SUPERCHARGE YOUR ONLINE VISIBILITY! CONTACT US AND LET’S ACHIEVE EXCELLENCE TOGETHER!
Why Agentic SEO Is Suddenly Everywhere
If you’ve been anywhere near marketing Twitter/X, LinkedIn, SEO newsletters, or AI product launches lately, you’ve probably seen the term “Agentic SEO” pop up—often alongside bold claims like “SEO is automated now” or “AI agents will replace SEO teams.” The truth is more nuanced, but one thing is clear: Agentic SEO is a real shift in how search optimization is executed, and it’s becoming a serious conversation because it responds to a very real problem marketers are facing today—SEO has become too complex and too fast-moving to manage with purely manual workflows.

To understand why Agentic SEO or Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) is suddenly everywhere, we need to look at what SEO used to be, what it became, and what it’s turning into now.
The Evolution of SEO: From Manual to Autonomous
SEO didn’t start as a sophisticated discipline. For many marketers, it began as a checklist: add keywords to titles, write a meta description, build a few links, and wait for rankings to move. Over time, SEO evolved—both because search engines became smarter and because the web became more competitive.
A simple way to think about SEO’s evolution is this:
Manual SEO → Rule-based automation → AI-assisted SEO → Agentic SEO
Manual SEO was exactly what it sounds like: humans doing nearly everything by hand. Keyword research, competitor analysis, writing content briefs, optimizing pages, tracking rankings, fixing technical issues—most of it was manual, repetitive, and time-heavy. It worked when the web was smaller and rankings changed more slowly.
Then came rule-based automation, where tools helped speed up repetitive tasks. Think: automated site crawls, backlink alerts, rank trackers, and templated reports. But these tools weren’t “thinking.” They were executing predefined rules and presenting outputs for humans to interpret. The work still depended heavily on human decision-making and follow-through.
Next, we entered the era of AI-assisted SEO, which most marketers are already familiar with. AI tools started helping with content outlines, rewriting, title variations, cluster suggestions, FAQ generation, schema, summaries, and more. The difference here is important: AI-assisted SEO still requires the marketer to drive the process—the AI helps, but the human remains the planner, strategist, and executor.
Now we’re seeing the rise of Agentic SEO, where AI doesn’t just assist—it begins to operate more like an autonomous teammate. Instead of you asking AI for an outline or keyword list, an agentic system can identify a goal (e.g., “increase organic leads for product X”), analyze the gap (keywords, pages, competitors), propose a plan, execute steps (draft updates, internal links, structured data suggestions), and monitor performance—often repeating the cycle continuously.
This is why “doing SEO” is no longer enough in 2026. Traditional SEO assumes the marketer can:
- run audits periodically
- prioritize fixes manually
- update content on a schedule
- react when rankings drop
- stay ahead of competitors with limited bandwidth
But modern search doesn’t wait for quarterly audits or weekly reporting cycles. SERPs change faster, competitors publish more, and search engines interpret intent more intelligently than ever. In many industries, SEO has shifted from a one-time optimization activity to a continuous optimization system. And that’s exactly where Agentic SEO fits in.
Why Marketers Are Talking About Agentic SEO Now
Agentic SEO didn’t appear out of nowhere—it’s the result of three forces colliding at the same time.
1) The rise of LLMs, AI agents, and autonomous workflows
Large language models (LLMs) made it possible to generate, summarize, classify, and rewrite content at scale. But the bigger jump is happening now: systems aren’t just generating text—they’re becoming agents that can plan tasks, use tools, make decisions, and iterate. In marketing terms, this means AI can move from “content helper” to “workflow operator.”
2) Google’s increasing complexity: EEAT, intent, and helpful content expectations
Modern SEO isn’t just about keywords. It’s about usefulness, credibility, structure, and intent match. Google is better at detecting whether a page actually satisfies a query and whether the brand or author seems trustworthy. That makes SEO less about tricks and more about producing consistent, high-quality, user-first outputs across dozens or hundreds of pages—something that’s hard to maintain manually.
3) The explosion of content and shrinking human bandwidth
This is the part every marketer feels. Content volume is exploding—your competitors publish more, platforms multiply, and expectations rise. Meanwhile, teams aren’t scaling at the same pace. One SEO manager can’t manually refresh 200 blog posts, optimize every landing page, manage technical SEO, run experiments, and monitor SERP shifts all at once. Even agencies struggle to keep pace with “always-on” SEO across multiple clients.
Agentic SEO or Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) is being discussed now because it promises a solution to the bandwidth problem: continuous SEO work without continuous human labor. Not “set and forget,” but “set direction and supervise”—which is a major difference.
Who This Guide Is For
This guide is written for marketers who want to understand Agentic SEO without needing a computer science degree or getting lost in hype.
It’s for:
- SEO beginners who want to understand what “agentic” means and why it matters
- Content marketers trying to scale quality content and updates without burning out
- Growth marketers looking for repeatable systems that compound organic traffic
- Agency owners who need to deliver better outcomes with leaner operations
- Founders and in-house teams who want predictable organic growth but don’t have big SEO headcount
If you’ve ever felt like SEO is becoming too much to manage manually, you’re exactly the person who should understand what Agentic SEO is and what it changes.
Because whether you adopt it immediately or not, Agentic SEO represents a new operating model: SEO as a continuous loop of analysis → decision → execution → learning, rather than a set of tasks you occasionally complete.
What Is Agentic SEO?
Agentic SEO is one of those terms that sounds complex at first but becomes surprisingly intuitive once you break it down. At its core, it represents a shift in how SEO work is done—from humans and tools executing tasks manually to AI agents that can think, decide, and act on their own within defined boundaries.

To understand Agentic SEO properly, we first need to understand what the word “agentic” actually means.
Simple Definition of Agentic SEO
The term agentic comes from agency—the ability to act independently to achieve a goal. In AI systems, an agent is not just responding to instructions but actively working toward an objective by making decisions, using tools, and learning from outcomes.
In SEO, this means the system is no longer limited to following predefined rules or waiting for human input at every step. Instead, it can:
- Analyze data on its own
- Decide what actions matter most
- Execute SEO tasks autonomously
- Evaluate results and adjust future actions
A simple one-line definition for beginners would be:
Agentic SEO is a form of search optimization where AI agents independently analyze, decide, execute, and improve SEO actions based on predefined goals.
Unlike traditional SEO tools that assist humans, agentic SEO systems behave more like proactive team members. You define the goal—such as improving rankings, increasing organic traffic, or fixing technical issues—and the agent figures out how to get there.
