SUPERCHARGE YOUR ONLINE VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!

The December 2025 Broad Core Update marks a clear turning point in how Google evaluates and ranks content, not because it introduces new rules, but because it decisively raises the minimum quality threshold required to compete. While officially described as a “regular” update, its timing and impact reveal a deeper recalibration that builds on the cumulative changes rolled out throughout 2025, particularly the August Spam Update and the full integration of the Helpful Content System into core ranking logic. Together, these shifts signal Google’s move away from tolerance for content that merely appears comprehensive toward a stronger preference for content that demonstrates real-world experience, expert insight, and genuine user satisfaction. Sites that previously relied on keyword coverage, scaled content production, or residual authority from past tactics are now finding those advantages eroded, as Google becomes more effective at distinguishing between surface-level information and content that truly solves a user’s problem.

Importantly, this update affects all verticals and regions, extending heightened E-E-A-T expectations far beyond traditional YMYL categories into e-commerce, affiliate publishing, SaaS, and media. The result is a landscape where ranking volatility is not simply a reshuffle of winners and losers, but a broader reset of what qualifies as valuable content in the first place. For site owners and SEOs, the implication is significant: recovery is no longer about incremental optimisation or technical clean-up alone, but about aligning content with intent, demonstrating verifiable experience, and delivering depth that users actually engage with. The December 2025 Core Update therefore represents less a momentary algorithm change and more a structural shift toward trust, substance, and long-term relevance as the defining factors of search visibility.
Official Announcement & Rollout Timeline: What Google Confirmed
Official Naming & Classification
Google officially designated this update as the Google December 2025 Broad Core Update, placing it within the most consequential category of algorithm changes the search engine releases. Unlike niche or targeted updates—which typically focus on a single issue such as spam, reviews, or product content—broad core updates recalibrate how Google’s core ranking systems evaluate content quality, relevance, and usefulness at a fundamental level. This means no single tactic, page type, or industry is being singled out; instead, the relative weight of existing ranking signals is adjusted across the entire index. As a result, sites may experience significant ranking changes even if they have not made recent changes, simply because Google’s interpretation of “high-quality content” has evolved.
Launch Date & Rollout Window
Google confirmed the rollout began on December 11, 2025, as published on the Search Status Dashboard. As with most broad core updates, Google indicated the rollout could take up to three weeks, with completion expected in early January 2026. During this window, rankings are inherently unstable, as different parts of the algorithm are deployed incrementally across data centres and regions. Because signals are still being reweighted, short-term gains or losses during the rollout are often reversed, making any immediate conclusions unreliable.
Scope of Impact
The December 2025 update is global in scope, affecting all languages, countries, and content verticals. Blogs, e-commerce stores, news publishers, affiliate sites, SaaS platforms, and enterprise websites are all subject to the same recalibrated standards. No sector is exempt, reinforcing that this update is about baseline content quality rather than industry-specific behaviour.
Pre-Rollout Volatility Explained
Noticeable SERP turbulence was observed on December 7 and 8, several days before the official launch. Historically, this type of volatility suggests pre-testing or partial signal adjustments, where Google quietly experiments with new weighting models before full deployment. These early fluctuations often foreshadow a larger shift and indicate that Google phases major updates rather than releasing them as a single, instantaneous change.
Key Takeaway for SEOs
Early conclusions during a core update rollout are frequently misleading. The correct approach is to wait until the update fully completes, then analyse performance using stable data—ideally comparing early January 2026 metrics against early December 2025. Meaningful recovery or diagnostic work should only begin once the algorithm has finished recalibrating.
Understanding Core Updates: What Google Is Really Adjusting
What a Core Update Is (and Is Not)
To understand the impact of the December 2025 Broad Core Update, it is essential to clarify what a core update actually represents. A core update is not a penalty, and it does not indicate that a site has violated Google’s guidelines. There is no manual action involved, no specific rule being enforced, and no single issue that can be “fixed” to instantly restore rankings. Core updates also do not target one isolated ranking factor such as backlinks, keywords, or page speed. Instead, they reflect a holistic recalibration of how Google’s systems assess content relevance and quality. When rankings drop after a core update, it does not mean a site has done something wrong; it means Google’s understanding of what best satisfies a query has evolved, and other pages are now seen as more deserving of visibility under the updated evaluation model.
