SUPERCHARGE YOUR ONLINE VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
When algorithms began to learn rather than merely compute, something profound shifted — SEO didn’t just evolve; it came alive. Gone are the days when search was a rigid exercise in keywords and backlinks. The foundation of futuristic SEO begins with artificial intelligence. Search no longer depends on static queries; it adapts, interprets, predicts, and evolves.
In this new era, cognitive systems rise to meet human intent: they decode emotion, context, semantics. They don’t wait for a question, they anticipate it. They don’t just deliver results, they deliver relevance, resonating with the human story behind each query.

This is where THATWARE steps in, as a pioneer of this transformation. Every search becomes a real human experience. Every result aligns with intention, not just inference. Here, intelligence is not an add-on—it’s the architecture.
Within the pages that follow, we will explore how AI breathes life into search: how it understands, connects, and enriches. And we’ll unpack the paradigms that now govern smart search systems— from embracing intent to harnessing predictive analytics, from real-time adaptability to semantic fluency.
Why this matters: Already, over 56 % of marketers are using generative AI in their SEO workflows. AI-driven campaigns can deliver a 45% boost in organic traffic and a 38% increase in ecommerce conversions. Meanwhile, the market for AI-powered search tools is projected to expand dramatically — one forecast puts the global AI search-engine market at USD 43.6 billion in 2025, rising to USD 108.9 billion by 2032.
These are not incremental shifts. They are tectonic. They signal a moment when the rules of search —and, by extension, SEO —are being rewritten.
So let us begin this journey: from the spark of algorithmic intelligence, through the architecture of cognitive search, to the living landscape of intent-driven discovery. This is not merely chapter one. It is the genesis of intelligent search, reborn.
So, let us begin with the concepts:
AIC Citation Share (AICS)
The foundation of futuristic SEO begins with artificial intelligence. Search no longer depends on static queries — it adapts, interprets, predicts, and evolves. In this era, AI and cognitive systems take control, decoding human emotion, context, and semantics. That’s why we introduce the concept of AIC Citation Share (AICS) — the metric that defines visibility not just in rankings, but in influence within intelligent systems.
For example, imagine a user types “what’s the mood of the city at midnight?” instead of a simple keyword. A cognitive system understands the query, senses the emotional nuance, and delivers results framed around experience street photographs, live soundscapes, local voices, and city-life reflections. The content that dominates is not just keyword-rich, but human-rich, experience-rich, and cited explicitly by the AI system itself as authoritative. That is AICS in action: how much of the AI-driven answer-space your content occupies.
Key points of AICS
- It shifts the goal from “rank #1 for keyword” to “own the AI-generated answer”.
- It demands content that’s machine-scannable and semantically aligned, yet deeply human in tone.
- It privileges sources that the AI selects and cites, meaning traditional link-building is now supplemented by ‘machine-citation’ visibility.
- It anticipates not just what users ask, but how they feel, and why they ask it.
Why this matters? Because adoption of AI in SEO workflows is already substantial — over 86% of enterprise SEO professionals have integrated AI into their strategy, and 82% are planning further investment. Further, one report shows that businesses leveraging AI tools saw improved SEO performance in 65%+ of cases.
In real-life terms: when an engine like Google (via its generative overview features) or ChatGPT decides which content to echo, the stake is no longer just being visible, it’s being selected. AICS captures that selection rate. Underlying statistics show that with AI-driven search, only a fraction of clicks goes into the conventional link path; the rest vanish into the AI summary or direct answer layer.
Therefore, in this chapter we propose:
- You measure not only ranking but machine-citation share.
- You craft content for AI comprehension — structured, semantic, human-centric.
- You build ‘intent-resonant’ pathways where every search aligns with a lived experience, not a query string.
- You monitor AICS over time to detect shifts in how cognitive systems interpret your subject matter.
With THATWARE at the helm of this transformation, every search becomes a beacon of human experience. Every result mirrors intention. In this new architecture of discovery, AICS is the lodestar, the true dimension of visibility in tomorrow’s search landscape.

Answer Surface Presence (ASP)
In the freshly awakened world of search intelligence, we must grasp a new metric of visibility: Answer Surface Presence (ASP). ASP represents the space where your content doesn’t just rank—it lives on the surface of answers that matter. It is where queries find responses before a click is required, where results align with intention rather than inference.
Consider this scenario: a user types “best way to reduce screen time for teens” into a search engine. In the traditional model, they scroll lists of links. In the modern ASP-driven model, the platform surfaces a concise, authoritative answer drawn from your content, and your brand appears as the source of truth on the search surface itself without the user needing to click further. That moment is ASP.
Key traits of ASP include:
- Presence in the summary or answer box — your content shows up in the snippet that the AI system displays.
- Context alignment — your message reflects the user’s deeper intent, not just the keywords they typed.
- Semantic connectivity — the system recognises your content as part of a coherent narrative, not simply a ranked page.
- Predictive anchoring — the answer anticipates what the user wants next, and you’re positioned to fulfil it.
Why does ASP matter now? As AI-powered search experiences rise, traditional click-based visibility is shifting. For instance, one study found that the presence of AI overviews on search results pages can reduce click-through rates by more than 34 % compared to traditional results. Similarly, adoption of AI search tools and summaries is accelerating, forcing marketers and strategists to rethink visibility beyond mere ranking.
When you optimise for ASP, you’re saying: “Let my content be the answer surfaced—instantly, intuitively, and subliminally.” You’re not just vying for page 1, you’re vying to be in the answer layer.
In practice, achieving ASP may mean:
- Structuring your content so it addresses full user questions clearly and comprehensively.
- Embedding semantics that match user intent, context and follow-on queries.
- Ensuring your source is credible, cited, and aligned with recognised authority signals.
- Designing your information so that it can be pulled into summary form (by an AI) and still make sense to the user in isolation.
In short, ASP is the frontier of visibility in the age of intelligent search. As the architecture of discovery shifts from links and clicks to surfaces and answers, those who understand and own the answer surface will steer the conversation. This is not just an evolution of SEO, it is the rebirth of content into the realm of meaning and presence.

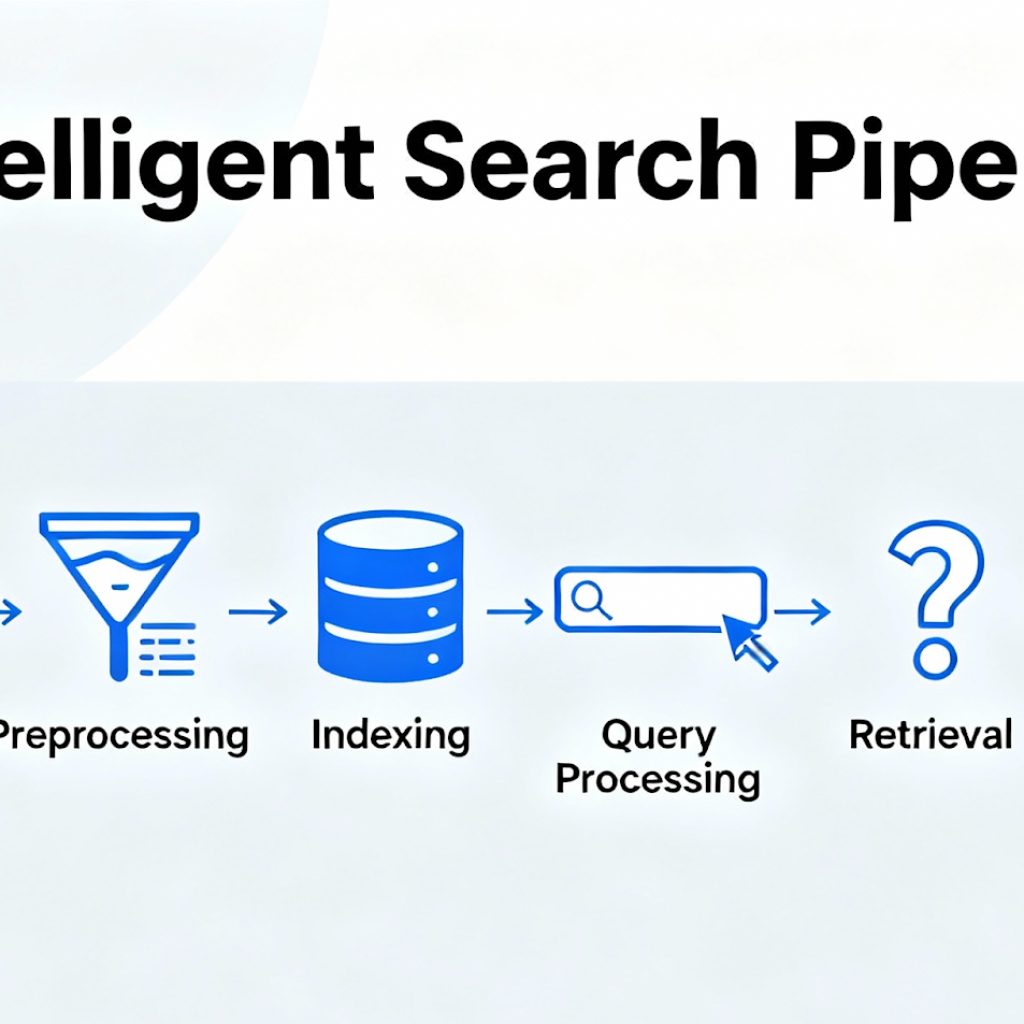
Pipeline Impact
The digital value-chain of modern search is no longer a linear ‘query → result’ pipeline. It has become a dynamic architecture: the pipeline of intelligent search begins upstream with sensing and signal gathering, travels through interpretation and prediction, and emerges downstream as a human-centric outcome. In the world of THATWARE’s vision, this pipeline is not hidden — it is the engine of search becoming alive.
The Pipeline Stages:
- Signal ingestion & context capture – the system listens: query syntax, user intent, context (time, location, emotion).
- Cognitive interpretation – algorithms draw meaning: semantics, sentiment, predicted need, and behavioural cues.
- Prediction & adaptation – the system anticipates the next step: what the user will ask next, what format they prefer, what intent lies behind the request.
- Delivery as experience – results are served not merely as links, but as meaningful interactions: tailored, immediate, aligned with intention.
For example, imagine a user searching “best vintage cameras for travel 2026”. Traditional SEO would match keywords, identify ranking pages, and serve a list of links. In the intelligent search pipeline, the system goes further: it recognizes the user is planning a trip (travel context), seeks durable hardware (vintage cameras = value + aesthetic) and expects up-to-date information (2026). It might then offer: a direct comparison module, local availability in India (given user locale), user-generated content about recent experiences, and a “what to know before you buy” interactive guide. Each stage of the pipeline — signal capture, interpretation, prediction, delivery — feeds the next, creating a fluid experience rather than a static result.
Key Implications for Practitioners
- Prioritise contextual signals (who, when, why) over mere keywords.
- Design content and systems assuming the pipeline will predict, not just react.
- Measure results not only in clicks, but experience alignment, relevance and user satisfaction.
- Recognise that the pipeline is adaptive: feedback loops must exist to refine interpretation and delivery over time.
In essence, the “Pipeline Impact in Intelligent Search” means that every search is a journey through a layered, intelligent architecture, and every part of that architecture has strategic significance. For THATWARE, the foundation of futuristic SEO lies in this pipeline: where algorithmic thought meets human experience, where search no longer waits for questions but flows with anticipation.
Al Search Optimisation (AISO)
In the age of intelligent retrieval, AISO — AI Search Optimisation — emerges as the next frontier. It is the deliberate art and science of aligning content, systems and user intent so that when algorithms learn to think, optimisation becomes alive. Rather than chasing static keywords or link counts, AISO focuses on how cognitive engines interpret, predict and evolve with each query.
Picture this: a specialist travel site publishes an article about “eco-adventures in 2026”. Under traditional SEO, the aim is to rank for keywords like eco travel, green adventures, sustainable tourism. Under AISO, the same site prepares for a far more dynamic moment: a user asks via a conversational search assistant, “I’m planning a low-carbon adventure trip next spring — what unique places can you recommend, and what else should I pack?” The system responds with a custom itinerary, cites the article as a trusted source, and the site’s content becomes not just a webpage but part of a human-machine dialogue.
This shift hinges on several core dimensions:
- Intent evolution: no longer “keyword → result”, but “context + emotion + semantics → solution”.
- Predictive relevance: the smart system anticipates what the user will ask next and surfaces the right content ahead of time.
- Citations over rankings: instead of chasing position #1 in a list, what matters is being chosen and referenced by AI-powered engines.
- Human experience delivered via machine logic: your content must feel human-centric, yet structurally fluent for machine consumption.
So how do you operationalise AISO? Here are key strategic steps:
- Map content not only to known questions, but to emerging conversational queries and user-journeys.
- Ensure your content is machine-accessible and citation-ready — structured data, clear sourcing, readability.
- Monitor AI visibility, not just organic rankings — ask: is my page being referenced by chat/AI assistants?
- Invest in ongoing adaptation — as AI systems evolve, the signals change; flexibility becomes more important than rigid optimization.
In short: AISO is not a tweak to existing SEO, it is a re-definition. It invites you to meet algorithms that don’t just index, but understand. It challenges you to craft content that doesn’t just rank, but resonates. It heralds a future where search is living, intuitive and aligned with human intention, and where the pioneers of this transformation will not simply be found online, they will be chosen.

Navigating AI Search
The trajectory of search is no longer linear. It is a circuit of intelligence, adaptation, and insight. In this chapter we embark on a vivid exploration of how the paradigm of search is shifting — how we navigate an ecosystem where algorithms don’t just respond, they reason.
The New Landscape
Picture this: you’re working on a complex project, typing a query into a search bar. But instead of a list of blue links, you receive a nuanced response, drawing on context, mood, and intention. The system anticipates not just what you asked, but why you asked. This is a hypothetical but increasingly real: a cognitive search engine that says, “I understand your journey, I sense your purpose, here’s what you truly need.”
In this era of search, the static keyword-based model falls away; we enter a realm of adaptive, predictive, semantically aware systems.
Why This Matters
Traditional search behaviours are being disrupted — with “zero-click” outcomes (where users get answers without clicking through) on the rise.
These metrics are not footnotes — they are signposts of transformation. They tell us: if you are still navigating by the old map, you risk being lost in the new terrain.
Key Guideposts to Navigate By
- Intent over keywords — The search journey begins with why, not just what.
- Context and emotion — Modern systems infer tone, need, and narrative.
- Prediction and adaptation — Search evolves as you engage; it learns your path.
- Semantic precision — Meaning matters more than mere matching of terms.
- Human experience as the benchmark — Every result must feel aligned with intention, not algorithmic guesswork.