Agentic SEO vs AI SEO
A common point of confusion is the difference between AI-powered SEO and Agentic SEO. While both use artificial intelligence, they operate at very different levels.
AI SEO tools typically act as assistants. They help humans by:
- Suggesting keywords
- Generating content drafts
- Highlighting SEO issues
- Recommending optimizations
However, the human still makes the decisions and performs or approves most actions.
Agentic SEO, on the other hand, treats AI as an agent, not an assistant. The agent:
- Chooses which SEO tasks to prioritize
- Decides when and how to execute changes
- Uses multiple tools without manual prompting
- Operates in continuous optimization loops
Another key difference is decision-making.
- In AI SEO, humans decide what to do.
- In Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO), humans define goals and guardrails, while the agent decides how to achieve them.
This also changes the role of humans:
- AI SEO: Human-in-the-loop (constant supervision)
- Agentic SEO: Human-on-the-loop (strategic oversight)
Instead of managing tasks, marketers manage strategy, quality, and risk.
What Makes SEO “Agentic”?
Not every AI-powered SEO system qualifies as agentic. What truly makes SEO “agentic” is a combination of four core characteristics:
Goal-oriented behavior
Agentic SEO systems are driven by objectives, not instructions. They work toward outcomes like ranking improvements, traffic growth, or crawl efficiency rather than executing isolated tasks.
Continuous feedback loops
An agent doesn’t act once and stop. It monitors results, evaluates performance, and feeds that data back into future decisions—creating an ongoing optimization cycle.
Tool usage and orchestration
Agentic systems can use multiple tools together, such as crawlers, analytics platforms, content editors, and CMSs, without human intervention. They decide which tool to use and when.
Self-improvement over time
As the system observes what works and what doesn’t, it refines its decision-making. This allows it to improve accuracy, prioritization, and effectiveness with continued use.
Together, these traits transform SEO from a series of manual actions into an autonomous, adaptive system—one that can operate at a scale and speed impossible for humans alone.
Understanding Agentic AI
Before we talk about Agentic SEO, it’s important to understand the technology behind it: agentic AI. Don’t worry—this isn’t a technical deep dive. Think of this as a marketer’s explanation of how AI agents actually work and why they’re different from the AI tools you already use.
What Is an AI Agent?
Most marketers are familiar with AI chatbots like ChatGPT or other content tools. These tools respond when you ask a question, write a paragraph, or request an idea. Once the response is delivered, the job is done.
An AI agent, however, works very differently.
An AI agent is a system designed to work toward a goal on its own, not just respond to prompts. Instead of waiting for instructions, it can decide what to do next based on the goal you’ve given it—such as improving organic traffic or fixing SEO issues.
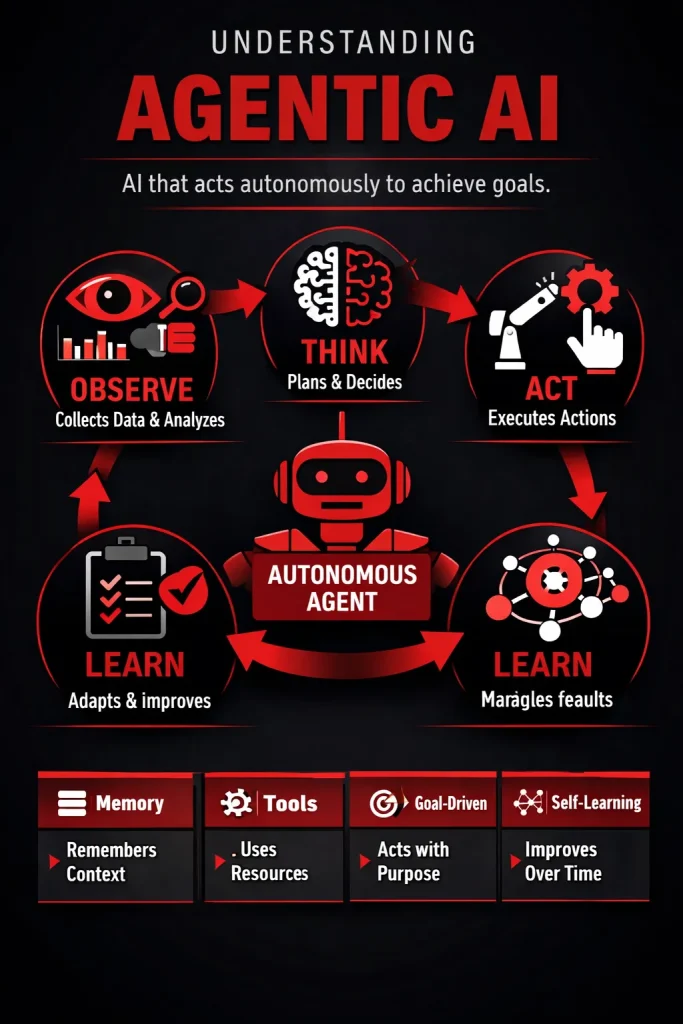
What makes an AI agent “agentic” comes down to four key abilities:
- Autonomy: It can act without constant human input.
- Memory: It remembers past actions, results, and context.
- Tools: It can use software tools like analytics platforms, crawlers, or content editors.
- Planning: It can break big goals into smaller tasks and prioritize them.
In simple terms, a chatbot answers questions. An AI agent does the work.
How Agentic AI Works (Step-by-Step)
Agentic AI follows a continuous loop that looks like this:
Observe → Think → Act → Learn
First, the agent observes data. In SEO, this could be search rankings, traffic drops, crawl errors, or competitor movements.
Next, it thinks. The agent analyzes what the data means. For example, it might detect that a page lost rankings because search intent has changed or competitors updated their content.
Then, it acts. The agent may update on-page content, adjust internal links, or recommend technical fixes—sometimes automatically, sometimes with human approval.
Finally, it learns. The agent monitors the results of its actions. If rankings improve, it reinforces that strategy. If not, it adjusts its approach.
A helpful analogy is to think of an AI agent as a junior SEO executive who works 24/7. It monitors performance constantly, takes initiative, learns from mistakes, and improves over time—without getting tired or distracted.
Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent Systems
Some agentic SEO systems rely on a single agent that handles everything. More advanced setups use multiple specialized agents, each focused on a specific SEO task.
Common types of SEO agents include:
- Keyword Agent: Discovers keyword opportunities, tracks trends, and identifies gaps.
