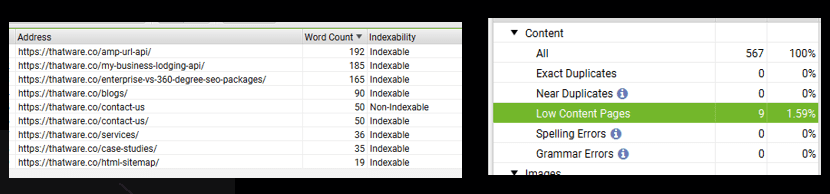
Observation:
There are 9 pages with Low content:
Recommendation:
There are several ways you can improve low content pages on your website:
Add more content: If a page has very little content, consider adding more relevant and useful information.
Expand existing content: If a page has some content, but it is thin, you can expand on the existing content to make it more comprehensive.
Update outdated content: If a page contains outdated information, consider updating it with fresh and accurate content.
Improve formatting: Poor formatting can make a page look cluttered and unprofessional. Consider using headings, bullet points, and white space to improve the formatting of your content.
Chapter 65:
Scroll & Interaction Mapping (Evaluation or Guidance)
Scroll and interaction mapping is a technique used to analyze the behavior and engagement of users on a website. It involves tracking and analyzing the actions of users as they navigate and interact with the website, such as scrolling, clicking, and hovering over elements.
Chapter 66:
SEO testing is the process of conducting experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies and techniques for improving the visibility and ranking of a website in search results. An SEO testing model is a framework or approach for conducting these experiments in a systematic and organized way.
Chapter 67:
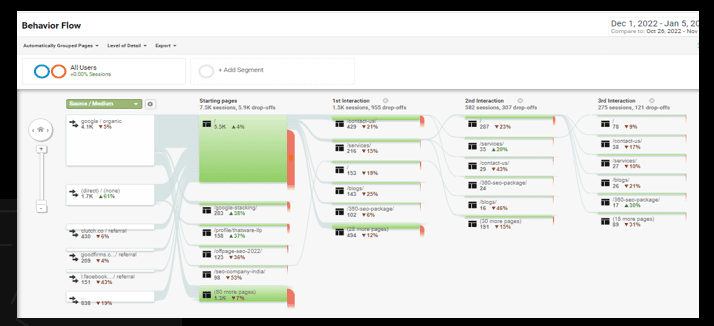
SERP / User Behaviour POGO Analysis
POGO analysis is a method of analyzing the performance of a website in search results and understanding the behavior of users on the website. POGO stands for “profits, opportunities, growth, and objectives,” and the analysis involves evaluating the website in terms of these four factors.
Behaviour POGO Analysis based on Channels:
Chapter 68:
Secondary inlinks are links from other websites to a specific page or piece of content on your website, rather than to the homepage or other main pages of the website. Evaluating the content of the secondary inlinks can be helpful for understanding the relevance and value of those links to your website and identifying any issues or opportunities for improvement.
Chapter 69:
A content strategy is a plan for creating and distributing valuable and relevant content to a target audience. It typically includes goals and objectives for the content, a plan for creating and publishing the content, and a schedule for distributing and promoting the content.
Observation:
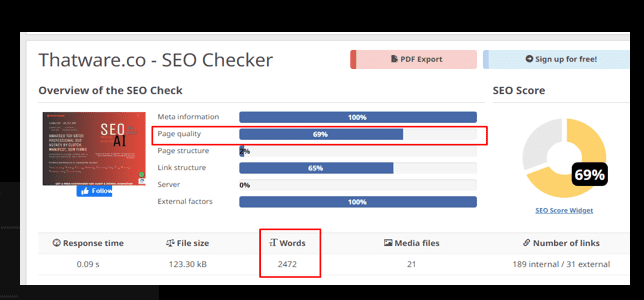
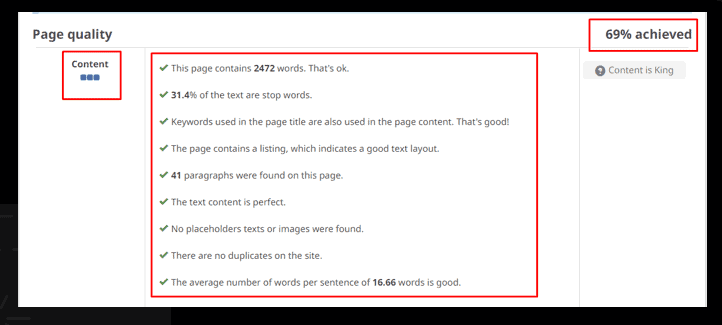
There are 21 pages with duplicate content for the website.
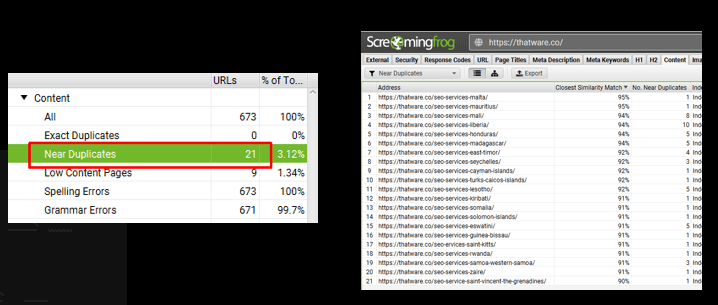
Recommendation:
Consolidate the content:
If you have multiple pages with very similar content, consider consolidating the content onto a single page. This will help prevent confusion for users and search engines, and may also help improve the overall quality of your content.
Use a 301 redirect:
If you have multiple pages with duplicate content that you cannot consolidate, you can use a 301 redirect to send users and search engines from the duplicate pages to the original page. This will help prevent any negative effects on your search engine rankings.
Chapter 70:
Striking Distance Opportunities
“Striking distance” refers to the state of a website that is relatively close to meeting the goals and objectives of its content strategy but may require some refinements or optimizations to fully achieve those goals.
There are 199 keywords are ranking between 11 to 20th position on Google SERP:
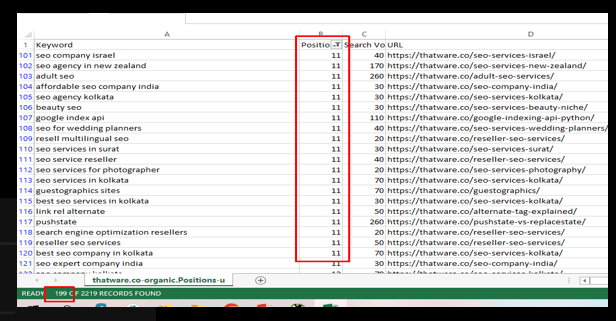
Recommendation:
Incorporate the keywords into your content: Use the keywords you identified in your website’s content, including in the page title, headings, and body text. Make sure to use the keywords naturally and avoid keyword stuffing.
Use meta tags: Include the keywords in the meta tags of your website, including the title tag and the meta description. This will help search engines understand the content of your page and may increase its ranking for those keywords.
Use alt tags: If you have images on your website, include the keywords in the alt tags of the images. This will help search engines understand the content of the images and may increase the ranking of the page for those keywords.

Thatware | Founder & CEO
Tuhin is recognized across the globe for his vision to revolutionize digital transformation industry with the help of cutting-edge technology. He won bronze for India at the Stevie Awards USA as well as winning the India Business Awards, India Technology Award, Top 100 influential tech leaders from Analytics Insights, Clutch Global Front runner in digital marketing, founder of the fastest growing company in Asia by The CEO Magazine and is a TEDx speaker and BrightonSEO speaker.