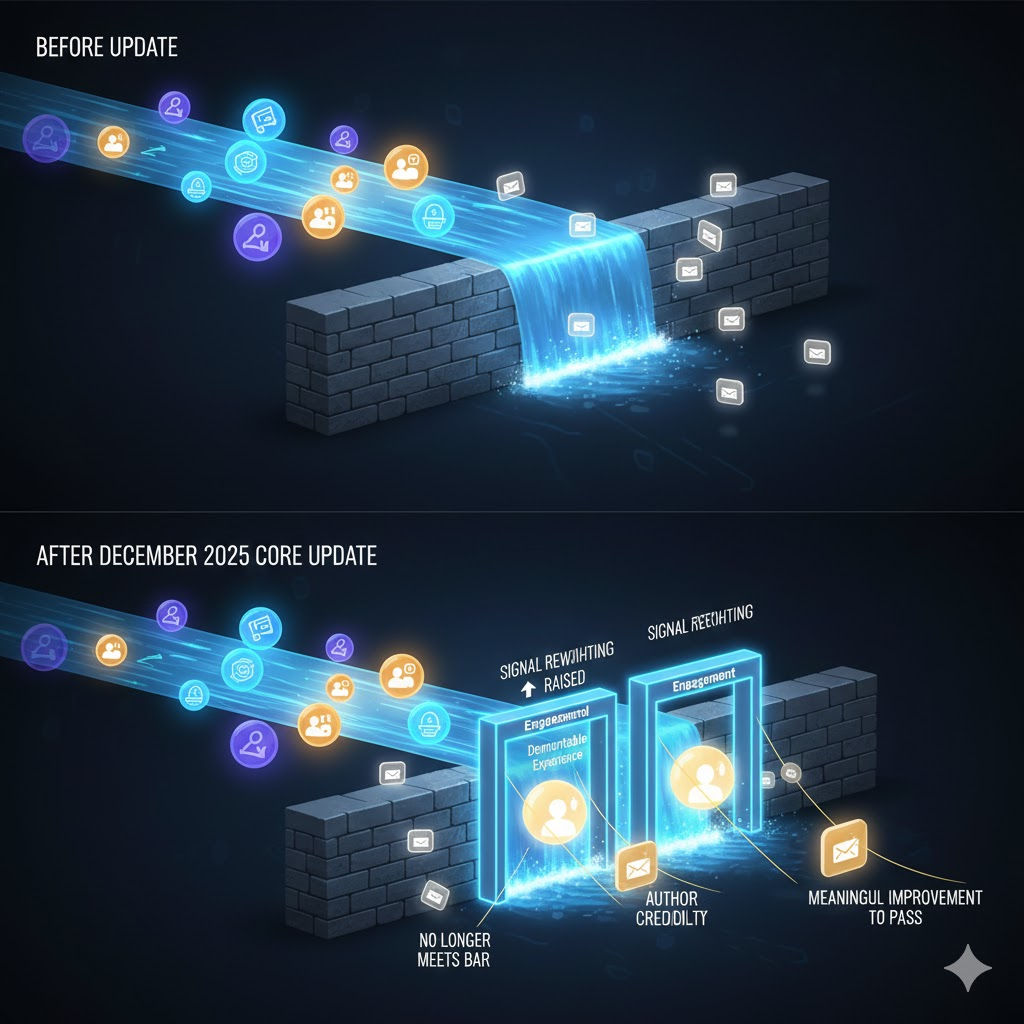
Signal Reweighting Explained
At the heart of every broad core update is signal reweighting. Google already uses hundreds of signals—ranging from content depth and topical authority to user satisfaction and trust indicators—to rank pages. During a core update, Google does not introduce an entirely new set of signals; instead, it adjusts how much importance is assigned to existing ones. For example, signals related to demonstrable experience, author credibility, or engagement may suddenly carry more influence than before, while weaker or more easily manipulated signals lose weight. This is why the common reaction of “nothing changed on our site” is not a valid defence. Even if a website remains static, the competitive landscape shifts around it. Pages that align more closely with the newly prioritised signals can rise, while others fall, simply because Google’s definition of quality has become more refined.
The Quality Threshold Concept
One of the most misunderstood aspects of core updates is the idea of a quality threshold. Rankings are not determined solely by outperforming competitors; pages must first meet Google’s evolving minimum standard for quality, usefulness, and trust. If that threshold rises—as it clearly has with the December 2025 update—some pages may drop even if no competitor has visibly improved. In these cases, the issue is not that other sites became better, but that the affected content no longer meets Google’s baseline expectations for fully satisfying user intent. This explains why recoveries often require more than incremental optimisation. To regain visibility, content must be meaningfully improved to clear the new quality bar, not just adjusted to marginally outperform competing pages.