- Content Agent: Optimizes existing pages, suggests updates, and aligns content with search intent.
- Technical SEO Agent: Monitors site health, crawlability, indexing issues, and performance metrics.
- Link Analysis Agent: Evaluates internal and external links, detects broken links, and improves authority flow.
These agents can work independently or collaborate with each other, much like a real SEO team—only faster and more scalable.
Understanding this agent-based structure is key to grasping why Agentic SEO is fundamentally different from traditional AI-powered SEO tools. It’s not just about automation—it’s about intelligent, goal-driven execution.
How Agentic SEO Works in Practice
Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) isn’t just “SEO with AI.” It’s a different operating model. Traditional SEO is largely batch-based: you audit, plan, publish, and revisit on a schedule (weekly, monthly, quarterly). Agentic SEO is loop-based: an AI agent (or a team of agents) continuously observes your site + the SERPs, makes decisions against a goal, executes changes through tools, and then learns from results. To understand what changes in the real world, it helps to compare the “before” workflow with the “after” workflow.

Traditional SEO Workflow (Before Agentic SEO)
In most teams, classic SEO follows a predictable rhythm. It works — but it’s slow, manual, and heavily dependent on human time.
Manual audits
A traditional audit is usually performed periodically (monthly or quarterly). An SEO specialist runs a crawler, exports reports, checks indexation issues, reviews Core Web Vitals, identifies broken links, and flags technical problems. The insights are valuable, but the process is time-intensive. By the time an issue is discovered, prioritized, assigned to devs, and fixed, the site may have already lost weeks of performance.
Manual keyword research
Keyword research is also a human-led workflow: gather seed keywords, use SEO tools to find volumes and variations, assess intent, check competition, build clusters, and map keywords to pages. It’s effective but time-consuming — and it’s usually done as a campaign activity, not continuously. That means you might miss emerging queries or intent shifts until after competitors capitalize on them.
Static content publishing
Most content calendars are planned and executed like publishing pipelines: write, edit, publish, promote. Once an article goes live, it often stays mostly unchanged. Updates happen only when traffic drops or when the team has capacity. This creates a common problem: your highest-traffic pages can quietly become outdated, while the team is busy creating new pages.
Periodic optimization
Traditional optimization is typically reactive and scheduled: refresh content every few months, optimize metadata when rankings slip, update internal links occasionally, and run link-building sprints. The team is always choosing what to optimize based on limited bandwidth. As a result, many “small but important” improvements never happen because they’re not urgent enough to make the list.
In short: traditional SEO depends on smart people, but it runs in bursts. It’s not always-on.
Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) Workflow (After)
Agentic SEO shifts SEO from a calendar-driven workflow to a continuous improvement system. Instead of a marketer repeatedly telling tools what to do, agents use tools themselves under defined constraints.
Continuous crawling
An agentic system doesn’t wait for a quarterly audit. It can crawl key sections of your site continuously or on a frequent cadence, watching for changes and issues as they happen: new broken links, pages that accidentally noindexed, sudden drops in internal links, thin content, cannibalization signals, schema errors, template problems, and more. Think of it as an “always-on site health monitor,” but with the ability to act.
Real-time SERP analysis
Instead of checking rankings once a week and reacting late, agents can monitor SERP changes continuously: new competitors entering, shifts in featured snippets, changes in People Also Ask questions, intent drift (informational → commercial), or a new pattern in the top results. This matters because SEO often moves gradually — and catching changes early can be the difference between maintaining a top position and losing it for months.
Autonomous decisions
This is where “agentic” becomes real. The system isn’t only gathering data; it’s deciding what to do next based on a goal. For example:
- “Increase non-brand organic signups by improving top-of-funnel pages.”
- “Recover rankings for product category pages without changing tone.”
- “Improve click-through rate for pages ranking 3–8.”
The agent prioritizes actions (what’s most likely to move the metric), chooses tactics (update content vs adjust internal links vs rewrite title), and plans a set of steps — much like a junior SEO would, but faster and more consistently.
Automatic execution
Agentic SEO systems can execute changes through integrations: updating briefs, creating optimization recommendations, generating rewrite drafts, proposing internal links, updating metadata, creating schema markup suggestions, or pushing changes directly into a CMS (depending on permissions and guardrails). The point is not “auto-publish everything,” but “reduce the friction between insight and action.”
In short: agentic SEO turns SEO into a closed-loop system: observe → decide → act → measure → repeat.
A Day in the Life of an Agentic SEO System
Here’s a simple example to make it tangible.
It finds a ranking drop
An agent monitors rankings and traffic for priority pages. It detects that a page that used to rank #2 for a high-intent keyword is now hovering around #6, and organic clicks have dropped week-over-week.
It diagnoses the cause
The agent checks signals like:
- Did the page change recently (content, template, metadata)?
- Did competitors update their pages?
- Did SERP intent shift (e.g., more “how-to” results replaced “best” lists)?
- Are there technical issues (indexing, canonicals, speed regressions)?
- Is the snippet less competitive (title/description mismatch with current intent)?
Rather than guessing, it forms a hypothesis:
“Competitors now answer comparison questions earlier, include updated stats, and use clearer headings. Also, the SERP shows more ‘pricing’ modifiers.”
It updates content
Based on the diagnosis, the agent proposes a set of actions:
- Add a short “quick comparison” section near the top
- Refresh outdated examples and include a new section answering emerging questions
- Improve headings to match how Google is interpreting intent
- Suggest internal links from related pages to strengthen topical authority
- Rewrite the title to improve CTR without clickbait
Depending on your setup, it may produce a draft for approval or push updates automatically to a staging environment.
It monitors recovery
After publishing (or after approval), it tracks changes:
- CTR changes in Search Console
- Position shifts
- Engagement signals (time on page, scroll depth)
- Whether the snippet or SERP features changed
If recovery doesn’t happen, it loops: adjust hypothesis → test next change.
That’s the key difference: it’s not “optimize once.” It’s optimize until outcomes improve.
Human Role in Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO)
Even with autonomous agents, humans don’t disappear — they move up the ladder from execution to supervision and strategy.
Goal-setting
Humans define what “success” means. Agents need clear objectives: traffic growth is vague; “increase qualified leads from non-brand queries in cluster X” is actionable. The better the goal, the better the agent’s decisions.