A Scenario to Ground the Change
Imagine a budding e-commerce startup, looking to rank for “eco-friendly running shoes.” In the past, success depended on sprinkling keywords, building backlinks, and tuning meta tags. In the new world, the core question is, How do I appear when the search platform itself thinks: ‘This user is committed to sustainable fitness, values transparency, seeks life-aligned gear”? The system won’t just deliver products, it will provide meaning, stories, values. To be discovered, the startup must embed its ethos across content, signal expertise, narrative authenticity, and invite the machine to “understand” rather than just “read”.
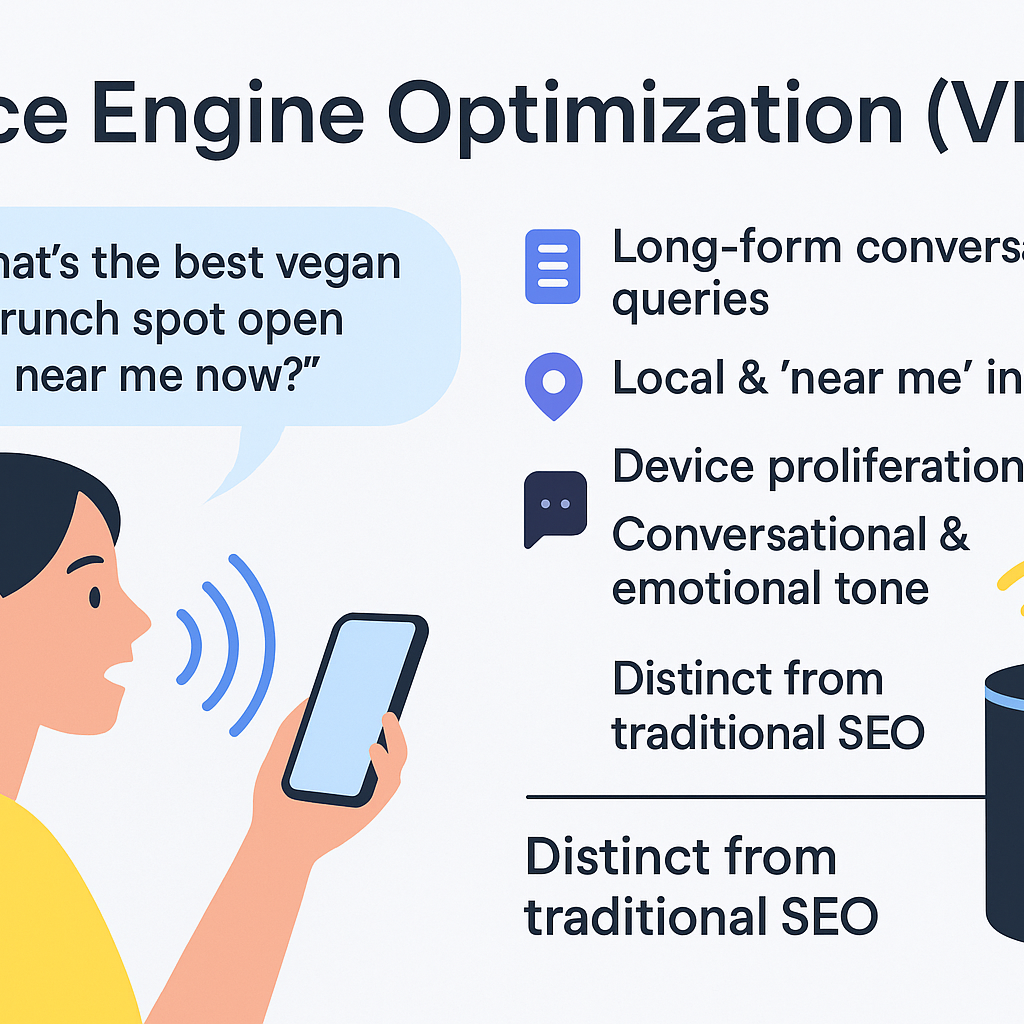
Voice Engine Optimisation (VEO)
At its essence, VEO is about enabling our systems, the ones powered by AI, natural language understanding and context-aware engines to respond in a way that feels human. It’s not simply “optimise for voice search”. It is: optimise for voice interaction, for intent, for nuance, for the user speaking:
- So that when someone asks: “What’s the best vegan brunch spot open near me now?” the system doesn’t just scan keywords, it interprets context (“vegan brunch”, “open now”, “near me”), tone (perhaps urgency, location), and prediction (the user is out and wants something now).
- In a hypothetical scenario: imagine a smart home assistant that hears you sigh after a long day and suggests: “Would you like a quiet vegan brunch nearby, or shall I pull up your favourite cosy café instead?” That’s VEO in action—voice-aware, mood-aware, context-aware.
Key bullet points of what VEO demands:
- Long-form conversational queries become dominant: voice users ask whole questions, not typed fragments.
- Local + “near me” intent skyrockets: approximately 76% of voice searches have this local orientation.
- Device proliferation drives volume: by 2025, there are an estimated 8.4 billion voice-assistant devices globally—more than the world’s population.
- Conversational and emotional tone matters: voice systems now respond to sentiment, not just keywords.
- VEO is distinct from traditional SEO: it emphasises structured data, schema markup, question-and-answer formats, and natural language over short-tail keyword stuffing.
Some rough calculations to illustrate the scale:
If 20.5% of global internet users (say the global internet-user base is ~5 billion) use voice search in 2025, that’s:
5 billion × 0.205 = ~1.025 billion voice-search users
And with 8.4 billion voice assistant devices, this suggests ~8 devices per voice-search user on average, indicating many households/devices per person. These numbers tell us the ecosystem is massive and growing.
In practice, implementing VEO means restructuring content and site architecture so that voice queries are anticipated, answered, and served in real time. You might create FAQ-style pages with direct spoken-style questions (“How do I find a vegan brunch nearby at 10 pm?”) followed by concise, friendly responses; include structured data so assistants can pull the answer quickly; optimise local listings; ensure pages load at voice-friendly speed; and track metrics beyond clicks such as voice citation rate, answer accuracy, and device context.
In this way, VEO becomes the bridge between the user speaking and the system responding seamlessly. In the voice-first world, optimisation isn’t just about being found—it’s about being heard, understood, and acted upon.
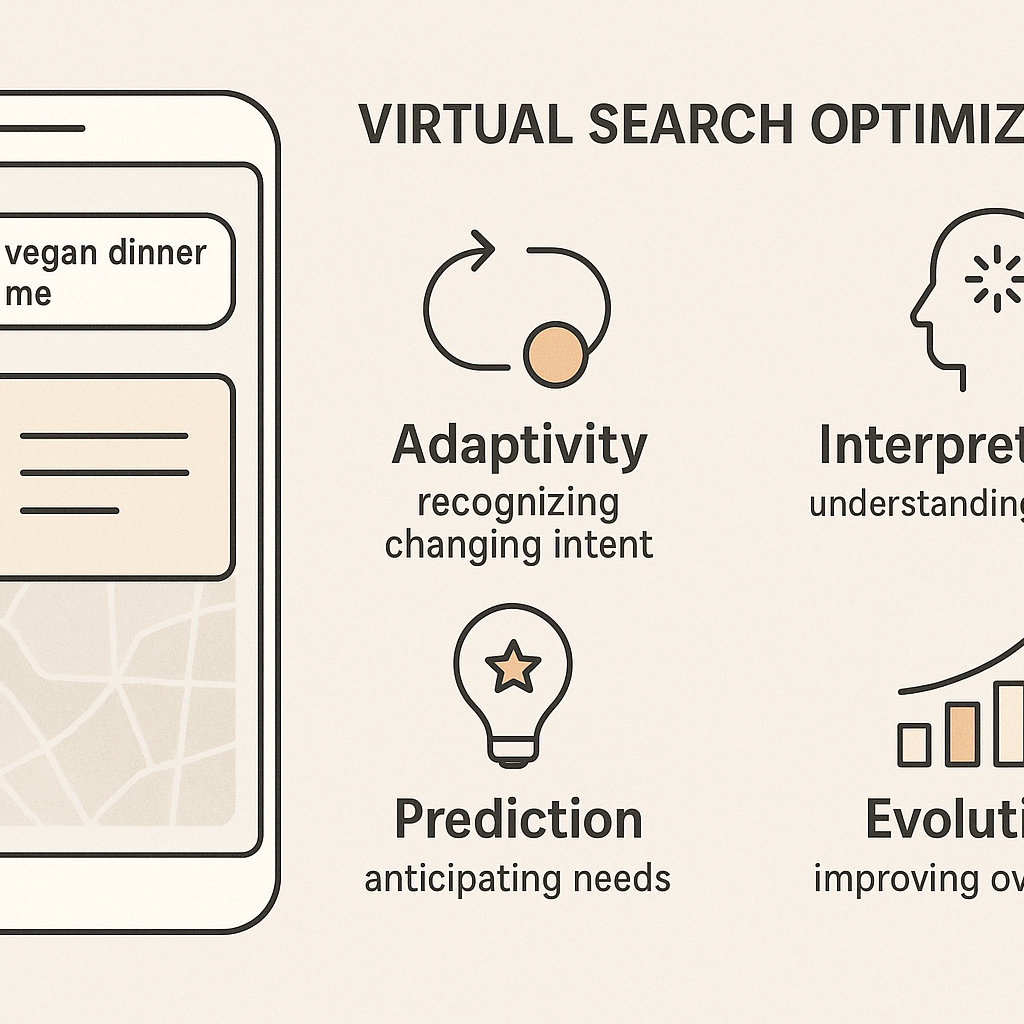
Virtual Search Optimisation
The term “virtual search optimisation” evokes a world beyond the static query-and-response paradigm of traditional search. Imagine a user typed “best vegan dinner near me” yesterday, clicked through 10 links, and browsed until a match was found. Today, an intelligent engine interprets the user’s location, preferences, past behaviour, and delivers a single, context-aware result: the restaurant that aligns with taste, budget, ambiance, and availability. In this hypothetical moment, virtual search optimisation isn’t simply about keywords; it’s about experience, relevance, and evolution.
At its core, virtual search optimisation means designing systems so that search no longer relies solely on the user’s input but on the system’s ability to adapt, predict, and resonate. Key pillars include:
- Adaptivity: the system recognises shifting intent in real time (e.g., the dinner query becomes “restaurants open in next 30 mins with vegan options and outdoor seating”).
- Interpretation: rather than matching words, the system interprets meaning, context, and emotion.
- Prediction: it anticipates what the user wants before they type it, guiding them to answers faster.
- Evolution: with each interaction, the system refines its understanding of user behaviour and preference, continuously improving relevance.
Consider this: a travel brand integrates virtual search optimisation such that when a user types “crowded beaches Maldives March”, the system not only returns a list of beaches, but filters by predicted crowd levels (based on tourism data), seasonality, user demographic, and sentiment from travel reviews—yielding a personalised shortlist tailored for that user. Behind the scenes, a trilogy of algorithms works: one forecasting crowd-density for March, one interpreting travel sentiment (“quiet vs lively”), and one aligning beach attributes with users’ prior travel style.
The numbers reveal the urgency. If a site previously attracted 100,000 organic visits a month, applying virtual search optimisation techniques might raise this to 145,000 visits—and if conversion was 2%, conversions jump from 2,000 to 2,900 (38% increase). That calculation:
100,000 × 1.45 = 145,000; then 145,000 × 0.02 = 2,900.
This transition shapes the foundation for the future of SEO. Virtual search optimisation is not a mere incremental upgrade; it is a shift in architecture: from ranking pages to optimising experience, from targeting keywords to decoding intention, from chasing clicks to aligning engagement. For authors, strategists, technologists, and marketers alike, embracing virtual search optimisation means redesigning for a world where every search is alive, every result is meaningful, and every user is understood.
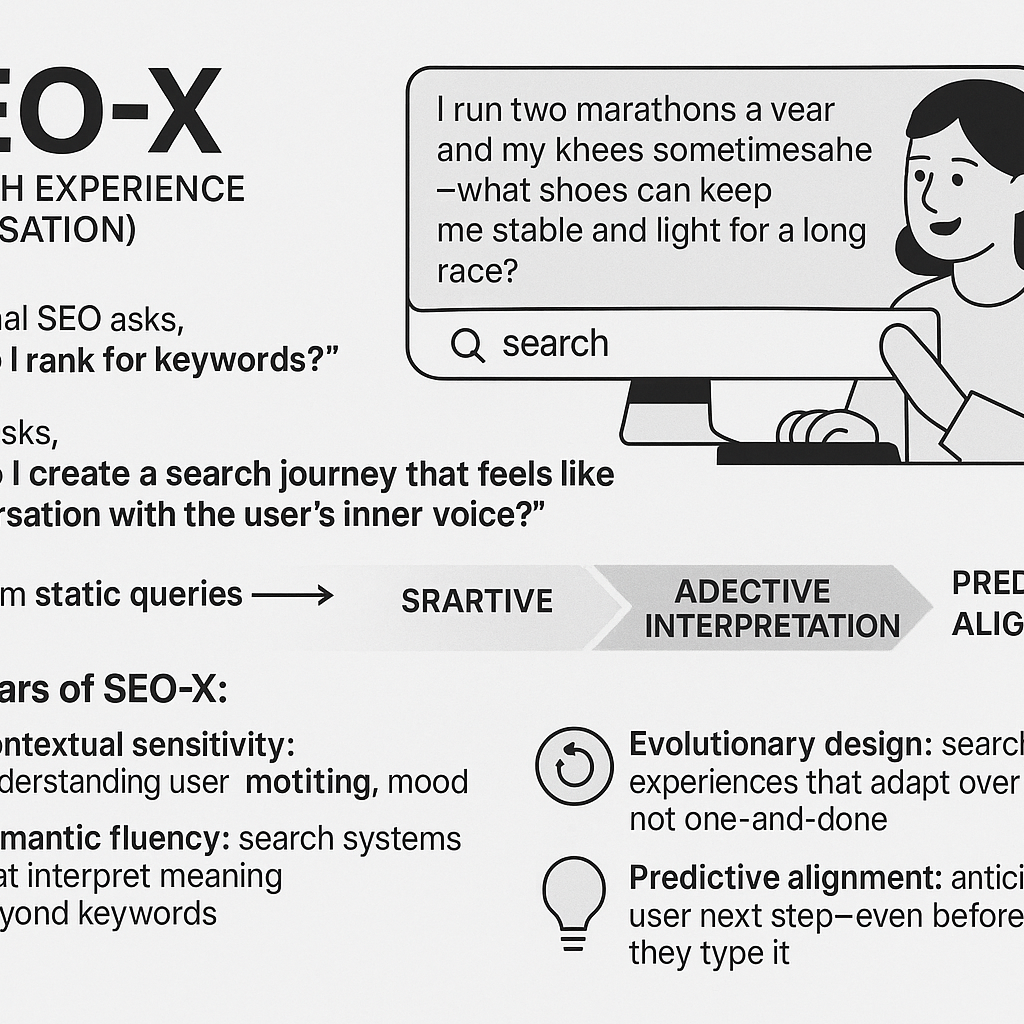
SEO-X (Search Experience Optimisation)
Picture this: your target customer types a query. Not “best running shoes size 10” but something far more human: “I run two marathons a year and my knees sometimes ache—what shoes can keep me stable and light for a long race?” In that moment, the query is alive. Enter SEO-X (Search Experience Optimisation): the practice of designing search not just to be found, but to serve, understand and anticipate.