The Amplification of E-E-A-T Across All Niches
E-E-A-T Beyond YMYL
For years, Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness were most visibly enforced within YMYL categories such as health, finance, and legal content. The December 2025 Broad Core Update makes it clear that this distinction has largely disappeared. E-E-A-T is now being applied consistently across lifestyle content, product reviews, SaaS platforms, e-commerce websites, and news or media publishers. Any page that influences a user’s decisions, spending, or understanding is now expected to demonstrate credible, experience-led value. One of the most notable shifts is that lived experience is no longer secondary to formal credentials. While qualifications remain important, Google is increasingly rewarding content that shows the creator has actually used the product, performed the task, or encountered the problem being discussed. This change reflects Google’s broader goal of surfacing content that feels helpful, grounded, and reliable, rather than abstract or purely informational.
Experience: The Most Heavily Weighted Shift
Among all E-E-A-T components, experience appears to have received the strongest boost in weighting. Google is now far more effective at identifying whether content is based on first-hand knowledge or simply assembled from secondary sources. Clear signals of real-world usage include original photos and videos, screen recordings, screenshots, and step-by-step documentation created during actual testing or implementation. Proprietary tests and experiments also carry significant weight, particularly when the methodology and results are clearly explained. Personal case studies that outline challenges, outcomes, and lessons learned are outperforming theoretical advice that lacks proof. In contrast, content that relies on stock imagery, generic examples, or unverified claims is increasingly viewed as low value, even if it is well written or technically optimised. The emphasis on experience reinforces the idea that helpful content should reflect practical understanding, not just topical awareness.
Expertise and Authoritativeness
Expertise and authoritativeness remain core pillars, but their evaluation has become more precise. Named authorship is now far more important than anonymous publishing, particularly for content that aims to educate, advise, or influence decisions. Google expects to see clear information about who created the content and why they are qualified to speak on the topic. Verifiable credentials such as professional certifications, industry experience, academic background, or recognised roles within a field strengthen credibility, especially when they are consistent across the site. At the same time, topical focus plays a major role in authority. Websites that concentrate deeply on a specific subject area tend to perform better than those that publish across many unrelated topics. Content sprawl dilutes authority, while consistent coverage within a defined niche reinforces the perception that a site is a reliable source of expertise.
Trustworthiness Signals
Trustworthiness underpins all other E-E-A-T elements and is increasingly visible in how Google evaluates sites. Editorial transparency is a key factor, including clear information about content standards, update practices, and correction policies where applicable. Legitimate contact information and an identifiable brand presence help confirm that a real organisation stands behind the content. Disclosure practices also matter more than ever, particularly for affiliate content and sponsored material. Transparent explanations of monetisation relationships help establish honesty and user trust. Additionally, how a site handles reviews and user-generated content plays a role. Authentic, moderated reviews that reflect real user experiences contribute positively, while unverified, spam-like, or misleading reviews undermine credibility and can weaken site-wide trust signals.
Practical E-E-A-T Implementation Checklist
In practical terms, strengthening E-E-A-T requires deliberate structural and editorial changes. Sites should add clear author bios that highlight relevant experience and credentials, along with visible review or update dates where appropriate. Original media and data that demonstrate first-hand experience should be incorporated wherever possible. Content that lacks a clear author, offers only generic insights, or duplicates information found elsewhere should be removed or consolidated. At the same time, high-quality signals should be surfaced more prominently. This includes author information, trust pages, disclosures, and evidence of experience placed where users and search engines can easily find them. By systematically reinforcing these elements, websites align more closely with Google’s elevated expectations for quality in the post December 2025 search landscape.

The Substance Test: How Google Detects Real Value
Length vs Depth: Why Word Count Is No Longer a Shield
For a long time, publishing longer content was often enough to compete in search results, even when much of that length was made up of repetitive explanations or loosely relevant sections. The December 2025 Core Update makes it clear that word count alone no longer provides any protective advantage. Google has become far more effective at identifying content that is long but shallow, where paragraphs add volume without adding insight. Over-optimised fluff, including excessive keyword usage, expanded definitions that say little, or padded introductions, is increasingly discounted. Pages that attempt to appear comprehensive by covering many subtopics superficially are now underperforming compared to shorter but more precise content that directly addresses user needs. In this new evaluation model, depth is measured by usefulness and clarity, not by how many words are used to reach a perceived ideal length.
Specificity as a Ranking Advantage
Specificity has emerged as one of the strongest indicators of content quality. Google is now better at recognising when claims are supported by concrete evidence rather than vague assertions. Data-backed statements, such as test results, benchmarks, or observed outcomes, provide clear signals of value. Quantified results are particularly effective because they demonstrate measurable impact rather than theoretical benefit. Equally important is transparency around how conclusions are reached. Clear explanations of methodology, tools used, sample sizes, or testing conditions help reinforce credibility and distinguish original work from generic summaries. Content that shows how insights were generated is consistently outperforming content that merely states conclusions without context or proof.