Guardrails
Guardrails are non-negotiable. Humans set boundaries such as:
- Brand voice requirements (tone, banned phrases, reading level)
- Compliance rules (regulated industries, claims, disclaimers)
- Risk levels (which pages agents can edit automatically vs only suggest)
- SEO constraints (no keyword stuffing, no manipulative link schemes)
This ensures the agent optimizes like your brand, not like a generic bot.
Validation
Humans review the agent’s work where it matters most: money pages, sensitive topics, legal claims, PR-sensitive messaging, and major structural changes. Many teams use a tiered approach:
- Low-risk updates → auto-approved
- Medium-risk updates → human review
- High-risk changes → strategist approval + QA
Strategic oversight
Humans remain responsible for the big decisions:
- Which markets to target
- What positioning to own
- What content to create that competitors can’t easily replicate
- What trade-offs to make (traffic vs conversion vs brand perception)
Agentic SEO is strongest when humans treat agents like a high-output team member: powerful, fast, and tireless — but still guided by human judgment.
Key Components of an Agentic SEO System
An agentic SEO system isn’t “one AI tool.” It’s a stack of connected parts that work together like an autonomous SEO team: gathering signals, deciding what matters, taking actions, and learning from results. Understanding these components helps marketers evaluate tools, set guardrails, and avoid the “black box” trap.
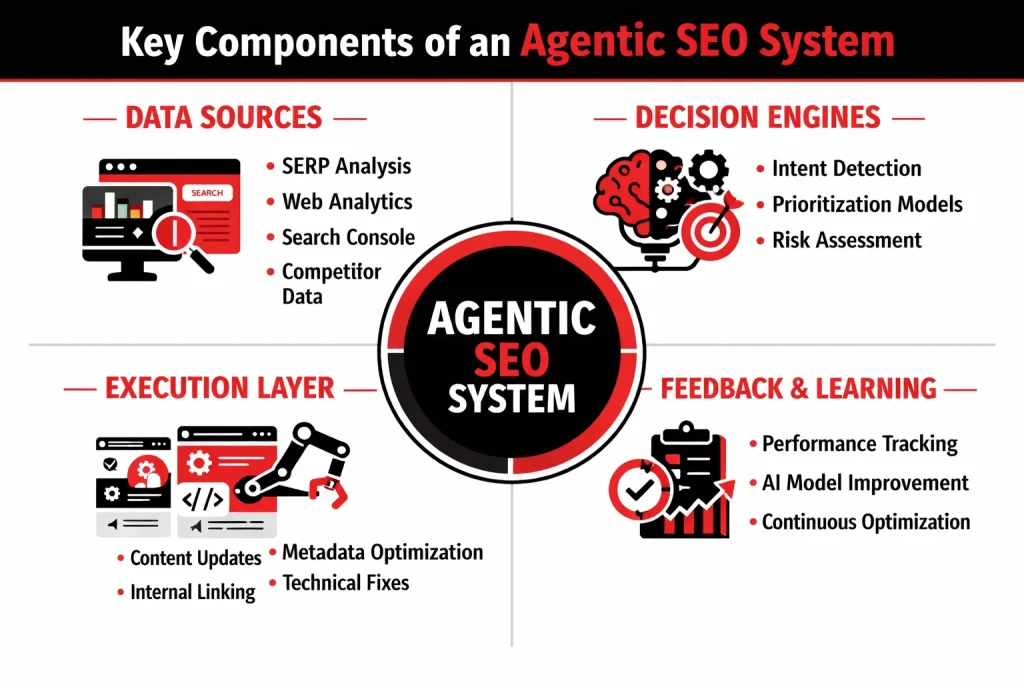
Data Sources (Where the Agent Gets Its Signals)
Agentic SEO is only as good as the inputs it can observe. The main difference between basic automation and agentic behavior is that agents continuously monitor environments, not just run tasks on command. Here are the most important sources:
SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages)
SERPs are the agent’s “battlefield view.” They reveal:
- Ranking positions over time (your pages and competitors)
- SERP features (featured snippets, People Also Ask, videos, local packs)
- Search intent shifts (e.g., a query changing from informational to product-focused)
- Content format preferences (listicles vs guides vs category pages)
A strong agentic system doesn’t just track rankings—it watches how the SERP is structured, which tells the agent what Google is rewarding for that query right now.
Analytics (GA4, Adobe, etc.)
Analytics reveal what happens after the click:
- Engagement signals (time on page, scroll, bounce/exit behavior)
- Conversion performance (leads, purchases, signups)
- Drop-offs by device, source, and landing page
- Content performance by cohort and segment
For marketers, this matters because the agent can optimize not just for rankings, but for business outcomes—improving pages that drive revenue, not vanity traffic.
Search Console (GSC)
Search Console is the closest thing to “direct feedback” from Google:
- Queries and impressions (even when you aren’t ranking high)
- Click-through rate (CTR) issues, page-level performance
- Indexing and coverage problems
- Core Web Vitals metrics (in many setups)
In agentic SEO, GSC often acts like the agent’s health monitor—flagging indexing or visibility problems before traffic drops.
Crawlers (Site crawls, log analysis, technical scans)
Crawlers map your website as a search engine would:
- Broken links, redirect chains, orphan pages
- Duplicate content, thin pages, missing canonicals
- Site architecture issues and internal PageRank flow
- Renderability and JavaScript issues (depending on crawler depth)
Agentic systems use crawling data to spot “silent killers”—technical issues that don’t show up in analytics until damage is done.
Competitor data
Competitor monitoring gives the agent context for what “good” looks like:
- New pages competitors publish (and which keywords they target)
- Content updates that cause ranking changes
- Backlink acquisition patterns
- SERP share changes over time
This helps the agent make smarter decisions: sometimes the best move isn’t rewriting your article—it’s matching a new intent pattern competitors are already serving.
Decision Engines (How the Agent Decides What to Do)
Once the system has signals, it needs a brain—actually, multiple brains—responsible for interpreting inputs and choosing actions. This is where agentic SEO goes beyond automation.
Intent detection
Search intent drives everything. Intent detection answers:
- Is the query informational, commercial, transactional, navigational—or mixed?
- What sub-intents appear (comparisons, pricing, “best,” “how-to,” alternatives)?
- What format wins (tool page, category page, long guide, video, FAQs)?
An agentic system might notice, for example, that a keyword’s SERP is shifting from “how-to guides” to “product pages,” then recommend (or execute) a page restructure to match.