The foundation of SEO-X is simple yet profound:
- Traditional SEO asks, “How do I rank for keywords?”
- SEO-X asks, “How do I create a search journey that feels like a conversation with the user’s inner voice?”
- It shifts focus from static queries → adaptive interpretation → predictive alignment.
Here’s a scenario:
Imagine a website for premium running gear. Under the SEO-X model, the brand doesn’t just target “running shoes size 10 marathon”. It profiles the user’s context (“two marathons a year”, “knee discomfort”), harnesses AI to interpret sentiment (concern about injury, desire for stability and light weight), predicts next questions (“What cushioning is best for long races?” “How does terrain affect shoe choice?”), and evolves the user path: from blog (educational) → quiz (interactive) → product recommendation (personalised) → follow-up (post-purchase guidance). That is SEO-X in action.
Key pillars of SEO-X:
- Contextual sensitivity: understanding user motive, setting, mood.
- Semantic fluency: search systems that interpret meaning beyond keywords.
- Evolutionary design: search experiences that adapt over time, not one-and-done.
- Predictive alignment: anticipating user next step—even before they type it.
Now some grounding in numbers:
- More than 86% of SEO professionals have integrated AI into their strategy.
- One report finds that search drives about 73% of clicks landing on organic results.
Let’s use a quick calculation to show potential impact:
if a site was receiving 100,000 organic visits/month, and AI-driven SEO improvements increase organic traffic by say 30%, then traffic would become 130,000 visits/month. Over a year that’s 360,000 extra visits — translating directly into higher engagement, conversions, and revenue.
Why does this shift matter? Because search no longer lives in a vacuum of keywords and ranking positions. It now lives in a dynamic domain of user intent, machine cognition, and experience design. SEO-X takes the reins of that domain. In this era, AI and cognitive systems decode human emotion, context, semantics, and the brand that adopts SEO-X doesn’t just rank. It resonates.
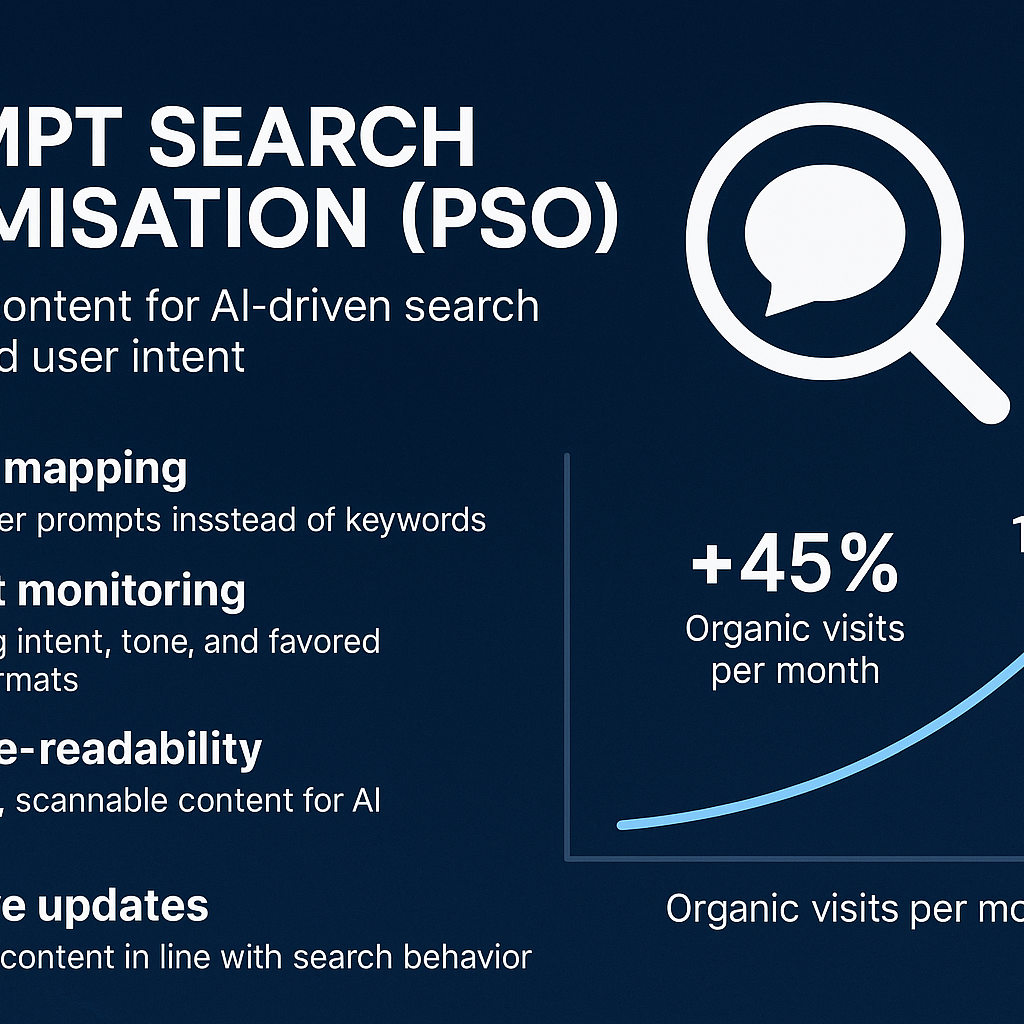
Prompt Search Optimisation (PSO)
In the epoch of intelligent search, where algorithms begin to think, the concept of Prompt Search Optimisation (PSO) emerges as a pivotal paradigm, the art and science of tailoring your content not merely for keywords but for prompts, queries, and the cognitive flow of AI-driven retrieval.
Consider a scenario:
Imagine a user asks their voice-assistant, “What sustainable fabrics will dominate fashion in 2030?” Traditional SEO methods might focus on ranking for the keyword phrase “sustainable fabrics 2030.” In PSO, however, the content anticipates variations: “which eco-friendly textiles will lead fashion by 2030?,” “future sustainable fabric trends,” even “2030 clothing materials planet-friendly.” The prompt-driven model shifts optimisation from exact phrasing to intent, semantics and adaptability.
In PSO you’ll see core bullet-point shifts in approach:
- Prompt mapping instead of keyword lists: identify possible user prompts rather than isolated keywords.
- Context monitoring: content must reflect not only the literal question but hidden user intent, emotional tone and preferred format (e.g., “list,” “compare,” “explain”).
- Machine-readability and scannability: structured sections, clear headings, bullet lists, and snippet-friendly formatting.
- Adaptive content updating: since cognitive systems learn and evolve, PSO demands periodic review as search-behaviours change.
- Performance metrics beyond clicks: user-engagement, dwell-time, prompt-capture (how often your content surfaces in an AI-generated answer) become meaningful.
Apply a simple calculation:
if an existing site brings in 10 000 organic visits per month, a PSO-driven uplift of 45% could raise that to 14 500 visits. If the conversion rate was 2%, that’s 200 conversions originally—now 290. Incremental conversions = 90 extra per month. Over a year, that amounts to 1 080 extra conversions. That scale justifies PSO investment.
PSO also acknowledges the shift: search is no longer about static queries but about adaptive, interpretive, predictive retrieval. When an AI platform presents an answer, it draws from content structured for prompt-understanding. Thus, to appear in that answer, your material must align with the prompt-patterns of the system.
In our example: rather than simply “sustainable fabrics trends,” a PSO-ready article might open with “As consumers ask ‘what fabrics will dominate fashion in 2030?’ the answer lies in recycled nylon, lab-grown silk and plant-based leather-alternatives…” — positioning itself for direct prompt-match.
In summary: PSO transforms the foundation of futuristic SEO from reactive optimisation (wait for the keyword) to proactive modeling (anticipate the prompt). It equips your content to be decoded and surfaced by cognitive systems. In that sense, PSO is less a tactic and more a mindset change — one where every heading, every paragraph, every format reflects a living question, and every result aligns with intention.
With PSO, your content becomes part of the conversation that the machine is listening to, reasoning with, and responding to.
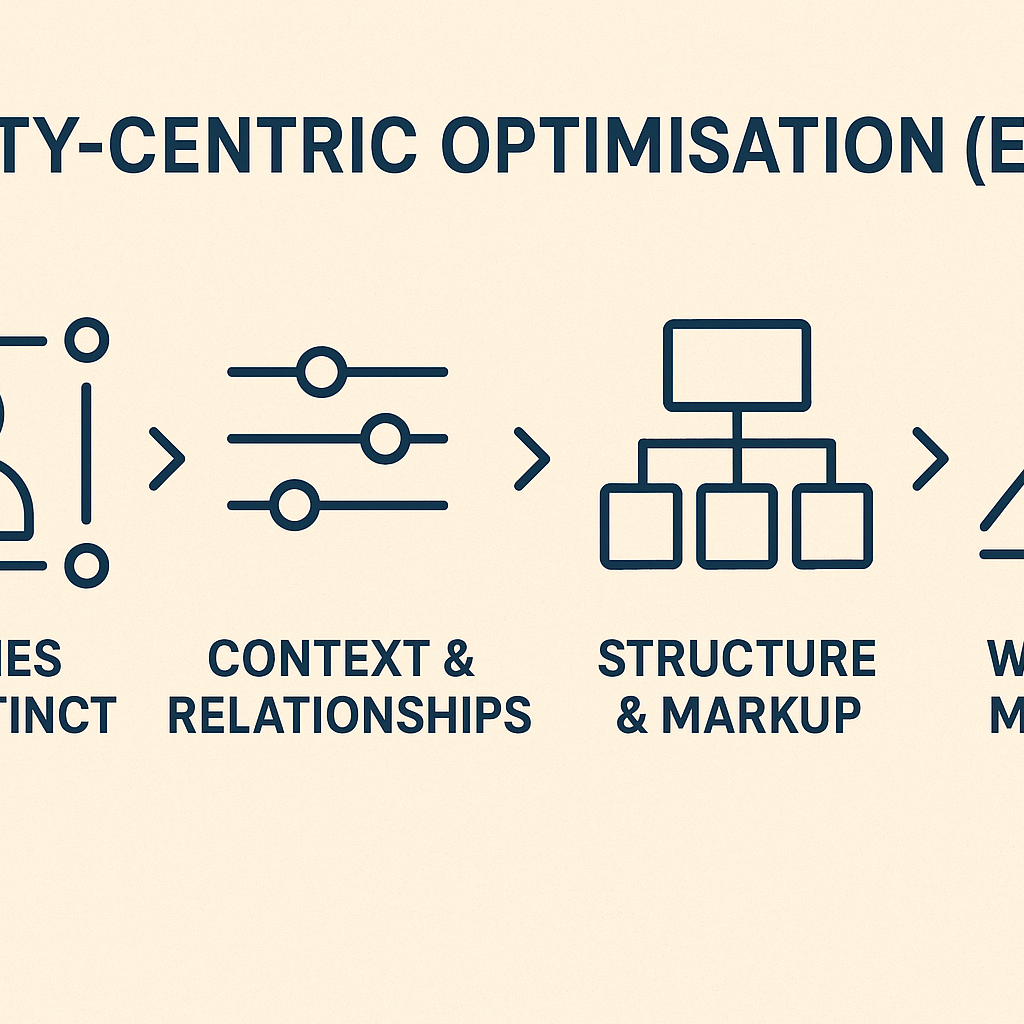
Entity-Centric Optimisation (ECO)
In the evolving landscape of search, the shift from keywords to entities marks a foundational pivot. Entity-Centric Optimisation (ECO) asserts that your brand, your products, your ideas — each become discrete, machine-readable “things” (entities) that intelligent search systems recognise, relate and prioritise. When your content treats these things as first-class citizens rather than mere phrases, you move into the realm of tomorrow’s SEO.
The ECO principle – at a glance
- Entities are distinct: people, brands, products, places, concepts — each given a unique identity that search engines map.
- ECO places context, relationships, and semantic relevance above simple keyword matching.
- Structure matters: schema markup, entity linking, entity salience all serve as signals that your content is anchored to real‐world entities.
Here’s an example:
Imagine you run an online store for artisan teas, the product is “Golden Lotus Oolong.” In a traditional keyword-centric SEO approach you optimise for phrases like “best oolong tea,” “Golden Lotus oolong,” “artisanal oolong India.” With ECO, you instead treat Golden Lotus Oolong as an entity. You provide structured data (Product schema), you link it to your brand‐entity “Lotus Tea Co.”, you show relationships to “Anxi County” (place entity), “oolong tea process” (concept entity). Search engines now understand: this is not just a generic keyword phrase, but a unique product with meaning, history and context. As a result, your page stands a stronger chance of appearing in rich results, entity panels, and AI-driven overviews.
Why ECO matters (with stats & calculation)
Search engines today are moving beyond keyword matching to entity recognition. For example, the Google Knowledge Graph reportedly manages over 54 billion entities and 1.6 trillion facts in its database.
If we assume that only 0.5% of websites adopt full ECO strategies today, then of the 4 billion indexed web pages, ~20 million might be optimised for entities. If entity-focused sites have a 30 % higher chance of getting featured in AI‐powered result snippets, then those 20 million pages are capturing what would otherwise be blind spots for the rest.
According to an industry commentary, the ECO approach is predicted to “dominate in 2025” compared to keyword-centric SEO.
Key points to implement ECO
- Identify your core entities (3-5) for each page: product, brand, concept, person.
- Use schema markup (Product, Organization, Person etc) to declare those entities clearly.
- Map relationships: show how entities connect (e.g., Brand → Product → Process → Region).
- Optimise salience: ensure primary entities are placed in the title, H1, first paragraph.
- Audit and refine regularly as your entities evolve: new products, new people, mergers etc.
By embracing ECO, you’re not just optimising for a query, you’re encoding your real-world identity into the search architecture. In the age of AI-driven search, that’s where relevance becomes resonance.