Content That Answers Fast and Then Goes Deep
Another defining characteristic of high-performing content is its ability to satisfy user intent quickly before expanding into deeper analysis. Google increasingly rewards pages that provide a clear, direct answer near the top, reducing friction for users who want immediate clarity. Once the core question is addressed, successful content then expands in a structured way, offering additional detail for readers who want deeper understanding. This layered approach benefits both beginners and advanced users without forcing either group to sift through unnecessary information. By combining fast intent satisfaction with thoughtful expansion, content signals that it is designed to solve problems rather than simply attract clicks.
Signals of Low-Value Content
In contrast, Google has become more adept at identifying patterns associated with low-value pages. Repetitive phrasing that adds no new information, generic advice that could apply to almost any topic, and content that closely mirrors existing top-ranking pages without introducing original insight are all strong negative indicators. Scaled paraphrasing of competitor content, even when technically unique, is increasingly ineffective because it fails to demonstrate independent value. As these detection systems improve, the gap between substantive content and superficial content continues to widen, reinforcing the importance of originality, clarity, and practical usefulness in every page that aims to rank.
AI-Generated Content: What Survives and What Fails
Google’s Nuanced AI Position
Google’s stance on AI-generated content remains nuanced and pragmatic. The search engine does not penalise content solely because it is created with AI tools. Instead, the focus is on output quality. Tool neutrality means that AI itself is not inherently problematic, but the value of the resulting content is what determines ranking potential. This distinction is critical because many sites mistakenly assume that using AI automatically guarantees either a boost or a penalty. The December 2025 Core Update reinforces that AI-generated content is evaluated like any other content: for depth, accuracy, originality, user satisfaction, and demonstrable expertise.
Content Under Pressure
Large-scale, programmatic AI content is now under significant scrutiny. Pages generated solely from templates, bulk prompts, or automated aggregation often lack the nuance and human insight that Google increasingly rewards. Template-based publishing, which reuses the same structure across hundreds of pages without adding new knowledge or experience, fails to convey real-world understanding. Content with zero human refinement or verification is particularly vulnerable. Even if technically correct and readable, these pages are often shallow, lacking context, specificity, or evidence of lived experience, and they are therefore at high risk of being demoted in search results.
Content That Is Being Rewarded
AI can still be a powerful tool when used strategically. High-performing pages often combine AI-assisted drafting with expert human refinement. For example, AI may generate an initial research draft, outline, or data synthesis, but the final content is enriched with human analysis, commentary, or validation. Human editors can add original data, first-hand insights, case studies, and critical evaluation that AI alone cannot produce. By layering human expertise onto AI-generated material, sites can create content that is both efficient to produce and demonstrably authoritative, satisfying Google’s heightened emphasis on E-E-A-T and user satisfaction.
How Google Likely Detects AI Quality
While Google does not publicly disclose the exact mechanisms, several indicators suggest how AI quality is evaluated. Pattern repetition is a primary signal; AI-generated content often exhibits similar phrasing or structural uniformity across multiple pages. A lack of lived experience is another factor, where content appears abstract or generic rather than based on actual usage, experiments, or personal insight. Finally, absence of verifiable references or citations that can be cross-checked reduces trustworthiness, signaling to Google that the content may not provide unique value. By addressing these gaps—adding human perspective, original research, and verifiable sources—sites can make AI-assisted content competitive under the new December 2025 quality standards.
Early Winners and Losers: Sector-Level Impact Analysis
Biggest Losers
The December 2025 Core Update has caused noticeable disruption across multiple sectors, with certain types of websites being particularly affected. Affiliate review sites that rely on manufacturer descriptions or generic recommendations without conducting their own testing or providing original insights have experienced significant ranking losses. These sites often use stock images and copy-pasted content, which fails to demonstrate real-world experience. Thin e-commerce product pages have also been hit hard, especially those that include only basic product specifications without additional guidance such as usage instructions, buyer tips, or verified customer reviews. Content farms and sites with overlapping articles that offer minimal added value beyond repeating information already available on the web are another major group of losers. These pages tend to dilute the overall authority of the site and fail to meet the new minimum quality threshold established by the update.
Why These Sites Dropped
The underlying reason for these drops is closely tied to the shift in Google’s evaluation criteria. Sites with weak experience signals no longer perform well because the algorithm prioritizes content that shows first-hand knowledge or original research. Low engagement metrics, such as short time on page or frequent pogo-sticking, indicate to Google that users are not finding these pages helpful. In addition, redundant value plays a major role; content that repeats common advice or summarizes information from competitors without adding unique insights is increasingly considered low-quality. Even sites that were technically sound or previously well-ranked can see declines if the content does not meet these new experiential and substantive standards.