Prioritization models
Agents can’t fix everything at once, so prioritization determines:
- Which pages to update first (based on potential impact)
- Which technical issues are urgent vs “nice-to-have”
- Which keywords represent the best opportunity (low effort, high gain)
A good prioritization engine balances:
- Impact (traffic, conversions, revenue potential)
- Effort (how complex the fix is)
- Confidence (how likely the change will help)
- Time sensitivity (seasonality, trend spikes, algorithm changes)
Risk assessment
This is the “safety layer” that prevents reckless changes:
- Could updating this page hurt conversions or brand trust?
- Is the agent about to over-optimize anchor text or keyword density?
- Could a rewrite introduce inaccuracies or compliance issues?
- Will this change affect other pages (cannibalization, internal linking shifts)?
For marketers, risk assessment is crucial. The best systems make changes incrementally, with rollback options and human review checkpoints for high-risk pages.
Execution Layer (Where Decisions Become Real Changes)
This is the action part: the agent applies its decisions through tools, CMS access, or task workflows. Execution typically falls into four categories:
Content updates
Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) content actions can include:
- Refreshing outdated sections (facts, stats, screenshots)
- Improving structure (headings, FAQs, scannability)
- Expanding for missing subtopics (closing content gaps)
- Aligning content to intent (e.g., adding comparison tables)
- Enhancing EEAT signals (author bios, citations, trust elements)
The most effective systems treat content as a living asset, not a one-time publish event.
Internal linking
Internal links are one of the highest-leverage SEO levers because they’re fully under your control. Agents can:
- Add contextual links to relevant pages
- Fix orphan pages by connecting them into the site graph
- Optimize anchor text naturally (without spammy repetition)
- Strengthen topical clusters and distribute authority
Done well, internal linking is how agentic systems improve crawlability, relevance, and conversions at the same time.
Metadata optimization
Metadata influences CTR and relevance signals:
- Title tag variations based on SERP patterns
- Meta descriptions tuned to intent and value props
- Header alignment (H1/H2 structure)
- Schema markup suggestions (FAQ, HowTo, Product, Article)
Agentic systems can test title/meta variants and learn which patterns lift CTR, then apply those learnings at scale.
Technical fixes
Technical execution may include:
- Fixing broken links and redirect issues
- Resolving canonicalization problems
- Improving Core Web Vitals recommendations
- Handling index bloat (noindexing low-value pages)
- Optimizing sitemap structure and internal crawl paths
Depending on access, the agent might automatically apply fixes or open structured tasks for dev teams with clear reproduction steps.
Feedback & Learning Loops (How the System Improves Over Time)
This is the piece that makes it truly “agentic.” Instead of doing tasks once, the system runs in loops: act → measure → adapt.
Performance tracking
The agent monitors outcomes tied to its actions:
- Ranking movements and SERP feature wins/losses
- CTR improvements after title/meta changes
- Engagement and conversion changes after content updates
- Crawl health and indexing improvements after technical fixes
This ensures the system isn’t blindly “optimizing”—it’s measuring whether changes help.
Model refinement
Based on results, the agent adjusts:
- Which page types work best for certain intents
- Which content patterns correlate with ranking gains
- Which technical fixes lead to the biggest improvements
- Which changes are risky or volatile (and should require review)
Over time, the system becomes smarter about your specific niche, site structure, and audience.
Continuous improvement
Agentic SEO thrives on iteration:
- Updating winners more frequently
- Scaling successful tactics across similar pages
- Pausing or reversing changes that underperform
- Discovering new opportunities through constant monitoring
The key takeaway for marketers: a true agentic SEO system doesn’t just produce “SEO output.” It builds a self-improving optimization engine that gets better the longer it runs—especially when you supply clear goals and strong quality guardrails.
Agentic SEO vs Traditional SEO: What’s the Real Difference?
As SEO evolves, one of the most common questions marketers ask is: How is Agentic SEO actually different from traditional SEO?
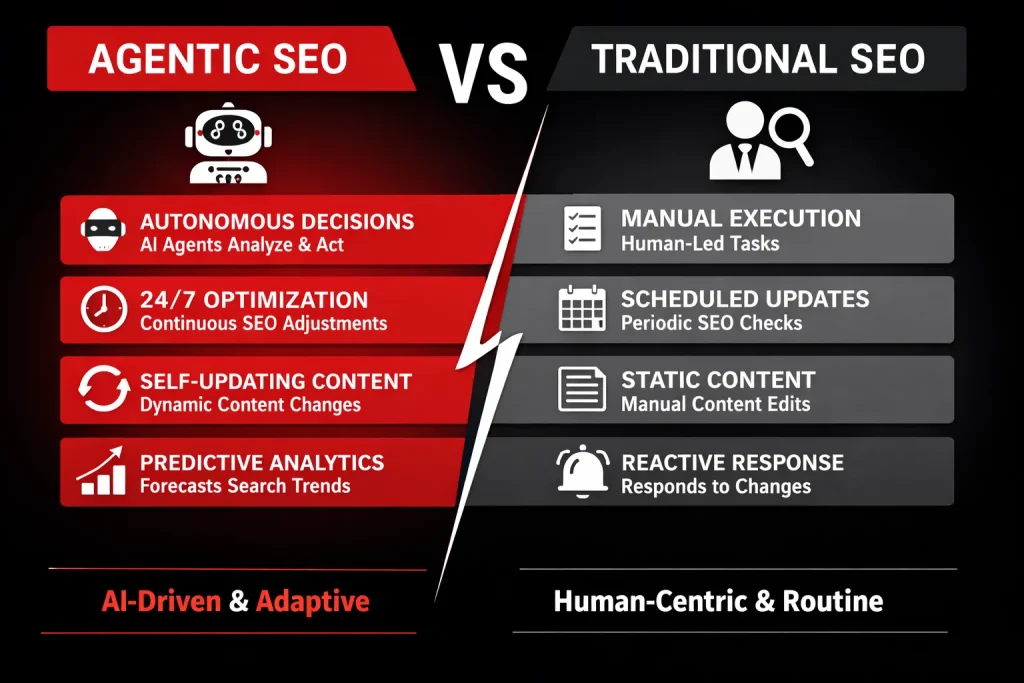
While both aim for the same goal—better visibility, rankings, and traffic—the way they operate is fundamentally different.
Traditional SEO is human-led and process-driven, whereas Agentic SEO is AI-led and goal-driven. To understand this shift clearly, let’s break it down.