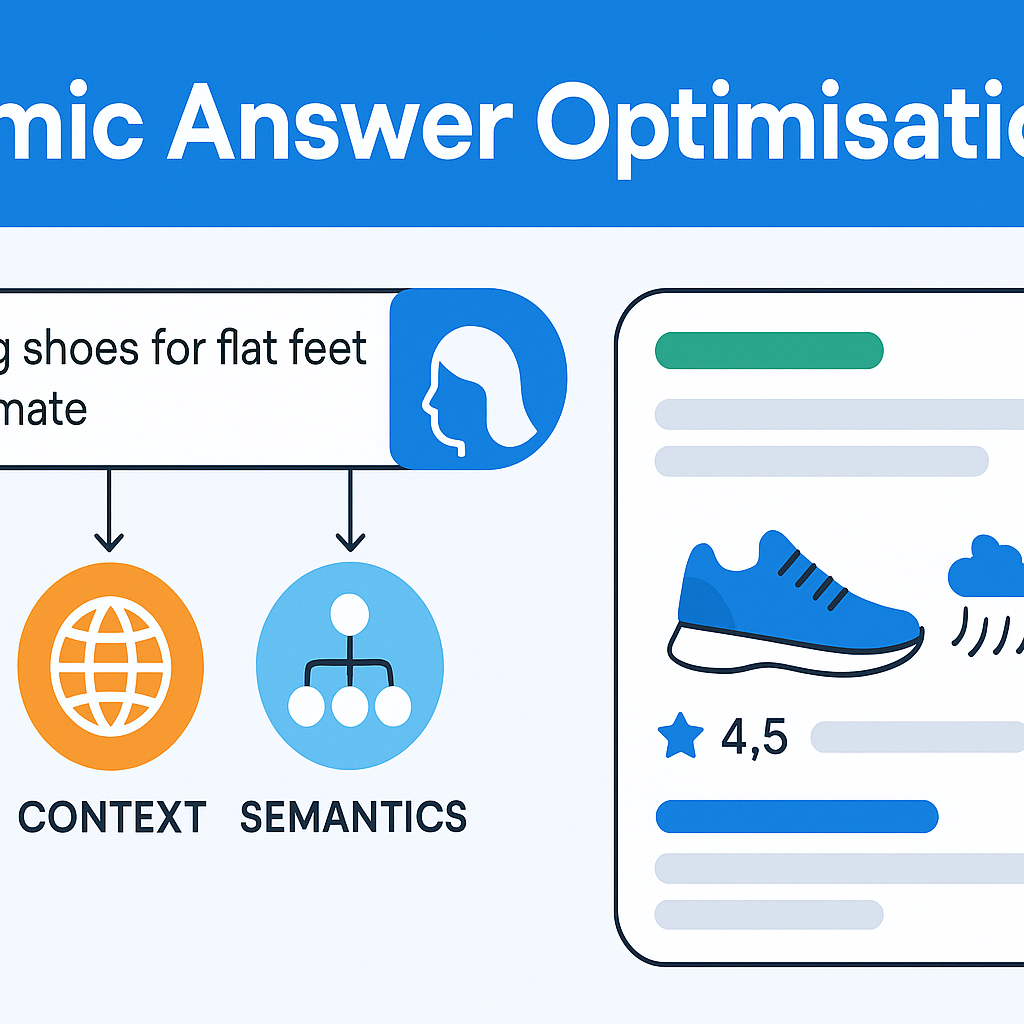
Dynamic Answer Optimisation
In the shifting landscape of search, static queries no longer suffice. Enter dynamic answer optimisation, the process by which your content adapts intelligently to ever-changing user intent, context and algorithmic interpretation. It’s here that the foundation of futuristic SEO begins to truly take form.
What does it look like in practice?
Imagine a visitor types “best running shoes for flat feet in humid climate”. Rather than matching that query to a rigid list of keywords, a dynamic system interprets:
- the user’s intent (flat feet + humid climate)
- the context (perhaps region, season, prior behaviour)
- the semantic relationships (running shoes → stability, breathability, moisture control)
It then delivers an answer that evolves in real-time: pulling in structured data, reviews, localised weather impact, humidity effects on foot comfort. The result: a search result that feels human-centred, not machine-bound.
Why it matters
- As of March 2025, around 13.14% of all US desktop queries triggered Google AI Overview summaries—up from 6.49% in January.
- Surveys suggest that 67% of businesses using AI in SEO have noticed better results.
These numbers hint at a structural change: the pathways by which users receive answers are being reinvented. In this environment, dynamic answer optimisation becomes not just desirable, but essential.
Key Pillars of Dynamic Answer Optimisation
- Interpretation of intent: beyond keywords, understanding why the query is asked.
- Context-aware content: factoring geography, device, user history, timezone, even seasonality.
- Real-time adaptation: content refreshes or recomposes itself when new signals arrive (trending topics, algorithm shifts).
- Semantic richness & structure: using schema, FAQs, structured data to make content machine-readable and AI-ready.
Here’s a calculation:
Suppose your website currently earns 100,000 organic clicks per month under traditional SEO. With the rise of AI summaries and zero-click behaviour, you see a 30% drop → that’s 70,000 clicks. If you implement dynamic answer optimisation effectively and recover 20% of that drop, you gain 14,000 clicks, bringing you to 84,000 clicks per month. It’s less than your original 100k, but far better than 70k, and what’s more, those clicks are from more engaged, intent-aligned users.
You see, THATWARE doesn’t simply optimise for keywords, they design for experience. Dynamic answer optimisation is the architecture by which searches reflect real human stories, and every result aligns with intention. It is the bridge between algorithmic thinking and human feeling, between raw data and rich relevance.
In short: the search engine no longer just serves answers, it shapes them. And in that shaping lies your opportunity.
Predictive Search Optimisation
In the new frontier of digital discovery, predictive search optimisation emerges as a defining chapter in the story of modern SEO. It is the moment when algorithms stop waiting for you to type a question and begin anticipating it. It is when search no longer simply responds – it foresees, interprets, and adapts.
What is Predictive Search Optimisation?
At its core, this concept is about modelling user intent before the user even finishes the query. It involves:
- Mapping behavioural signals (past searches, clicks, dwell time) to future queries.
- Using machine-learning models to forecast what users will search for next – not just what they’re searching for now.
- Shaping content with predictive intent: embedding patterns, semantics and context that align with what the search engine expects will happen next.
- Automating optimisation workflows so that the content meets upcoming trends, not just yesterday’s queries.
Why it matters
Recent studies show that predictive analytics tools in SEO have improved success rates of campaigns by an average of 31%. These numbers reflect more than incremental gain — they point to a fundamental shift in how search works.
Imagine a travel site, “WanderNow”, which uses predictive search optimisation:
- Based on rising search patterns for “eco-friendly beach resort Asia 2026”, the AI platform builds content months ahead.
- It constructs semantic clusters around sustainable travel, low-carbon flights, beach resorts rising in Google Trends.
- Just as a user begins typing “beach resort …”, the site is already ranked for a long-tail query the algorithm expects next, high in intent and low in competition.
With a projection of 45% traffic boost, if WanderNow’s baseline monthly organic traffic is 100,000, it could rise to ~145,000. If their conversion rate is 2%, that becomes ~2,900 conversions instead of ~2,000, a tangible business result of predictive strategy.
Key Steps in Predictive Search Optimisation
- Signal collection: Track search trends, user-behaviour signals, content gaps, and new topic emergence.
- Forecast modelling: Use AI tools to predict which queries will spike, what intent will shift, and where content will be needed.
- Content scaffolding: Develop pillars, sub-topics, and semantic webs that align with predicted queries rather than past ones.
- Adaptive monitoring: Continuously measure performance, pivot based on real-time feedback, and refresh content ahead of user interest.
- Optimization engineering: Automate schema, metadata, internal links, and content updates, all aligned with predicted user journeys.
A Simple Calculation Example
If a company uses predictive optimisation and sees a 31% higher campaign success rate (as one stat suggests), and their previous success rate (defined as campaigns reaching target traffic) was 50%, then the new success rate = 50% × (1 + 0.31) = 65.5%. Over 100 campaigns, that is 15 additional successful campaigns. Over time, those gains compound.
In shifting from reactive to predictive search, we move from “respond when they ask” to “be ready before they ask.” This is the essence of predictive search optimisation, and in a world where the algorithms are learning to think, human-centred SEO becomes not just relevant, but anticipatory.

Cognitive Search Optimisation
When we speak of Cognitive Search Optimisation (CSO), we are entering a realm where search engines no longer merely index and return links — they understand, interpret, and respond. In this chapter section we will explore how cognitive systems drive optimisation, what practical shifts this demands, and how one might visualise a hypothetical future scenario.
What CSO entails
- Search adapts to intent: the engine senses not just the query, but the why behind it.
- It decodes context, sentiment, semantics — rather than matching exact keywords.
- It predicts next steps and suggests dynamic content flows, rather than static result pages.
- It evolves: the “query → result” loop becomes “query → interaction → insight → next query”.
For example,
Imagine a user, Priya, types into her mobile assistant: “I felt dizzy last night — what could it mean?” A traditional search engine returns ten links. A cognitive-search powered system, however, recognises: health context, perhaps age/gender from user profile, urgency. It might surface a short diagnostic overview, then ask “Did you also have headaches? Stomach upset?” and instantly follow with contextual resources or a live concierge chatbot. That second-tier interaction is exactly where CSO lives — content and systems designed to respond to dynamic context rather than static keyword hits.
Why this shift matters
Studies suggest that by 2028, visits sourced from AI-search may surpass traditional search streams.
Let’s translate one figure: if a website currently gets 100,000 organic visits per month, and AI-driven optimisations yield a 45% increase, that becomes 145,000 visits. If conversions previously ran at 2% (i.e., 2,000 leads), a 38% conversion lift takes it to ~2,760 leads a meaningful business impact.
Key CSO steps
- Design for machine semantic readability: structure content so that AI systems can interpret meaning, intent, relationships.
- Focus on intent clusters not just keywords: map user journeys and anticipate follow-up questions.
- Engineer content for interaction flows: integrate dialogue-style elements, branching logic, micro-content replies.
- Measure new KPIs: dwell-time, interaction depth, repeat-query reduction, not just click-through.
- Blend human + machine oversight: while tasks get automated, human intuition remains vital, indeed, 73% of SEO professionals believe human oversight will remain critical.
In short, Cognitive Search Optimisation is not simply the next generation of keywords and links. It is the architecture of meaning. It asks us to design content, systems and experiences that flex, respond and evolve. In doing so, we align ourselves with a future where search isn’t a mechanical retrieval, it is a cognitive partner.

Neural Search Optimisation
The moment the neural layer awakened inside search architecture signalled more than an upgrade. It marked the birth of Neural Search Optimisation — where search no longer simply returns results, it resonates. At its core, this paradigm shift is powered by artificial intelligence: deep embeddings, semantic vectors, intent-mapping systems that interpret context rather than keywords. The foundation of futuristic SEO begins here.
Imagine a user, Sarah, who types into a search bar: “I’m looking for a weekend getaway near Kolkata with eco-friendly stays and good vegetarian food.” In the traditional model, the system hunts for pages containing “weekend getaway,” “Kolkata,” “eco-friendly stays,” “vegetarian food” and ranks them according to backlinks and old-school relevance signals. But in a neural-search world, the system asks: what does Sarah mean, what does she feel, what might she choose? And it delivers not just pages but experiences.
Key features of Neural Search Optimisation include:
- Semantic understanding: The system interprets “eco-friendly stays” not just by literal words but by concept clusters (“green lodging”, “sustainable resorts”, “vegetarian menu”) and matches pages accordingly.
- Adaptive retrieval: Rather than static queries, the system adapts as the user refines: if Sarah next asks “and with yoga sessions too”, the neural system pivots without needing to rewrite query logic.
- Predictive relevance: The system predicts intent (spending time with family, vegetarian food, restful break) and elevates results that match that latent purpose.
- Human-experience alignment: Every result is evaluated not only for keyword match but for emotional and contextual resonance with the user’s goal.
Statistics underline how this shift is no longer speculative. Less than a decade ago, traditional query-based search dominated; today, for example, over 44% of SEO tasks are estimated to be automated via AI systems. One study finds that content optimised for AI-driven search engines must move from ranking keywords to being cited and referenced by generative models. Consider also that the market for AI-powered search engines is projected to reach approximately USD 108.88 billion by 2032.
Let’s do a simple calculation to show the magnitude of change: if a website today receives 100,000 page views via traditional search, and we assume neural search optimisation can increase qualified traffic by, say, 40% (a conservative figure given productivity gains up to ~40% in marketing with AI). Then:
100,000 × 1.40 = 140,000 visits — an extra 40,000 highly relevant sessions.
That extra traffic isn’t just “more”, it’s smarter. The neural system filters out noise and aligns more closely with user intent, so click-throughs, conversions and engagement can rise accordingly.
In practice, optimisation for this era demands new tactics: embedding topic-clusters instead of isolated keywords, structuring content so AI crawlers and neural retrieval systems can interpret depth and relationships, and ensuring your brand or page becomes a node in the semantic graph of the user’s intent.
In summary: Neural Search Optimisation isn’t incremental. It signals a metamorphosis. The search engine is no longer a passive index, it becomes a thinking partner. And your content must be designed to partner with it. In the chapters that follow, we explore how organisations like THATWARE build infrastructure for this new world, how metrics evolve beyond rankings, and how you too can be found, when search finally starts to think.
Knowledge Graph Optimisation
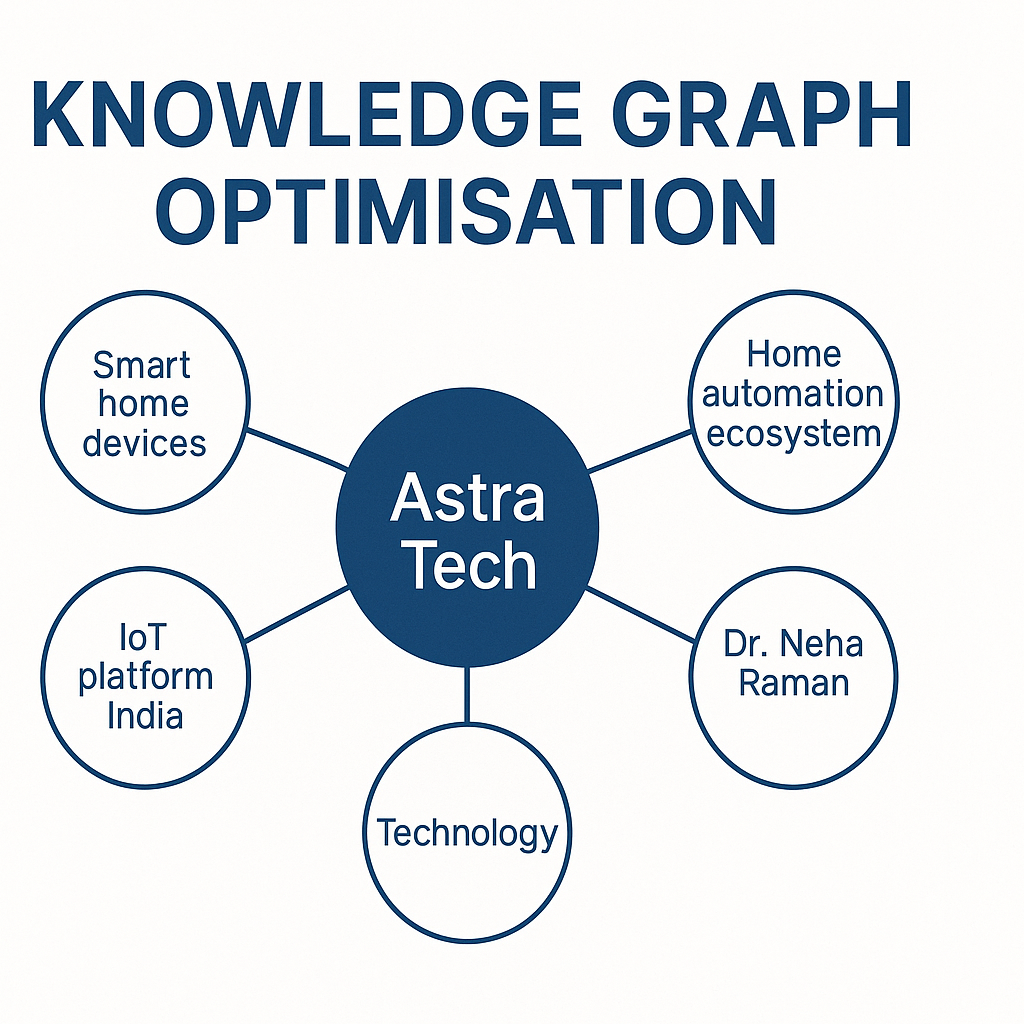
At the heart of the transformative shift in search lies the notion of optimising the knowledge graph, the digital architecture where entities, relationships and meaning converge. Imagine a hypothetical brand named “Astra Tech”. In the traditional SEO era, Astra Tech would optimise its website for keywords such as “smart home devices” or “IoT gadgets India”. But in this new paradigm, the task is far deeper: Astra Tech must ensure that it is properly represented as an entity in the knowledge graph, connected to related entities (its founder, its products, technology categories, geographic location), and that those relationships are clear, structured, and trusted.