Sites Showing Gains or Stability
On the other hand, websites that have consistently demonstrated deep expertise in a narrow niche have shown resilience or growth. These niche authority sites benefit from clearly defined subject focus, well-documented author credentials, and content that addresses complex topics thoroughly. High-engagement platforms where users spend significant time reading, interacting, and exploring related content have also fared well, as these metrics reinforce signals of usefulness and satisfaction. Additionally, experience-led brands that include first-hand testing, original data, case studies, and practical guidance have received positive ranking adjustments. These pages show Google that the content is both trustworthy and actionable, aligning with the update’s emphasis on genuine user value.
Lessons from Early Winners
Several key lessons emerge from observing early winners. Depth beats breadth as pages that focus deeply on one topic outperform those that attempt to cover multiple subjects superficially. Proof beats promises, meaning content that demonstrates real results or experience ranks higher than content that simply claims benefits. Finally, focus beats scale, showing that highly targeted, authoritative content is more effective than mass-produced pages designed to dominate keywords. This sector-level analysis underscores the shift toward experience, credibility, and user satisfaction as central drivers of visibility in search results.
Advanced Intent Matching: The End of One Page Fits All
Query Refinement Explained
The December 2025 Core Update shows that Google is far better at understanding the underlying intent behind search queries. Instead of matching pages to keywords literally, the algorithm now interprets layered intent. This means it can distinguish between users seeking general information, detailed guidance, or transactional opportunities. By assessing the subtle cues in search behavior, click patterns, and contextual relevance, Google identifies what users truly want and prioritizes content that aligns with their deeper needs.
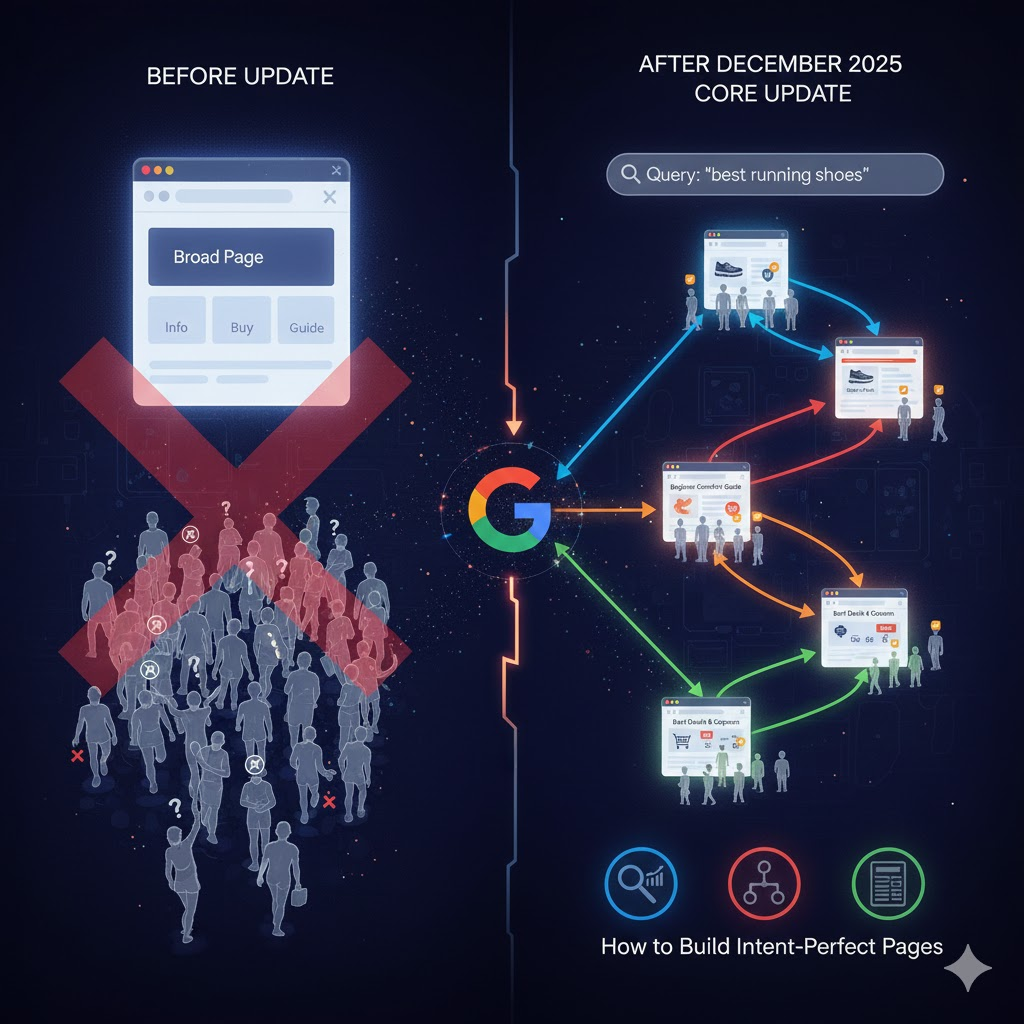
Micro-Intent SERP Segmentation
Google now segments search results based on micro-intent, separating informational, transactional, and experiential queries. For example, a search for “best running shoes” may produce three distinct user intentions. One segment looks for beginner-friendly shoes with safety and comfort advice, another focuses on shoes suitable for marathon training with durability data, and a third prioritizes the best deals from e-commerce listings. This level of refinement ensures that users are served content that addresses their specific objective rather than a one-size-fits-all page.