Side-by-Side Comparison: Agentic SEO vs Traditional SEO
| Factor | Traditional SEO | Agentic SEO |
| Speed | Slow to moderate; depends on human execution and schedules | Extremely fast; operates in near real-time |
| Scalability | Limited by team size and resources | Highly scalable across thousands of pages |
| Accuracy | High for strategic decisions, but prone to manual oversight | Data-driven and consistent, but depends on data quality |
| Human Effort | High manual involvement at every stage | Low operational effort; humans supervise, not execute |
| Risk | Lower risk due to human judgment | Higher risk if guardrails and oversight are weak |
In traditional SEO, tasks like audits, keyword research, content optimization, and reporting are usually done in batches—weekly or monthly. In contrast, Agentic SEO runs continuously, analyzing data, making decisions, and taking action without waiting for human intervention.
What Agentic SEO Does Better
Agentic SEO isn’t just “faster SEO.” It introduces capabilities that traditional workflows simply can’t match at scale.
1. Scalability
Agentic SEO excels when managing large websites, eCommerce stores, SaaS platforms, or content publishers. An AI agent can:
- Monitor thousands of pages simultaneously
- Optimize internal linking at scale
- Detect ranking drops or content decay instantly
What would take a human team weeks can be handled automatically and continuously.
2. Consistency
Humans get tired. Teams change. Processes drift.
Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO), on the other hand:
- Applies the same rules and standards every time
- Avoids missed optimizations or forgotten updates
- Maintains uniform SEO hygiene across the site
This consistency is especially valuable for long-term technical SEO and content maintenance.
3. Reaction Time
Search results change fast—sometimes daily.
Agentic SEO systems can:
- Detect SERP volatility
- Identify competitor changes
- React to ranking drops immediately
Traditional SEO often reacts after performance declines. Agentic SEO aims to react as changes happen.
What Traditional SEO Still Does Better
Despite its power, Agentic SEO is not a replacement for human marketers. Traditional SEO still holds key advantages that AI agents struggle to replicate.
1. Creativity
Human SEOs excel at:
- Creating original content angles
- Storytelling
- Thought leadership
- Emotional resonance
AI agents optimize existing patterns; humans create new ones. This is critical for brand-led content, campaigns, and differentiation.
2. Brand Nuance
Brand voice, tone, cultural sensitivity, and audience psychology are areas where humans still outperform autonomous systems. A human SEO understands:
- When not to optimize
- How brand perception impacts trust
- Subtle messaging differences across audiences
Without strong guardrails, agentic systems may over-optimize at the expense of brand identity.
3. Strategic Judgment
SEO is not just execution—it’s strategy. Humans are better at:
- Long-term planning
- Risk assessment
- Aligning SEO with business goals
- Navigating ambiguous situations
Agentic SEO is excellent at operational decisions, but humans remain essential for strategic direction.
Real-World Use Cases of Agentic SEO
Agentic SEO becomes real when it stops being “AI that suggests” and starts being an always-on system that detects opportunities, decides what to do, executes changes (with guardrails), and learns from results. Below are the most practical, marketer-friendly use cases you can implement today—each designed to reduce manual effort while improving speed, consistency, and performance.

Autonomous Keyword Research & Topic Discovery
Traditional keyword research is often periodic: you run a tool, export lists, pick keywords, and build a content plan that goes stale within weeks. Agentic SEO changes this into a continuous discovery engine that updates as the market shifts.
Search demand prediction
An agent can monitor early signals—query growth trends, seasonal patterns, competitor publishing velocity, SERP feature changes—and forecast where demand is heading, not just where it was. For marketers, this means:
- publishing content before the trend peaks (instead of after competitors already own it),
- planning seasonal pages earlier with better lead time,
- prioritizing topics with a rising intent match to your offer.
In practice, an agent might detect that “AI SEO workflows” is climbing while “SEO automation tools” is flattening, and recommend shifting upcoming content toward workflow-driven terms with higher growth potential.
Gap analysis
Gap analysis becomes more than “what keywords competitors rank for.” An agent can:
- crawl competitor topic clusters,
- map them to user intents (informational, comparison, transactional),
- compare with your existing coverage,
- and output a ranked list of “missing” pages that would strengthen topical authority.
More importantly, it can go beyond keywords into content depth gaps: where your page exists, but competitors cover subtopics, FAQs, visuals, or use cases that you don’t. The output isn’t just “write about X”—it’s “add sections A, B, C, and address these questions to match intent.”
Self-Updating Content
One of the most expensive parts of SEO is keeping content fresh. Posts decay as competitors update, SERP expectations shift, and user intent changes. Agentic SEO makes content refresh a system, not a quarterly project.
Refreshing outdated posts
Agents can monitor pages for “freshness triggers,” such as:
- declining rankings or CTR,
- outdated years, stats, screenshots, or product mentions,
- competitor pages that recently improved.
Then, instead of simply flagging the issue, the agent can propose or apply updates like:
- rewriting introductions for clarity and intent alignment,
- adding new sections based on current SERP patterns,
- improving structure with better headings and FAQs,
- updating internal links to newer resources.
For marketers, this is huge: your “old winners” don’t silently become “old losers.”
Optimizing for intent shifts
Search intent is not fixed. A keyword that once needed a beginner guide may later demand a comparison, a template, or a “best tools” list. An agent can detect intent drift by tracking:
- changes in top-ranking page formats,
- new SERP features (AI answers, videos, product blocks),
- shifts in query modifiers (“best,” “pricing,” “examples,” “template”).
Then it can recommend a transformation like:
- turning a generic explainer into a “how-to + checklist,”
- adding comparison tables when the SERP becomes tool-heavy,
- emphasizing actionable frameworks when “examples” start dominating.
Technical SEO Automation
Technical SEO issues are often repetitive, widespread, and easy to miss—perfect for autonomous agents that can continuously scan and recommend fixes.
Broken links
An agent can crawl your site regularly, detect:
- broken internal links (wasted crawl and poor UX),
- broken outbound links (trust + user frustration),
- redirect chains (crawl inefficiency),
then auto-suggest replacements or update links where appropriate. It can also prioritize fixes by page value (traffic, revenue, conversion importance) instead of treating all broken links equally.
Schema fixes
Structured data can improve eligibility for rich results, but schema implementations often drift or break after site changes. Agents can:
- validate schema markup site-wide,
- detect missing required properties,
- identify mismatches (wrong schema type for the content),
- and propose corrected JSON-LD.
For marketers, this means less time fighting technical debt—and more time focused on content and growth.