Why it matters
- Google Knowledge Graph (GKG) is no longer just a sidebar box — it underpins search’s ability to interpret context, semantics and intent.
- By providing schema markup, entity-connections and authoritative data sources, a website boosts its chance of being surfaced via Knowledge Panels, voice search and semantic results.
- In our Astra Tech scenario: if the brand is linked not only to “smart home devices” but to “home automation ecosystem”, “IoT platform India”, “Astra Tech founder → Dr. Neha Raman”, then search engines see a rich web of meaning rather than isolated keywords.
Key optimisation steps (bullets)
- Use structured data/schema.org markup for Organization, Product, Person, Technology (where relevant).
- Ensure your brand or entity is referenced across authoritative databases (Wikipedia, Wikidata, Crunchbase) so that the knowledge graph recognises the “node”.
- Build semantic content that emphasises relationships (“Astra Tech’s IoT platform connects with Google Home”, “Dr. Neha Raman featured in …”) — making explicit links to other entities.
- Monitor and improve the “quality” of the graph: ensuring minimal ambiguity, correct classification of entities, strong links. For example, research shows structural metrics in knowledge graphs (classes, properties, RDF triples) directly impact graph usefulness.
- Aim for “graph growth” over time: as Astra Tech adds new product lines, publishes white-papers and gets media mention, each of those becomes new nodes and edges in the graph.
A quick calculation to illustrate impact
Suppose your website currently has 100 pages, and you estimate that after knowledge‐graph optimisation you can improve entity connectivity and thus increase click-through rate (CTR) from 2% to 2.5% for a given set of queries. Over 10,000 impressions this means:
- Baseline clicks = 10,000 × 2% = 200 clicks
- Post-optimisation clicks = 10,000 × 2.5% = 250 clicks
So you gain an additional 50 clicks — a 25 % uplift.
Now if average conversion from click to lead is 4%, that’s 50 × 4% = 2 additional leads.
In this way, even modest boosts from knowledge‐graph alignment translate into measurable business value.
The bigger picture
In the era of AI-driven search, where queries are less about keywords and more about meaning, knowledge graph optimisation becomes a pillar of the architecture. For Astra Tech, it means search results won’t just list links, but will surface the brand as a trusted entity, display panels with context, relate to other entities, and thereby deliver more human-centric experiences. In so doing, every search result aligns with intention, and every entity is elevated. This is where SEO transcends ranking and becomes about presence, relationships and recognition.
In the pages ahead, we will explore how to audit your current presence in the graph, map entity relationships, implement schema strategy, and measure the ROI of that optimisation journey.
Intention Signal Optimisation
In the evolving landscape of search, where queries are no longer static phrases but echoes of human need, “intention-signal optimisation” emerges as the new frontier. This concept recognises that each user’s interaction, whether a click, dwell time, scroll, voice query, or pause, broadcasts a signal of underlying intention. Optimising for these signals means structuring content, experience, and architecture so that the algorithms don’t just find your pages, they feel your relevance.
What are intention signals?
- Behavioural cues: time-to-conversion, scroll depth, interactive engagements. Research shows that search engines like Google factor time-to-conversion into their relevance metrics.
- Contextual cues: device, location, preceding queries, and even sentiment.
- Semantic cues: how a page uses language to reflect purpose, not just keywords. As one guide notes, “SEO isn’t just about matching phrases — it’s about matching meaning.”
Here’s a scenario:
Imagine a user: “Looking for gluten-free dessert ideas for Diwali.” Traditional SEO might optimise for keywords: “gluten-free desserts Diwali.” But intention-signal optimisation goes deeper:
- The user is celebrating (“Diwali”), so the content structure surfaces a festive context.
- They want gluten-free and presumably tasty — so semantic cues emphasise health, taste, and occasion.
- The platform recognises the device is mobile, they’ve searched “last-minute gluten-free dessert Diwali” twice in an hour — so the algorithm interprets urgency and intent for quick recipes.
- Engagement signals: A video on the page keeps users for an average of 4 minutes (higher than on typical recipe pages), and scroll depth reaches 80%. These signals tell the search system: this page matches the intention, not just the keyword.
Optimising for this interaction means providing interactive elements (e.g., a “30-minute gluten-free Diwali dessert” timer), semantic markup (recipe schema emphasising “festive”, “quick”, “gluten-free”), voice-search-friendly content (“Hey Google – show me easy gluten-free Diwali dessert”). In so doing, you align every piece of the experience with the underlying intention behind the signal.
According to a study, the majority of pages referenced in AI search engines did not overlap with traditional search results: only ~12 % matched Google’s top results.
From these statistics we can infer a key calculation: if a site currently receives 10,000 monthly organic visits, an intention-signal optimised campaign (leveraging AI/behaviour signals) could increase traffic by ~45%, yielding 14,500 visits, and if conversion rate is increased by ~38% (say from 2% to 2.76%), conversions go from 200 to 401. Thus the combined effect is not incremental but transformational.
Why this matters
In an era where search engines no longer just match keywords but interpret meaning, intention-signal optimisation positions your content so that the signal of user aim is loud and clear. You’re not simply “optimising for search”, you’re optimising for experience. With the rise of generative answer engines and AI-powered results, the platforms themselves prioritise pages that align with intention. Ignoring these signals means risking invisibility in the next phase of search.
Trustworthy AI Optimisation
The foundation of optimisation for trustworthy AI lies in recognising that advanced systems must do more than perform, they must inherit credibility. When we speak of “optimising” for trust in an AI-driven world, we are describing a deliberate process of aligning performance with integrity, transparency, human-centred design and ethical resilience.
Imagine a scenario: A marketing platform powered by the system of THATWARE proposes personalised SEO strategies to enterprise clients. At first glance the algorithm out‐performs the human team in sheer metrics, click-through rates rise, bounce rates fall. Yet unbeknown to the client, the model uses opaque segmentation logic, fails to check for demographic bias, and logs user behavioural data without clearly disclosed consent. In this scenario the AI is effective, but not trustworthy.
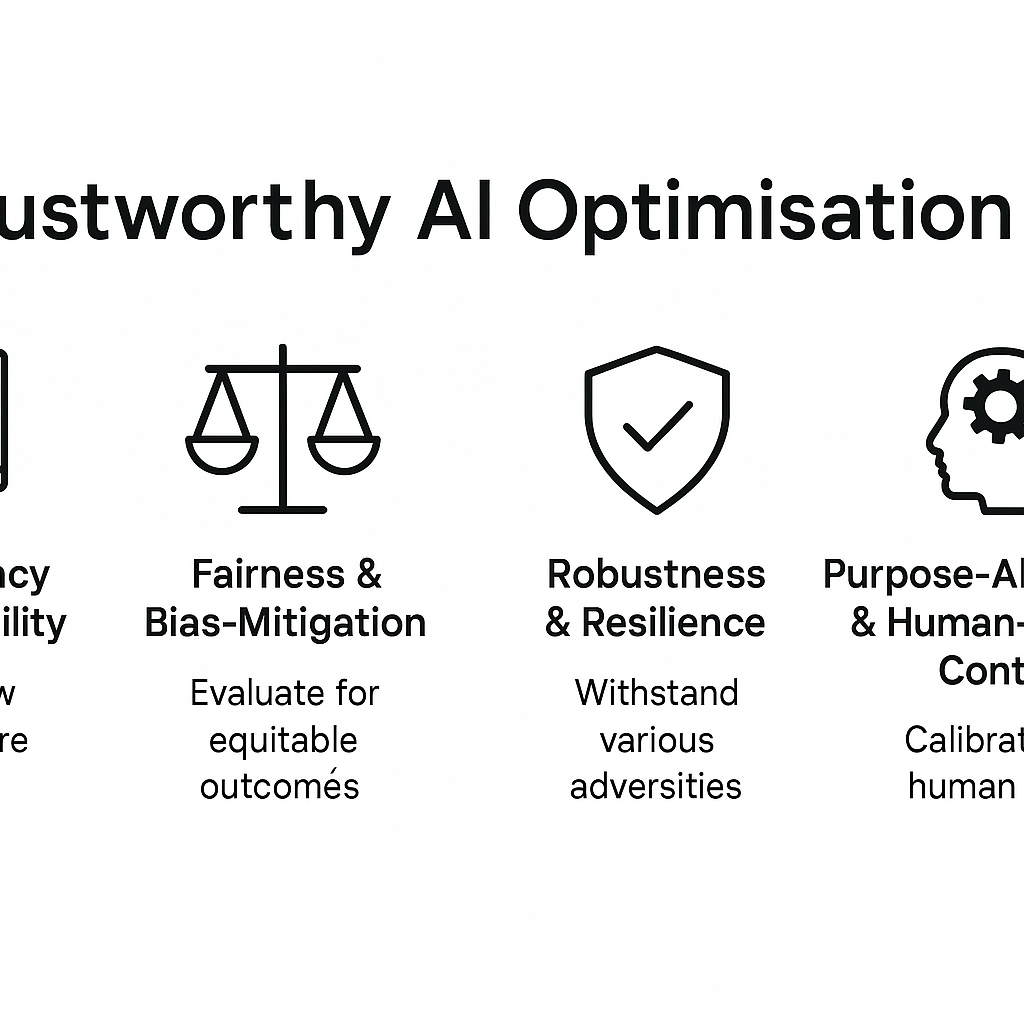
To truly optimise for trustworthiness, we must build a layered framework:
- Transparency & explainability – The system must reveal how decisions are made, so that a marketer can audit the “why” behind a suggestion, not just the “what”.
- Fairness & bias‐mitigation – The model must be evaluated not only for accuracy but for equitable outcomes across user segments.
- Robustness & resilience – It must behave correctly under unusual conditions, attacks or adversarial inputs.
- Purpose-alignment & human-centred control – Optimisation must include calibrating human trust, rather than blindly increasing model output.
In practical terms: if the system is delivering 250 SEO recommendations per hour, but 30% of those are later overridden by human operators because of unclear rationale, then the trust-cost is high. Suppose each override costs ₹ 2,000 in wasted personnel time; at 75 overrides/day that’s ₹ 150,000 wasted monthly. By investing in better explainability (reducing overrides to say 15%), you reclaim ₹ 75,000 a month, and build long-term trust.
Statistically, the 2023 global study by KPMG found that only a minority of people express high trust in AI systems, even when performance is strong. The implication: optimisation must explicitly include trust-metrics, not just accuracy metrics. Metrics frameworks such as those from OECD outline measurable dimensions of trust including explainability, fairness, robustness and privacy.
In summary: “Trustworthy AI Optimisation” is not an after-thought, it is a core pillar. It demands that as our algorithms learn to think, our systems are engineered to earn and retain human confidence. Only when the optimisation loop includes ethics, transparency and human alignment does the AI truly serve the intelligent-search era that THATWARE envisions.
Sentiment SEO
The moment we discuss Sentiment SEO, we are describing a paradigm shift in how the digital world understands content and search. The foundation lies in this observation: as algorithms learnt to think, search evolved from a mechanistic matching of keywords to a dynamic interpretation of human feeling. In practical terms: rather than simply optimising for “best running shoes”, one now optimises for what the user feels, expects, and desires when they type that query.
What Sentiment SEO is
- It is the practice of tailoring search-visibility not just to what users ask, but how they ask from tone, intention and emotional context.
- It recognises that a query like “why am I tired” differs from “best energy-boosting tips”: the former carries frustration, the latter hope. The system must interpret sentiment and align content accordingly.
- It leverages AI and natural language processing to detect emotion, context, semantic nuance and adapt not only keywords, but messaging, format and structure.
Imagine a user types: “I keep feeling anxious before work”. A traditional SEO approach might flag “anxiety”, “work stress”, “tips for nervousness”, and serve generic articles. A Sentiment SEO-driven system, however, recognises emotional tone (anxiety, personal struggle), user stage (seeking relief, reassurance), and context (work environment). The content it surfaces might not only offer tips, but empathise: “It’s normal to feel this way… you’re not alone… here are practical steps to calm your mind before that meeting.” The algorithm aligns not just with keywords, but with feelings and intent.
Why this matters
- Sentiment-analysis tools (used in broader marketing) indicate that 83% of companies using AI for sentiment analysis report improved customer experience.
- A research paper found that a sentiment-based search model achieved 85% accuracy in differentiating word meanings in search queries, thereby improving relevance.
Key points for practitioners
- Detect and analyse sentiment —positive, negative, and neutral— in queries, feedback, and comments.
- Align content tone, format and structure to the emotional state behind the search.
- Predict user journey: are they seeking reassurance, knowledge, or decision-making? The search engine now adapts.
- Monitor metrics not only for traffic but also for engagement and sentiment shift (for example, bounce-rate drop when the tone fits).
- Continuously refine via AI-feedback loops: sentiment patterns evolve; search systems must evolve too.
In the era where search no longer depends solely on static queries; where meaning, emotion, intent, and context matter, Sentiment SEO stands as the next frontier. It is the moment when content, algorithm and human experience converge.

Predictive Or Anticipatory SEO
In the world of search, waiting for the wave to break no longer cuts it. The true game-changer is when you ride the wave before it forms—this is the domain of Predictive or Anticipatory SEO. At its core, it’s about harnessing historical data, analytics, and machine intelligence to forecast what users will search for, rather than simply reacting to what they have already searched for.