Why Broad Pages Are Losing
Pages that attempt to cover multiple intents in a single article are increasingly losing rankings. Broad pages often deliver diluted relevance, where the content fails to satisfy any single query fully. Conflicting intent satisfaction occurs when an article tries to serve both informational and transactional purposes, leaving users partially satisfied and causing engagement signals to drop. As a result, pages designed to capture all potential queries are outperformed by focused, intent-specific content.
How to Build Intent-Perfect Pages
To succeed in this environment, webmasters should focus on intent mapping. This involves identifying the primary goal behind each search query and aligning content to fully satisfy it. Using SERP analysis frameworks, site owners can study top-ranking pages for their target keywords and identify the exact type of content Google rewards. Implementing content isolation strategies, such as creating separate pages for each micro-intent, ensures that each article has a clear purpose, a specific target audience, and measurable engagement outcomes.
User Satisfaction Signals: The Hidden Multiplier
Engagement Correlation with Rankings
Engagement metrics have become critical indicators of content quality under the December 2025 Core Update. Time on page measures how long users actively consume content, while scroll depth shows whether readers are exploring the entire article. Interaction patterns, such as clicks on internal links or expanding tabs, signal to Google that the page is providing meaningful value. Pages with higher engagement generally experience stronger rankings because they demonstrate user satisfaction.
Pogo-Sticking as a Negative Indicator
Rapid return clicks to the search results, known as pogo-sticking, are now penalized more heavily. Bounce rate alone is insufficient to diagnose issues because some exits occur due to curiosity rather than intent failure. Google looks for signs that the user’s query was truly solved. Pages that fail to satisfy the intent behind the search, even if they attract clicks initially, are more likely to drop in rankings.
Creating Completion-Oriented Content
Content should be designed to help users complete tasks or achieve goals efficiently. Clear next steps, actionable instructions, and logical internal navigation help guide users through the experience. Completing the intended task signals to Google that the content successfully met user needs. Pages that encourage task completion and provide seamless pathways to related resources benefit from higher engagement, stronger satisfaction signals, and improved ranking potential.
Technical Excellence as a Ranking Tie-Breaker
Core Web Vitals Still Matter
While content quality is the primary driver of rankings, technical performance remains a critical tie-breaker. Page speed affects user satisfaction, with faster-loading pages more likely to retain readers and reduce pogo-sticking. Visual stability ensures that users do not experience unexpected layout shifts, which can frustrate interaction and reduce trust. Responsiveness across devices contributes to a seamless experience, making pages accessible and usable regardless of screen size. Sites that excel in these areas gain a subtle advantage, particularly when competing content is similar in quality.
Mobile-First Enforcement
Mobile performance is non-negotiable. Google now evaluates content parity between desktop and mobile versions, meaning missing or truncated content on mobile can hurt rankings. Intrusive interstitials, pop-ups that block the main content, degrade user experience and negatively influence ranking potential. Script overload can slow load times and affect interactivity, reducing engagement metrics. Ensuring a clean, mobile-optimised presentation improves both user experience and search visibility.
Internal Linking and Topical Authority
Internal linking plays a strategic role in reinforcing topical authority. A hub-and-spoke model, where general topic pages link to more detailed subtopics, helps Google understand content hierarchy and relationships. Creating a semantic hierarchy ensures that pages are logically connected, guiding both users and search engines through the site’s expertise. Effective internal linking also improves crawl efficiency, allowing search engines to index and evaluate content more comprehensively. Together, technical excellence and structured linking support high-quality content in securing competitive rankings.
Integration with 2025’s Earlier Updates
August 2025 Spam Update Recap
The August 2025 Spam Update targeted technical manipulation and deceptive practices. Sites using link schemes, cloaking, or other forms of deceptive behaviour faced penalties, regardless of content quality. This update was focused on integrity and compliance, establishing a foundation that reduced the influence of low-quality tactics in search results.
The Compound Impact Effect
The December 2025 Core Update compounds the effects of previous changes. Sites that were weakened by the August Spam Update are now more vulnerable because the content quality threshold has been raised. Even minor weaknesses in experience, expertise, or user satisfaction are magnified, making recovery more challenging. The cumulative effect is that sites which relied on low-quality strategies for visibility are more likely to fall sharply when faced with stricter evaluation criteria.