Page speed suggestions
Agents can monitor performance trends and highlight what’s actually worth fixing:
- heavy images,
- render-blocking scripts,
- unused CSS,
- slow third-party tags.
Instead of generic “improve speed,” an agent can output prioritized actions such as compressing top offenders, lazy-loading images on key templates, or flagging scripts that impact Core Web Vitals the most.
Internal Linking at Scale
Internal linking is one of the most underrated SEO levers—and one of the most tedious to do manually. Agentic AI Optimization (AAIO) makes internal linking systematic and scalable.
Contextual links
Agents can analyze content semantically (not just exact-match keywords) and suggest links that make sense in context. That means:
- linking when a concept is mentioned naturally,
- using anchor text that supports understanding,
- avoiding spammy over-linking.
It can also enforce internal linking rules like “every new blog post must link to the pillar page and two supporting articles.”
Authority distribution
Beyond convenience, internal links are about distributing authority. An agent can:
- identify pages with high authority (strong backlinks/traffic),
- locate “orphan” pages with weak internal support,
- and recommend links that push authority toward high-priority pages (money pages, product pages, lead-gen content).
For marketers, this becomes a powerful way to improve rankings without publishing new content.
SEO Monitoring & Alerting
The biggest SEO losses happen quietly: rankings drop, pages deindex, cannibalization grows—and you notice weeks later. Agentic SEO turns monitoring into an active defense system.
Ranking drops
Agents can track rankings and trigger alerts when declines are statistically meaningful (not just daily fluctuations). Then they can diagnose likely causes:
- competitor update,
- SERP format change,
- intent mismatch,
- technical issues,
- content decay.
The best part: the agent can propose a plan—update sections, improve internal links, add missing subtopics—instead of simply saying “rank dropped.”
Indexing issues
Agents can watch for anomalies such as:
- sudden drops in indexed pages,
- canonicalization errors,
- accidental noindex tags,
- crawl spikes or crawl waste.
They can pair Search Console signals with crawling data to pinpoint the affected templates or sections quickly.
Cannibalization
Cannibalization happens when multiple pages compete for the same intent. Agents can detect this by analyzing:
- overlapping keywords and intents,
- fluctuating URLs for the same query,
- declining CTR due to confusing relevance.
Then they can suggest fixes such as:
- consolidating pages,
- clarifying page intent and structure,
- adding canonical tags where appropriate,
- improving internal linking to signal the primary page.
Benefits of Agentic SEO for Marketers
Agentic SEO is not just a technological upgrade—it represents a fundamental shift in how marketers plan, execute, and scale search optimization. By combining autonomous decision-making with continuous learning, agentic systems unlock advantages that are difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional or even AI-assisted SEO. Below are the key benefits marketers gain by adopting agentic SEO.

Time & Cost Efficiency
One of the most immediate benefits of agentic SEO is the dramatic reduction in manual effort. Traditional SEO requires repetitive tasks such as keyword research, technical audits, content updates, internal linking, and performance monitoring. Agentic SEO systems automate not just execution, but also the decision-making behind these tasks.
Instead of waiting for monthly audits or manual checks, AI agents continuously monitor site performance, identify issues, and act on them in real time. This significantly reduces the need for large SEO teams or constant human intervention, lowering operational costs while increasing output. Marketers can redirect time and budget toward strategy, creativity, and business growth rather than routine maintenance.
Scalability for Large Sites
Scalability is where agentic SEO truly outperforms traditional approaches. Large websites—such as eCommerce platforms, SaaS products, publishers, or marketplaces—often contain thousands or even millions of pages. Manually optimizing each page is impractical.
Agentic SEO systems can analyze and optimize large content inventories simultaneously. They identify patterns across pages, detect underperforming sections, and apply consistent improvements at scale. Whether it’s updating metadata, improving internal linking structures, or refreshing outdated content, agentic SEO enables marketers to scale optimization efforts without linear increases in time or resources.
Faster Experimentation & Learning
Agentic SEO allows marketers to test, learn, and iterate faster than ever before. AI agents can run continuous micro-experiments—such as testing title variations, content structures, or internal linking strategies—while monitoring performance in real time.
Because these systems operate continuously, they shorten feedback loops. Marketers no longer need to wait weeks or months to assess the impact of SEO changes. Instead, insights are generated quickly, allowing teams to double down on what works and abandon what doesn’t. This accelerates learning and improves overall SEO effectiveness.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Unlike manual SEO, which often relies on intuition or limited data snapshots, agentic SEO makes decisions based on large-scale, real-time data. AI agents analyze search trends, user behavior, SERP changes, and competitor movements simultaneously.
This data-driven approach helps marketers prioritize the highest-impact actions. Instead of guessing which pages to optimize or keywords to target, agentic systems recommend or execute changes based on measurable performance signals, reducing risk and improving ROI.
Always-On Optimization
Search engines, user intent, and competitors are constantly changing. Agentic SEO ensures that optimization is never static. These systems operate continuously, adapting to algorithm updates, ranking fluctuations, and content decay without waiting for human prompts.
For marketers, this means their SEO strategy stays responsive and resilient. Rather than reacting to problems after traffic drops, agentic SEO enables proactive optimization—keeping websites competitive, relevant, and aligned with search intent at all times.
Risks, Limitations, and Common Misconceptions
While Agentic SEO offers powerful advantages, it is not without risks. Like any advanced technology, its effectiveness depends heavily on how it is implemented, monitored, and governed. Understanding these limitations early helps marketers avoid costly mistakes and unrealistic expectations.
Can Agentic SEO Hurt Rankings?
Yes — poorly implemented Agentic SEO can negatively impact rankings. The technology itself is not the problem; misconfiguration is.
- Poor prompts:
Agentic systems rely on instructions, goals, and constraints. Vague or poorly designed prompts can lead agents to prioritize the wrong metrics, such as keyword density over user intent, resulting in low-quality or spammy outputs.
- Bad guardrails:
Without clear boundaries, agents may make aggressive optimization decisions—rewriting pages too frequently, altering critical metadata, or testing risky changes at scale. Guardrails ensure agents operate within SEO best practices and brand guidelines.
- Over-automation:
Fully autonomous execution without review can cause cascading issues, such as mass content changes that negatively affect rankings before anyone notices. Automation should be gradual, controlled, and monitored.
In short, Agentic SEO needs intentional oversight, especially during early adoption.
Brand Voice & Quality Risks
One of the biggest concerns for marketers is content quality and brand voice.