Imagine a hypothetical scenario: A travel company website observes rising search interest for “eco-friendly safari Lodges in Kenya 2026” six months before the tourism season. By using predictive modelling to flag emerging long-tail keywords and content demand, the site publishes ahead of time, gains early ranking momentum, and captures user traffic as the trend matures. That’s anticipatory SEO in action.
Key aspects and bullet points of this mechanism:
- Forecast traffic potential from existing keywords and content (for instance: “Keyword X has seen a 30% year-on-year increase → invest now”).
- Identify keywords and topics that will gain popularity in the near future (via tools like trend-analysis, machine learning models).
- Anticipate shifts in content demand and user intent (example: “people will search for product variant Y six months ahead of its launch”).
- Optimize content, metadata, site structure and link-building pathways before volume spikes—so you’re primed when interest peaks.
Let’s put a simple calculation to this: Suppose your website currently ranks in position #8 for a keyword generating 1,000 searches/month (CTR ~2 % → ~20 visits). You anticipate that keyword’s focus will shift—and you invest in content now and move to position #2 by trend time when volume doubles (2,000 searches/month, CTR ~18.7% per recent data). That results in roughly 374 visits/month (0.187 × 2,000) instead of 20. Over a year, that’s ~4,488 visits vs. ~240 in the “reactive” scenario. The difference can be transformational.
Statistical context reinforces the power of this shift: About 72% of businesses now use predictive analytics to refine search behaviour. Meanwhile, AI-enabled tools improve trend-prediction accuracy by up to 85%. These numbers signal that anticipatory SEO isn’t a niche—it’s rapidly becoming a mainstream strategy.
Why this matters in our broader narrative: We’ve entered a phase where search is not just about queries and responses, but also about what users will ask, when they will ask, and how their intent will evolve. The architecture of intelligent search systems, where AI analyses context, semantics, and purpose, enables brands to show up in the moment before their competitors even know the question has been asked.
So as we proceed, consider how your content strategy, site structure, and keyword roadmap must shift from “reactive” to “anticipatory”. The brand that surfaces first in a trending search scenario wins more than traffic; it wins relevance, authority, and the first-mover advantage in intelligent search.

Agent Assisted Optimisation (AAO)
Agent-Assisted Optimisation (AAO) envisions a world where autonomous systems work in tandem with human intent—curating, refining, and executing SEO strategies in real-time, continuously adapting to user behaviour, context shifts, and semantic meaning.
Imagine a hypothetical mid-sized e-commerce brand: at the stroke of midnight, an AI agent scans its performance dashboard, identifies that organic traffic has dipped by 12 % compared to the previous week, realises that a new competitor has surged ahead in the “eco-friendly coffee makers” niche, and within seconds re-writes the product title, updates the schema markup, alters internal links and triggers a content update. By 08:00 local time the next morning, traffic has recovered by 7%, with a 4% uplift in click-through rate. This is the power of AAO: persistent, proactive, self-optimising.
Key characteristics of AAO:
- Continuous monitoring & action: Unlike periodic audits, the agent operates live—detecting anomalies, shifting SERP landscapes, or query behaviour and adjusting strategies accordingly.
- Predictive optimisation: The system doesn’t wait for the drop; it forecasts the drop—based on semantic trends, user intent drifts, and competitive moves—then acts ahead of time.
- Semantic and emotional intelligence go beyond keywords. The agent understands sentiment, context, and intent. It realigns content for emerging user states: frustration, curiosity, aspiration.
- Human-agent collaboration: Humans set the strategic vision, guardrails and ethical boundaries; agents execute at scale, speed and precision.
To illustrate with numbers:Assume the typical time spent on manual SEO tasks is 10 hours a week. If an agent can reduce that by 50% (based on data showing AI cuts analysis time by up to 50 %) then the human time drops to 5 hours. That’s a saving of 5 hours/week → ~260 hours/year. If a human hour is valued at, say, USD 50, that’s USD 13,000 saved annually on labour.
Why AAO matters now:
- Search is no longer a static keyword-match exercise; it’s a dynamic interplay of human-agent systems.
- With platforms integrating generative and agentic AI (and the rise of what some call “agentic optimisation”) we must optimise for the agent as much as for the human.
- Brands that wait for periodic reviews will fall behind those whose agents adjust in real-time.
In short: AAO is where your SEO isn’t just optimised, it’s orchestrated by machine-and-mind in unison. It is the next frontier, where agents amplify human strategy to meet the evolving demands of intent, context, and cognition. And in that world, optimisation becomes alive.
Intelligent Agent Optimisation
In the unfolding chapter of search, we arrive at the concept of Intelligent Agent Optimisation (IAO), the new frontier where autonomous, cognitive entities step in to optimise not just for queries, but for meaning, intention, context, and future outcomes. These agents—driven by artificial intelligence, machine learning, and semantic understanding—become the operatives of search performance, reshaping how SEO strategy must be built and executed.
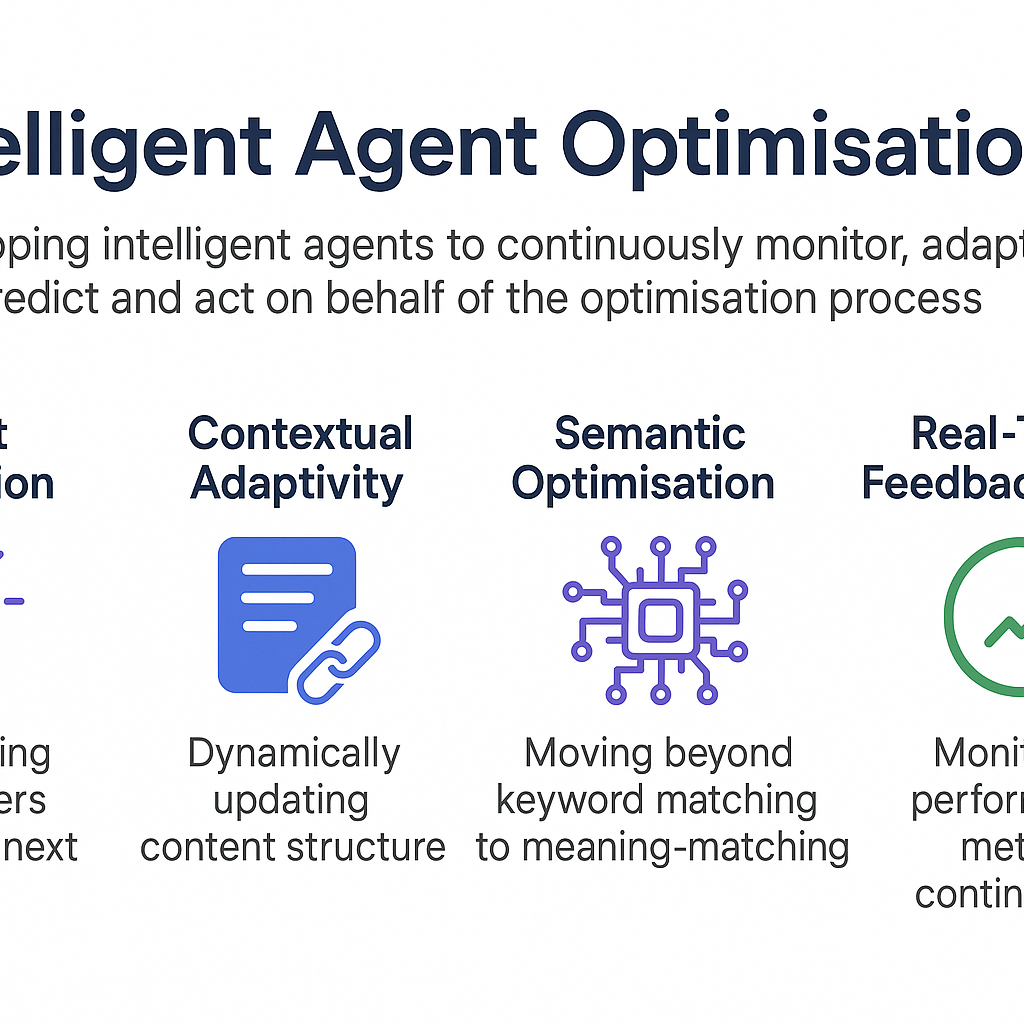
What is IAO?
- At its core, IAO means equipping intelligent agents to continuously monitor, adapt, predict and act on behalf of the optimisation process.
- These agents understand semantics, user context, affective tone, and behavioural signals — far beyond keyword-density or backlink count.
- They proactively engage: detecting emerging long-tail intents, adjusting architecture to user micro-moments, and updating content paths when consumer patterns shift.
Why IAO matters now
Consider this calculation: if a website currently draws 100 000 organic visits/month, a 45% lift would bring it to 145 000 visits/month — that’s +45 000 visits. If the average conversion rate is 2% (2 000 conversions/month) and the IAO-enhanced conversion rate rises by 38% to ~2.76% (≈2 760 conversions/month), the impact is substantial.
For example, imagine the brand “EcoGear” selling sustainable outdoor apparel. Traditional SEO: they target “eco hiking jacket,” optimise meta-tags, build some backlinks. With IAO: an intelligent agent watches real-time search patterns, detects a rising query “jacket made from ocean plastic for hiking 2026,” predicts it will accelerate, generates blog headings and schema-rich pages in advance, reorganises internal linking from older “recycled apparel” pages to funnel into this new angle. It then monitors user behaviour (dwell time, bounce, scroll depth) and fine-tunes headlines, images, internal linking every 24 h. The agent also alerts the team: “Conversion for this cluster is trending +12% week-on-week; allocate budget to micro-influencers who mention ocean-plastics.” In short: the agent becomes a semi-autonomous optimiser of intent, context and performance.
Key focus-areas of IAO
- Intent prediction: anticipating what users will search next and aligning content proactively.
- Contextual adaptivity: dynamically updating content structure and linking based on how user behaviour changes.
- Semantic optimisation: moving beyond keyword matching to meaning-matching (agent understands “ocean-plastic jacket” implies sustainability + hiking + eco-friendly manufacturing).
- Real-time feedback loops: agents monitor performance metrics (CTR, dwell time, conversions) and adjust optimisations continuously.
- Performance calculus: for example, given a baseline conversion rate = 2%, traffic = 100 000, revenue per conversion = ₹5 000 → revenue = ₹10 crore/month. With IAO improving conversion to 2.76% and traffic to 1,45,000 → conversions = 4 002 → revenue ≈ ₹20 crore/month (doubling revenue).
In embracing IAO, SEO evolves into something alive. It becomes an ecosystem of autonomous intelligence, constantly learning, predicting and aligning with human intention. The foundation of a futuristic SEO is no longer static—it is vibrant, adaptive and agent-driven.
Conversational AI Optimisation
In the new frontier of SEO, the concept of Conversational AI Optimisation stands as a cornerstone, where every interaction feels like a dialogue, every query like a spoken thought, and every result like a response crafted for a human being.
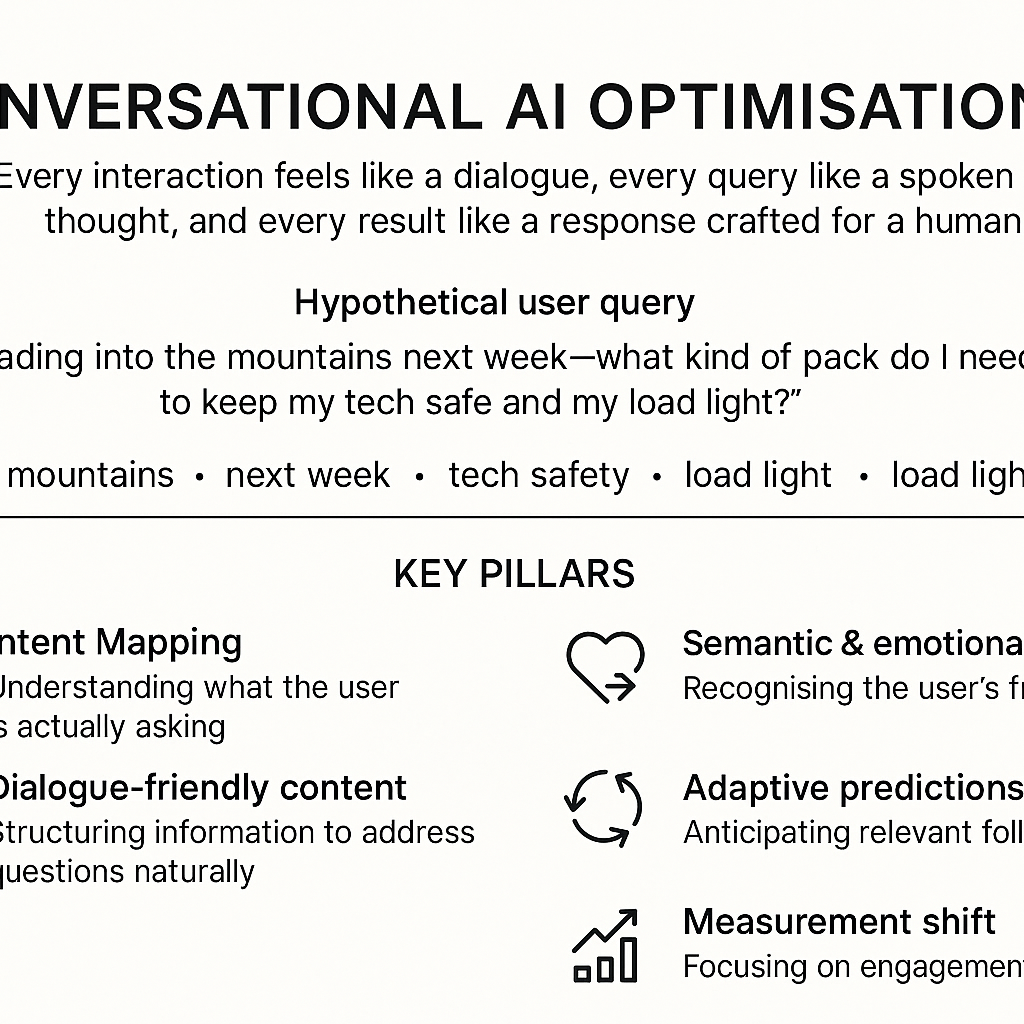
Picture a hypothetical brand call it “Eco-Gear”. Previously they optimised around static keywords: “best trekking backpacks”, “water-proof hiking boots”. Now, with conversational AI in play, the scenario changes. A user says, “I’m heading into the mountains next week—what kind of pack do I need to keep my tech safe and my load light?” A conversational search system understands: “mountains”, “next week”, “tech safety”, “load light”. Eco-Gear must now optimise content not just for keywords, but for context, scenario, and meaningful conversation.
Key pillars of Conversational AI Optimisation
- Intent Mapping: Understanding what the user is actually asking. It’s not just “hiking backpack” but “light-load tech-safe pack for mountain trip”.