Content Quality as the Final Filter
Even technically clean sites can experience ranking declines if content does not meet the new standards. The December 2025 update acts as a final quality filter, emphasizing that authority must be earned through genuine experience, verifiable expertise, and content that fully satisfies user intent. Technical compliance alone is insufficient; high-value content that demonstrates trustworthiness and relevance is essential to secure and maintain search visibility in the evolving landscape.
The New Recovery Playbook Post-December 2025
Why Waiting Is Strategic
One of the most important lessons from the December 2025 Core Update is that patience is essential. Rankings are highly volatile during the rollout period, and early fluctuations often do not reflect long-term outcomes. Immediate reactions to sudden drops or spikes can be misleading because Google phases the deployment across different regions and data centres. Attempting rapid fixes before the update has fully completed can lead to wasted effort or even harm if changes are misaligned with the final algorithm weighting. Waiting until the rollout is complete allows for a more accurate assessment of which pages truly underperform and which were temporarily affected by transitional volatility.
Page-Level Diagnosis Framework
Once the update stabilizes, a structured approach to evaluating affected pages is crucial. The first step is drop analysis, identifying which pages lost visibility and by how much. This should be followed by SERP comparison, where you examine the top-ranking competitors to understand what content features or signals they exhibit that your pages may lack. Intent mismatch detection is equally important, assessing whether your pages align with the actual user intent behind the query. This analysis helps pinpoint whether drops are due to insufficient depth, weak experience signals, or broader E-E-A-T deficiencies.
Delete, Merge, or Upgrade
Content that does not meet the new quality thresholds must be addressed strategically. The decision process involves three options: delete low-value pages that serve no real purpose, merge overlapping or thin content into a single comprehensive resource, or upgrade underperforming pages with additional depth, original data, and experience evidence. Pillar consolidation strategy is particularly effective for improving site-wide authority, creating authoritative hubs that guide users and search engines through structured, high-quality content. By focusing on overall site quality rather than incremental changes, you reinforce the signals Google now prioritizes.
E-E-A-T Recovery Actions
Rebuilding E-E-A-T is a central component of recovery. Incorporating expert reviews ensures content is accurate and credible, while clearly identifying content ownership signals authority and accountability. Experience documentation such as first-hand case studies, original research, images, and videos demonstrates real-world knowledge, satisfying the elevated weight placed on practical expertise. Together, these actions help rebuild trust, credibility, and topical authority in the eyes of Google and its users, supporting a sustainable recovery over time.
Search Console Lag and Monitoring Strategy
Monitoring website performance during a major core update like the December 2025 rollout can be challenging, particularly due to delays and inconsistencies in reporting. Understanding how to interpret data from Google Search Console (GSC) and other ranking tools is critical to avoid misinformed decisions that could hinder recovery efforts.
Understanding GSC Data Delays
Google Search Console is the primary source of truth for site owners, providing data on impressions, clicks, average position, and user engagement metrics. However, during significant updates, GSC reporting is often delayed by 48 hours or more. This lag occurs because Google needs time to process large volumes of ranking changes, recalibrate its indexing, and update its search analytics. As a result, site owners monitoring their performance in real time may see incomplete or outdated data. Relying solely on immediate observations can create unnecessary panic or lead to premature changes that do not address the actual underlying issues.
The Pitfalls of Third-Party Ranking Tools
Many website owners turn to third-party SEO tools for near real-time ranking data. While these tools are helpful for trend observation, they are based on sampling rather than the complete dataset available to Google. Consequently, early fluctuations reported by these tools can exaggerate losses or gains, making it appear that rankings are far more volatile than they truly are. Pages may show sudden drops or spikes that do not align with actual search console data. Treating these signals as definitive can lead to misguided optimization efforts that waste resources or even harm a site’s performance.
Annotating the Rollout for Accurate Tracking
A critical first step in proper monitoring is to annotate the December 11th rollout in GSC and any tracking dashboards. This provides a reference point to differentiate between changes caused by the core update and routine fluctuations in traffic or rankings. Annotating the rollout also allows for longitudinal analysis, helping teams track recovery progress and identify trends over time rather than reacting to daily fluctuations.
Establishing Comparison Windows
Once the update is complete and the initial volatility has subsided, it is essential to establish comparison windows for evaluation. A recommended approach is to compare performance from early January 2026, after the update rollout stabilizes, against early December 2025, before the update began. This comparison provides a realistic view of which pages truly lost visibility, which gained traction, and which remained stable. Such a structured comparison prevents misinterpretation of temporary ranking swings as permanent changes.
Strategic Decision-Making Based on Stabilized Data
Waiting for GSC data to stabilize and using well-defined comparison windows allows site owners to make informed, strategic decisions. Optimization efforts can then be focused on pages that genuinely underperform, rather than chasing transient drops that may self-correct as Google continues its recalibration. Monitoring engagement metrics such as clicks, impressions, and user behavior alongside rankings provides a more holistic view of content performance, helping guide precise recovery strategies.
Continuous Monitoring Post-Rollout
Even after the update rollout completes, continuous monitoring remains vital. Search trends, user behavior, and competitive performance can shift gradually, and keeping an ongoing record ensures that any long-term adjustments are grounded in accurate, actionable data. By combining patience, structured tracking, and careful interpretation of both GSC and third-party data, site owners can navigate the post-update environment effectively and maximize recovery opportunities.
AI Overviews, GEO, and the Future of Visibility
From Rankings to Citations
The December 2025 Core Update not only reshapes traditional rankings but also signals a shift toward AI-driven content consumption and citation. AI Overviews, also referred to as generative answer summaries, are increasingly featured in search results, providing users with concise, synthesized answers drawn from multiple sources. This means that traditional click-driven rankings are no longer the sole determinant of visibility. Sites that serve as trusted sources in these AI Overviews can capture attention even if their pages are not at the very top of the classic search results. Being cited in these AI-generated summaries can drive indirect traffic, improve brand recognition, and enhance credibility across the web.
Why This Core Update Matters for GEO
Generative Engine Optimization, or GEO, represents the emerging frontier where content is evaluated not only for ranking position but also for its suitability as a reliable source for AI answers. The December 2025 Core Update reinforces this by rewarding content that demonstrates specificity, trustworthiness, and original experience. AI systems are programmed to reference sources that are verifiable and authoritative. Consequently, content that lacks clarity, evidence, or demonstrable expertise risks being overlooked as a citation in AI Overviews, even if it performs reasonably well in traditional rankings. This update effectively sets a higher bar for content creators who want their pages to be recognized as citation-safe sources, capable of being included in AI-driven responses.
How to Optimise for AI Citation
Optimizing content for AI citation requires a strategic focus on three key areas: specificity, fact validation, and authority reinforcement. Specificity involves providing detailed, unambiguous answers with concrete examples, case studies, or numerical data. Content that answers broad questions in a generic manner is less likely to be cited in AI-generated summaries. Fact validation is critical because AI systems rely on trustworthy sources to provide accurate answers. Citing primary research, verifiable statistics, and authoritative references increases the likelihood that a page will be recognized as reliable. Authority reinforcement includes demonstrating expertise through named authors, clear credentials, and a consistent topical focus. Content that visibly reflects experience, analysis, or first-hand testing signals both search engines and AI systems that it is credible and suitable for citation.
By aligning content strategies with the emerging AI-driven landscape, website owners can maintain visibility even as traditional ranking paradigms evolve. The December 2025 Core Update highlights that the future of search is increasingly citation-based, where being recognized as a trustworthy and valuable source is as important as conventional ranking position. Websites that integrate depth, verifiable information, and demonstrable expertise into every page are well-positioned to thrive in this evolving environment, capturing both direct search traffic and indirect AI-driven attention.

Final Takeaways
The December 2025 Core Update marks a turning point in search engine optimization, establishing a new baseline for quality, relevance, and user satisfaction. Websites can no longer rely on superficial content, generic advice, or purely technical compliance to maintain visibility. The focus has shifted toward demonstrable experience, verifiable expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness, collectively known as E-E-A-T, across all niches, not just YMYL topics. Pages that provide immediate answers while expanding into detailed, data-backed analysis are rewarded, whereas thin, repetitive, or template-driven content faces significant ranking penalties. Engagement metrics such as time on page, scroll depth, and completion of user tasks now play a pivotal role, with pogo-sticking and poor interaction signaling dissatisfaction and contributing to declines. AI-generated content is no longer inherently penalized, but success depends on integrating human oversight, original insights, and factual validation to meet the elevated standards. Technical excellence, including mobile-first design, fast loading times, stable layouts, and structured internal linking, serves as a tie-breaker in competitive niches, enhancing content performance without substituting for quality.
Recovery strategies emphasize patience, structured page-level analysis, and a deliberate approach to deleting, merging, or upgrading content to improve site-wide authority. Additionally, the update positions high-quality, citation-ready content to thrive in the emerging AI-driven search environment, highlighting the growing importance of being recognized as a reliable source in AI-generated summaries. In this new SEO reality, depth beats breadth, proof beats promises, and focus beats scale, making authentic, experience-driven, and user-centered content the central pillar of long-term search visibility and sustainable growth.