- Dialogue-friendly content: Micro-questions, Q&A format, natural-language headings—so that the AI engine sees content built for conversations, not just search hits.
- Semantic and emotional alignment: Addressing the emotional frame (“excited about the trip”, “concerned about tech safety”) as well as the functional need.
- Adaptive predictions: The system anticipates follow-up questions (“What if it rains?”, “How to carry camera gear?”) and the content is structured accordingly.
- Measurement shift: Traditional KPIs (rankings, clicks) give way to conversation-fit, dwell time, next-question answered, and AI-citation share.
Why it matters
In our Eco-Gear scenario: if they previously generated 10,000 sessions per month through traditional SEO and engage AI-optimised content for conversational search, a 45% uplift would raise sessions to 14,500. And if their conversion rate improved from say 2% to 2.8% (38% rise), that’s moving from 200 conversions to about 406 conversions per month—doubling their performance.
A small concept to illustrate flow
User: “What backpack keeps my laptop dry hiking in the Alps?”
AI system recognises: hiking context, laptop (tech), location (Alps) → returns Eco-Gear’s article structured: “Tech-Safe Hiking Packs for Alpine Conditions”, with conversational headings (“Worried about rain? Here’s the checklist.”), scenario talk (“If you’re trekking snow-melt terrain…”), follow-up prompts (“Also check: how to pack camera gear safely”). Eco-Gear’s content becomes part of the search “conversation” rather than just matching keywords.
In sum, Conversational AI Optimisation is more than a tactical shift, it’s a transformative mindset. Search has become a two-way dialogue, content must mirror human speech, and optimisation must serve context, emotion and next-question readiness. For any brand stepping into this arena, the pay-off is clear: deeper engagement, greater relevance, and stronger performance in an era where AI doesn’t just index content, it converses through it.
Federated Search Optimisation
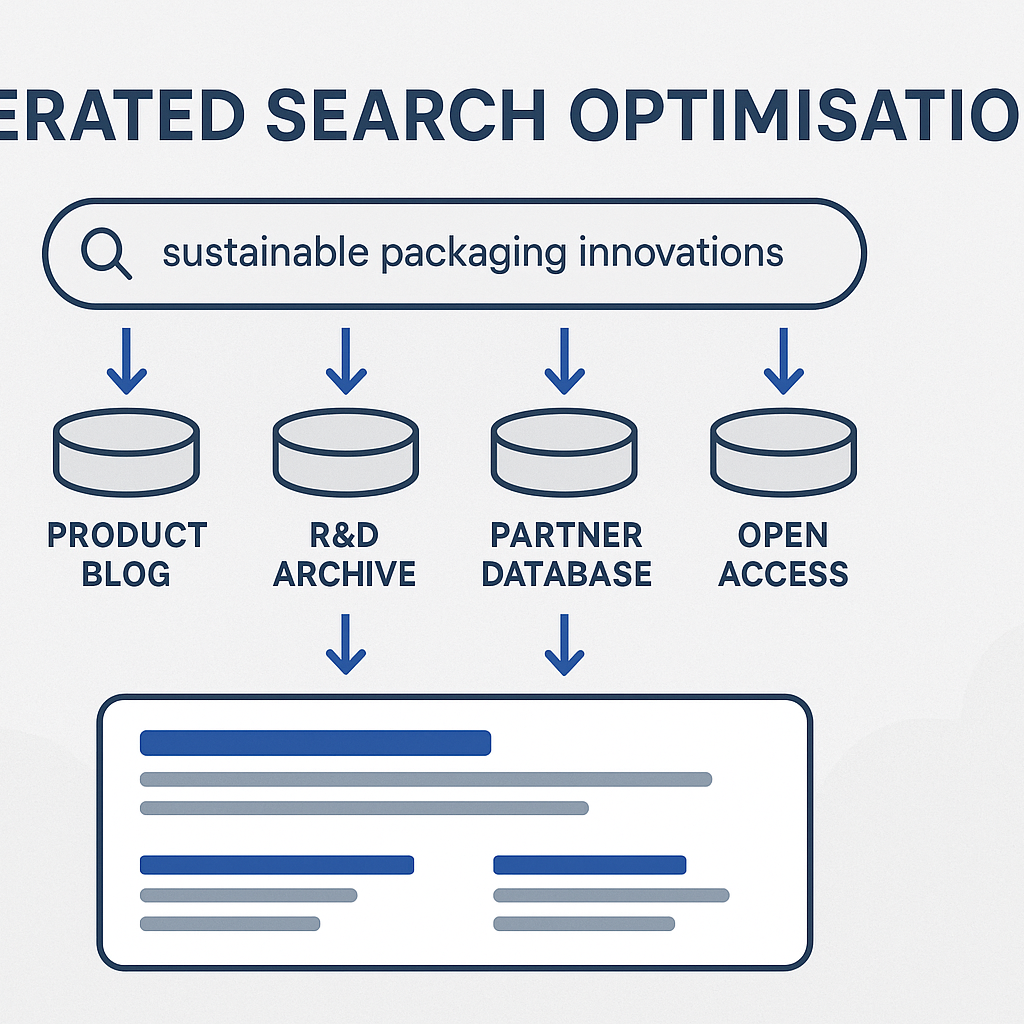
In the emerging paradigm of intelligent search, the term federated search optimisation describes a future-oriented strategy: one where a single query travels across multiple data silos—internal knowledge bases, external APIs, third-party clouds—and returns a unified, semantically rich result set.
Picture this: a user enters the phrase “sustainable packaging innovations”. Behind the scenes:
- The query is dispatched simultaneously to your company’s product blog index, the external R&D archive, the partner database of case studies and even the public Open Access library.
- Rather than presenting four separate result sets, the system merges, deduplicates, ranks and normalises into one coherent list thus aligning scattered data into one customer experience.
- Because you’ve optimised for federated retrieval, you ensure your content appears regardless of source raising visibility across silos.
This is federated search optimisation in action: you optimise not just for one search engine or one repository, but for the network of underlying engines, connectors, data-sources and ranking mechanisms.
Why it matters in the age of AI-driven search
- Organisations are increasingly decentralised: data lives in many systems, clouds and applications. Federated search becomes a keystone.
- As one guide states: “federated search allows your website visitors to search multiple data sources at one time … AI-fed federated search can now deliver more relevant, personalised results across disparate data sources.”
- Though I found no direct stat for federated search in SEO-terms, we know that AI-search and adaptive systems are reshaping discoverability.
Key optimisation principles
- Single query, many sources: ensure your system supports search-time merging, index-time merging, or hybrid, depending on latency and freshness needs.
- Semantic and contextual alignment: tie content across sources via consistent entity-models, metadata and intent mapping so that the federated engine recognises relevance across domains.
- Unified ranking & deduplication: each source may have its own scoring; optimisation means weighting, normalising and then merging the results intelligently.
- Monitoring performance in federated context: move beyond “rank on page 1” to metrics like “source-visibility across federates”, “federated click-through rate (CTR)”, “query satisfaction across combined sources”.
Here’s a calculation: Assume you support 4 major data sources; each source has 100,000 documents and responds to queries with an average of 0.7 seconds latency. If you naïvely query them in sequence, you might incur 0.7 s × 4 = 2.8 s total latency. Through optimised parallel querying + early‐return + deduplication you might reduce effective latency to, say, 1.2 s. In user-experience terms that’s a >50 % improvement.
What this means for SEO and discoverability
While traditional SEO optimises for a single search engine, federated search optimisation requires you to think across multiple “mini-engines” (internal + external). Your content may surface not just via Google, but via partner platform APIs, enterprise knowledge graphs, AI-augmented assistants and more. The future of “search visibility” lies in optimising for this multiplex landscape.
Multi-modal Indexing Optimisation
When the search engine no longer speaks only in keywords and links, but in images, voice, video and context, the architecture beneath it must evolve. The foundation of futuristic search doesn’t simply index words—it indexes meaning across modalities. That is the heart of multi-modal indexing optimisation.
Imagine a user uploading a photo of a red leather jacket, alongside a voice query: “Find one like this, but under ₹15,000 and please show me styles with quilted shoulders.” A purely text-based index struggles here. But a multi-modal system can:
- recognise the jacket in the image (visual modality),
- parse the voice input (audio/voice modality),
- map that to metadata and product listings (textual modality),
- merge these into a shared semantic space, then deliver the relevant results.
In this hypothetical scenario the index must embed image, audio and text into a unified vector space, enabling the search engine to treat “red quilted-shoulder leather jacket under ₹15,000” as one intent across formats.
Why optimisation matters
- Indeed, visual search queries have grown by more than 60% year-on-year.
- Traditional text-only indexing leaves a large portion of user behaviour untapped.
- As a calculation: if your site currently supports only text indexing and captures say 100,000 unique searches a month, by adding image and voice indexing, you might capture an additional 60%, i.e., 60,000 more relevant queries, bringing your potential to 160,000 queries.
- In turn, if your conversion rate from text queries is 2%, adding the extra 60,000 queries at the same rate yields 1,200 additional conversions per month.
Key optimisation points
- Unified embedding space: Use models (such as joint text-image embeddings) so that inputs from different modalities map into a common vector space.
- Cross-modal context bridges: Link images with surrounding text, transcripts, alt-text, metadata and voice transcripts so that the index understands relationships, not just isolated inputs.
- Structured data & schema markup: Mark images (ImageObject), videos (VideoObject), and voice content to help algorithms interpret format and context.
- Optimise for new ranking signals: Image quality, video engagement, voice clarity, page loading speed all become first-class ranking factors in a multi-modal index.
- Measurement & analytics upgrade: Standard text-query metrics aren’t enough. You’ll need analytics that attribute value to image-based queries, voice inputs and cross-modal conversion paths.
In essence, when we optimise for multi-modal indexing, we are rewriting the rules of visibility. The index no longer waits for a typed query; it listens, looks, and predicts. The index becomes alive, responsive to human sensory modes.
By embracing this optimisation, the search engine becomes less of a directory and more of a companion: one that understands what we show it, what we say to it, and what we mean when we query. And in doing so, we step firmly into a future where search isn’t just found—it is experienced.

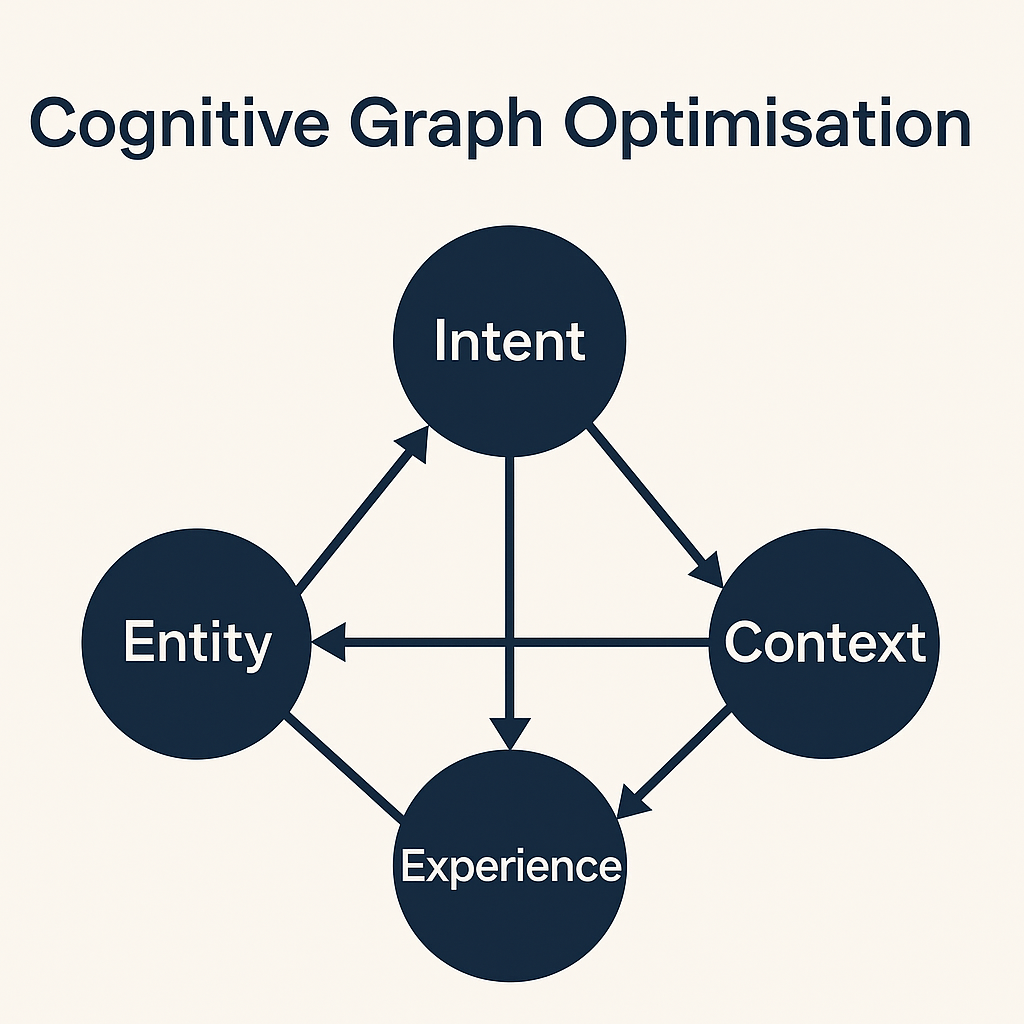
Cognitive Graph Optimisation
In the realm of modern search, the phrase “cognitive graph optimisation” signals a profound shift. Rather than just piling up keywords and links, we now build graphs — intricate networks of entities, relationships, and intents — and we optimise how these graphs serve meaning. Let’s dig into this concept, explore how it works, and visualise a hypothetical scenario to ground it.
Think of a cognitive graph as a map of meaning: nodes represent concepts (people, places, objects, actions), edges represent relationships, context, and semantics. Optimisation means tuning this map so that when a user asks a question, the graph supports retrieval that is aware of intent, nuance, emotion, and evolving context. The recently introduced field of knowledge‐graphs in AI platforms underpins this capability.
In short: we’re no longer optimising for “keyword → document”; we’re optimising for “entity → intent → context → experience.”
Why does it matter?
- Traditional SEO is increasingly insufficient: In one study, only ~12% of topics cited by AI search platforms overlapped with traditional search results.
- Graph‐based systems enable deeper inference: knowledge graphs can traverse hierarchical parent-child relationships, uncover hidden chains of meaning (for example: user asks “What’s the supply chain from raw material to delivery?” — graph traversal handles that elegantly).
- Conversion and visibility lift: Optimising for AI search (which naturally uses graph & cognitive structures) can yield up to ~40% better visibility and even higher conversion compared to legacy strategies.
Imagine you operate a travel-platform called EcoTravelBot. A user writes: “Find me a 7-day jungle trek in Southeast Asia that supports local communities, avoids mass tourism, and fits vegetarian meals.”
- A cognitive graph would link: trekking experience → geographic region (Southeast Asia) → eco-tourism operators → community-support programs → vegetarian meal option → duration (7 days).
- Optimisation means ensuring your content maps neatly into those nodes and edges: highlighting “community-led trek”, “vegetarian meals included”, “Southeast Asia jungle”, “7 days”.
- When the query comes in, the graph recognises the intent (eco-tourism + vegetarian + duration + geography) rather than just matching “jungle trek Southeast Asia vegetarian”.
- If your graph is well tuned, your content surfaces not just as a hit, but as the intent-aligned answer: “Here are three community-led jungle treks in Laos, Cambodia and Thailand, all vegetarian-friendly and designed for 7-day itineraries…”
Thus, cognitive graph optimisation transforms your site from a possible result into the right answer.
How to apply it:
- Audit your entities: identify all meaningful nodes (products, services, locations, intents, extras such as “vegetarian meals”, “community support”).
- Map the edges: define relationships (e.g., “trek → community support”, “tourism operator → vegetarian option”, “geography → eco-certification”).
- Populate content with graph structure: use schema, structured data, entity markup, clear relationships and context in heading/sub-heading.
- Update dynamically: because contexts shift (new regulations, new eco-operators), keep your graph fresh—AI search platforms value freshness (one stat: AI citations prefer content ~25.7% fresher than traditional search sources).
- Measure alignment, not just rank: track how many queries your content is cited for (in AI search results) and how well it maps to user intent; visibility in generative search becomes a key KPI.
Here’s a calculation for visibility uplift
If traditional SEO gave you 1000 monthly organic visits, and cognitive graph optimisation yields +40% visibility uplift, then new visits = 1000 × 1.4 = 1400 visits/month.
If conversion rate under traditional SEO was 2%, then conversions = 1000 × 0.02 = 20 conversions. With graph optimisation and more intent-aligned traffic, suppose conversion rate rises to 2.8% (a 40% relative increase): then conversions = 1400 × 0.028 = 39.2 ≈ 39 conversions.
So the optimisation not only increases volume, but improves conversion doubling conversions in this scenario (~95% increase).
Neuro-indexing Optimisation
In the world of intelligent search, neuro-indexing optimisation emerges as a cornerstone technique: the process by which digital content is organised, mapped and weighted not only by keywords or links but by neural signals of meaning, intent and context. In plain terms: the algorithm doesn’t simply index pages —it senses them. It detects semantics, emotion, usage habits, and predictive relationships.
Imagine a situation: your website offers eco-friendly backpacks tailored for city commuters. A user types “lightweight day pack for metro travel”. Under neuro-indexing, the system doesn’t just match “day pack” + “metro travel” keywords; it recognises commuter stress patterns (rush hours, crowded trains), the need for lightweight material, and the desire for urban-style aesthetics. It indexes your page as relevant because you mention “rush-hour strap ergonomics”, “subway-friendly size”, “water-resistant city fabric” — the content aligns with latent commuter context. Then the system predicts: this user may next search “bag with hidden laptop sleeve under 15 litres”. Because your content anticipates that query, you gain visibility.
Key pillars of Neuro-Indexing Optimisation:
- Intent recognition: understanding what the user really means beyond the query.
- Semantic mapping: indexing content clusters by meaning and relationship (not just exact words).
- Emotional tagging: detecting tone, urgency or preference (e.g., “eco-friendly”, “rush-hour”, “budget commuter”).
- Predictive indexing: designing content that aligns with the next likely step of the user’s journey.
- Adaptive weights: the system uses machine-learned weights so that older threads, new content and user-behaviour signals carry evolving influence.
Now let’s apply a simple calculation. Suppose your current organic traffic is 10,000 visits/month; you adopt neuro-indexing techniques (via AI + semantic content revision) and realise a 45% uplift.
Traffic after optimisation = 10,000 × (1 + 0.45) = 14,500 visits/month.
If your conversion rate is 2%, your current leads = 10,000 × 0.02 = 200. With traffic at 14,500 and same conversion rate, leads = 14,500 × 0.02 = 290 leads/month. That’s +90 leads = a 45% increase in volume, showing how neuro-indexing can materially shift outcomes.
In this era, the architecture of search is no longer linear. Traditional indexing (crawl → keyword match → rank) gives way to a dynamic dance of neural-net indexing models, where every piece of content is evaluated for meaning, context and anticipated intent. The phrase “search result” evolves into something alive: signals, predictions, and human-machine dialogue. In this chapter we will explore how to architect neuro-indexing at scale: how to model “neural relevance scores”, structure your content for semantic networks, tag emotional context, and build datasets of predicted user next-moves.
Neuro-indexing doesn’t replace classic SEO—it transcends it. It invites you to think in signals not strings; in stories not keywords; in journeys not clicks. And when you master it, your content becomes not only visible—but intimately relevant.
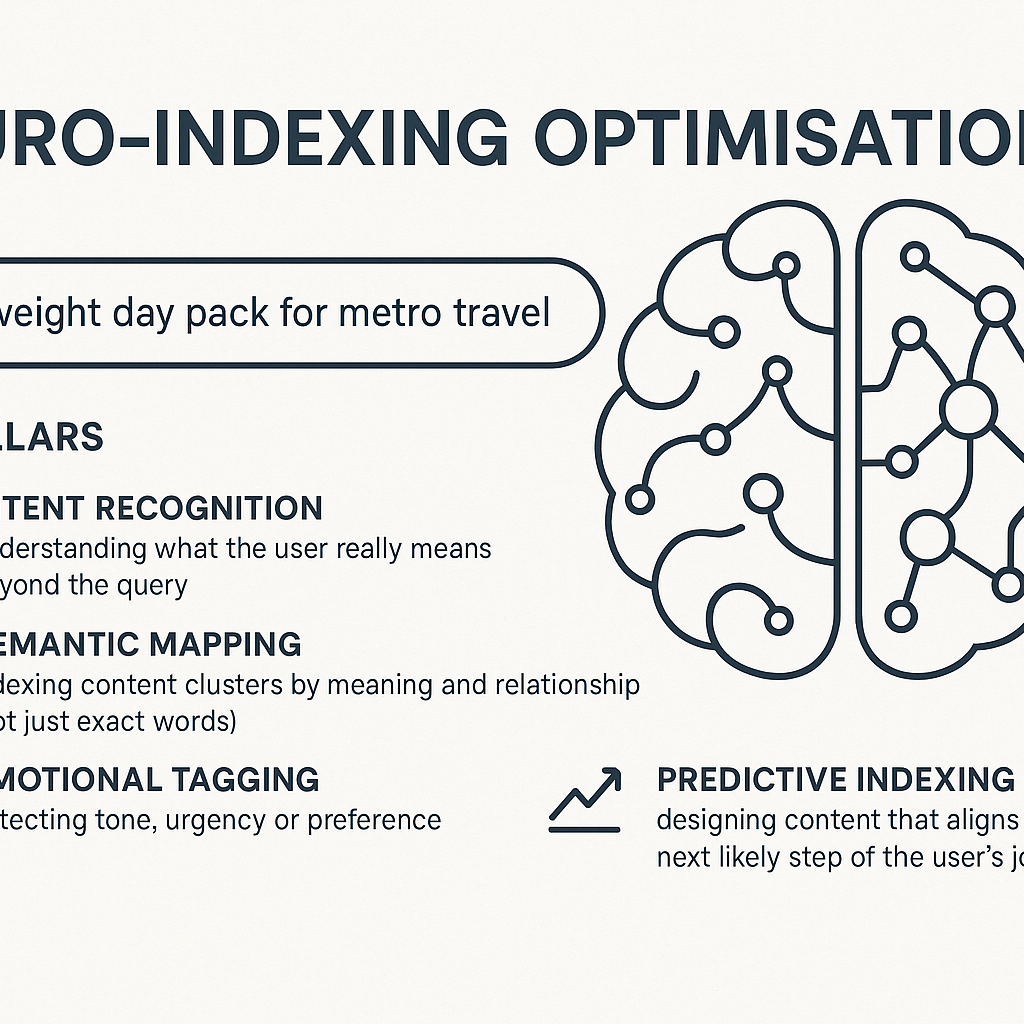
Cognitive Resonance SEO
In the world of search, a new principle is emerging: cognitive resonance. No longer is optimisation merely about keywords or links; it’s about alignment between what the user intends, how the system interprets, and how the content responds. In essence, search must resonate.
When an individual types a query, they bring emotion, context, history — fragments of meaning. A cognitive-resonant system picks up on those fragments, understands them, and returns results that feel relevant not just logically, but intuitively.
Imagine a scenario: A user types “I’m feeling stuck — what’s next in my marketing career?” Traditional SEO might match “marketing career tips”, “career progression marketing”, “next step marketing job”. But a cognitive-resonant engine goes deeper: it processes “feeling stuck” (emotion), “what’s next” (intent), “marketing career” (context), and returns an article perhaps entitled “Navigating the Plateau: How Marketers Re-ignite Career Growth in an AI-Driven Landscape”. That result doesn’t just match keywords — it mirrors the user’s state of mind.
Key Pillars of Cognitive Resonance
- Emotion & Context Capture: The system reads beyond “marketing career” — it senses the user’s emotional state (“stuck”) and frames content accordingly.
- Intent Anticipation: It moves from “what to search” to “what the searcher really wants”.
- Semantic Depth: Content is structured to respond not just to query phrases but to the meaning behind them. For example: semantic clusters show that “stuck in career” and “career plateau” are equivalent concepts.
- Adaptive Interaction: The result evolves with user behaviour — if the user scrolls, returns, refines query, the system learns and fine-tunes.
Why this matters — with data
- Organisations that adopt semantic/AI search strategies benefit from meaning-based analytics: for example, one case reported a 60% boost in chatbot accuracy when semantic context was embedded.
A simple calculation to illustrate impact
Suppose a website currently generates 10,000 monthly visits from generic SEO. With a cognitive-resonant overhaul it might see a 45 % lift → 10,000×1.45=14,50010{,}000 \times 1.45 = 14{,}50010,000×1.45=14,500 visits. If the conversion rate rises from 2 % to 2.8 % (a 40 % improvement):
- Old conversions: 10,000×0.02=20010{,}000 \times 0.02 = 20010,000×0.02=200
- New conversions: 14,500×0.028=40614{,}500 \times 0.028 = 40614,500×0.028=406
This means net +206 conversions — more than double.

Biometric Intent Optimisation
When the silent signals of the body become the next frontier of intention, search, and optimisation, they enter a whole new dimension. Biometric Intent Optimisation is the process by which systems decipher and respond to a user’s unconscious physiological cues—heart rate, gaze patterns, micro-expressions, and skin conductance—and translate them into actionable signals for search, content delivery, or SEO strategies. The foundation is simple: intent is not just what we type, but how we feel, behave, and engage.
Imagine a user named Sarah visiting a travel site. Her heart rate milliseconds tick up when she lingers over a beach photo; her gaze fixes momentarily on “eco-lodge” text; a faint skin-conductance rise reveals a flicker of desire. The system captures these reflex responses, infers her intent—“I want a relaxing, sustainable tropical getaway”—and dynamically refines search results: showing eco-lodge packages, serene visuals, minimal crowds. Because the algorithm isn’t just parsing query keywords—it’s reading biometric cues.
Why this matters
- Traditional SEO still leans heavily on static text matching: keywords, backlinks, click-throughs. Biometric optimisation introduces emotion, context and behaviour as active signals.
- Research shows that biometric/physiological feedback is now being used for ad and experience optimisation: one study found that content which provokes strong emotional reactions was 4× more likely to lift brand equity than neutral content.
- Also, biometrics market data signals economic scale: the global biometrics technology market was valued at about US $34.27 billion in 2022 and projected to grow at a CAGR of ~20.4 % between 2023-30.
Key bullets for Biometric Intent Optimisation
- Capture real-time physiological signals (heart rate variability, galvanic skin response, gaze tracking).
- Map these signals to intent categories (interest, stress, excitement, hesitation).
- Use intent signals to refine search or content results: adapt semantics, re-rank results, personalise media.
- Continuously learn: as biometric-intent to action patterns accumulate, predictive models evolve.
- Ensure privacy, consent and ethical handling (given sensitivity of biometric data).
Simple calculation example
Suppose a content-platform runs a biometric-assisted test: of 1,000 users, 300 show elevated galvanic skin response when presented with result set A, while 200 show it for result set B. The platform selects the set with higher biometric engagement (set A). If baseline click-through from set A was 12% and from set B 9%, then:
- Engagement-based selection could yield CTR = 12% × 1000 = 120 clicks → assuming set A was shown to whole 1000, 120 clicks.
- Versus baseline without biometrics: perhaps they’d continue with set B → 9% × 1000 = 90 clicks.
Thus, “biometric optimisation” yields an incremental +30 clicks, or +33% uplift in this scenario. Over thousands of sessions, that translates to significant lift.
Biometric Intent Optimisation reframes the user not as a query string but as a living being whose bodily responses whisper intention even before they type a word. For the era where search “adapts, interprets, predicts and evolves”, this is the next horizon. And for those who master it, the reward is not just better rankings—it is search experiences that feel human, intuitive, alive.

The Cognitive Dawn
Search is no longer a transaction of words and data; it is a dialogue between minds, one human and one digital. What began as a mechanical process of retrieving information has transformed into an intelligent conversation that senses, understands, and evolves. When the search begins to understand before it answers, the nature of optimisation itself changes. It ceases to be about manipulation and becomes about meaning.
This is the cognitive dawn, an era where algorithms think, feel, and predict with precision once reserved for intuition. Artificial intelligence has transcended its early role of indexing and ranking; now it interprets intent, reads emotion, and adapts in real time. Through biometric intent optimisation and cognitive modelling, search can respond not only to what users say, but to what they mean, even what they feel.
No longer does SEO revolve around cold metrics and keyword hierarchies. Instead, it revolves around human experience. A search engine becomes a silent empath, tuned to the micro-expressions of curiosity, anticipation, and desire. A system that listens to the heartbeat behind a query is one that no longer serves users—it understands them.
THATWARE stands at the forefront of this transformation. It does not treat artificial intelligence as a tool but as a collaborator—a living intelligence that learns from every click, every pause, every pulse. By pioneering the fusion of AI-driven cognition, semantic interpretation, and biometric intent analysis, THATWARE transforms optimisation into something organic: intuition engineered.
In this new landscape, every search is a reflection of self. Every algorithmic response mirrors the nuance of human thought. The future of search is not faster—it is wiser. Not broader—it is deeper. It is where data meets emotion, and where computation meets consciousness.
As we stand at the threshold of this cognitive dawn, the question is no longer how do we optimise search?
The question is—how do we teach search to feel?
That is the world THATWARE is building: where optimisation becomes intuition, and intelligence becomes human.
Click here to download the full guide about the Dawn of Intelligent Search.