- Generic content:
If agents rely too heavily on patterns and templates, content may become repetitive, bland, or indistinguishable from competitors. This undermines brand differentiation and user trust.
- Over-optimization:
Autonomous systems may push SEO signals too hard—overusing keywords, excessively restructuring content, or prioritizing rankings over readability. This can hurt user experience and long-term performance.
Maintaining brand tone, messaging consistency, and editorial standards requires human-defined style guides and periodic reviews.
Hallucinations & Wrong Decisions
Like all AI systems, agentic models can occasionally hallucinate facts, misinterpret intent, or draw incorrect conclusions from incomplete data.
- Agents may misread search trends
- Infer incorrect causes for ranking drops
- Recommend changes based on flawed assumptions
This is why human oversight matters. Marketers should validate high-impact decisions, review content updates, and intervene when agents operate on uncertain data. Agentic SEO works best as a human–AI collaboration, not a fully hands-off system.
Common Myths About Agentic SEO
Let’s clear up two major misconceptions:
- “Agentic SEO replaces humans”
False. Agentic SEO replaces repetitive tasks—not strategic thinking, creativity, or judgment. Humans remain essential for goal-setting, brand strategy, and ethical decision-making.
- “Agentic SEO is black hat SEO”
Also false. Agentic SEO is a methodology, not a tactic. When aligned with search engine guidelines and focused on user value, it is entirely white hat. Abuse comes from misuse, not the technology itself.
Bottom line: Agentic SEO is powerful, but it requires thoughtful implementation, strong governance, and ongoing human involvement to deliver sustainable results.
Is Agentic SEO Safe According to Google?
One of the most common questions marketers ask before adopting Agentic SEO is simple but critical: Is this actually safe according to Google? The short answer is yes—when done correctly. The longer answer depends on how Agentic SEO is implemented and governed.

Google’s View on AI-Generated Content
Google has been clear and consistent on one key principle:
it does not judge content by how it’s created, but by how helpful it is.
In its guidance on AI-generated content, Google emphasizes that:
- The method of content creation (human, AI, or hybrid) is not the ranking factor
- Quality, usefulness, and relevance are what matter most
This means AI-generated or AI-assisted content—including content optimized or updated by agentic systems—is not inherently against Google’s guidelines. What Google actively discourages is low-quality, mass-produced content created solely to manipulate rankings.
Agentic SEO, when focused on improving relevance, clarity, and user satisfaction, aligns with Google’s broader Helpful Content System, which rewards content that genuinely helps users rather than gaming algorithms.
Where Agentic SEO Aligns with Google’s Guidelines
At its core, Agentic SEO is not about shortcuts—it’s about continuous optimization for user intent. This is where it naturally aligns with Google’s priorities.
Key alignment points include:
- Intent satisfaction: Agentic systems analyze search intent changes and adjust content to better answer real user queries.
- User-first optimization: Instead of keyword stuffing or rigid rules, agentic workflows prioritize readability, structure, topical coverage, and clarity.
- Ongoing improvement: Agentic SEO continuously monitors performance and refines content, which supports freshness and relevance—both important quality signals.
When used responsibly, Agentic SEO actually strengthens the principles Google wants publishers to follow.
Best Practices for Safe Implementation
While Agentic SEO is compatible with Google’s guidelines, guardrails are essential. The safest implementations follow these best practices:
- Human review: Humans should set goals, approve major changes, and audit outputs—especially for important pages.
- Transparency: Teams should understand what agents are doing, why decisions are made, and how changes affect users.
- Quality checks: Content must be reviewed for accuracy, originality, tone, and value before publishing or updating.
In short, Agentic SEO is safe when humans remain in control. It works best as a powerful co-pilot—not a fully unchecked autopilot—helping marketers scale quality, not compromise it.
Who Should Use Agentic SEO?
Agentic SEO is powerful, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its real value depends on scale, complexity, and operational maturity. Below is a clear breakdown of who benefits the most—and who should proceed with caution.

Ideal Use Cases
Content-heavy websites
Websites with hundreds or thousands of pages—such as blogs, knowledge bases, or media portals—are prime candidates for agentic SEO. These sites struggle with content decay, keyword cannibalization, outdated information, and internal linking at scale. Agentic SEO systems can continuously monitor performance, refresh content, fix gaps, and optimize pages automatically, something human teams simply can’t do 24/7.
E-commerce websites
E-commerce sites deal with massive product catalogs, frequent inventory changes, seasonal demand, and constant competition. Agentic SEO can autonomously optimize product pages, manage internal links, detect ranking drops, improve metadata, and adapt content based on real-time search intent—making it highly effective for large online stores.
SaaS companies
SaaS businesses rely heavily on inbound traffic, educational content, comparison pages, and feature-led SEO. Agentic SEO can help SaaS teams continuously optimize landing pages, update feature documentation, track competitor movements, and identify emerging keywords—while freeing marketers to focus on strategy and messaging.
Publishers and media platforms
News sites, publishers, and editorial platforms operate in fast-moving environments where freshness matters. Agentic SEO can monitor trending topics, optimize headlines, update evergreen content, and improve discoverability across large content libraries, making it especially valuable for high-volume publishing operations.
Who Should Be Careful
Small websites
For small sites with limited pages or traffic, agentic SEO may be unnecessary or even counterproductive. The overhead of setup, monitoring, and tool costs may outweigh the benefits. In such cases, traditional or AI-assisted SEO is often sufficient.
Brands with a strong, unique voice
If your brand relies heavily on tone, personality, or nuanced storytelling, fully autonomous optimization can risk diluting that voice. Without strong guardrails and human review, agentic systems may favor generic, overly optimized content.
Regulated industries
Industries like healthcare, finance, legal, or compliance-driven sectors must be extremely cautious. Autonomous changes to content could introduce inaccuracies or compliance risks. In these cases, agentic SEO should only be used with strict human oversight and approval workflows.
In short: Agentic SEO works best where scale, speed, and complexity demand automation—but it should always complement human judgment, not replace it.
Agentic SEO Tools & Platforms
As Agentic SEO gains traction, a new category of tools and platforms is emerging to support autonomous, goal-driven SEO workflows. Unlike traditional SEO tools that primarily report data or assist humans, agentic SEO tools are designed to analyze, decide, and act—often with minimal human intervention.

For beginners, it’s important to understand that agentic SEO tools don’t replace existing SEO software overnight. Instead, they often sit on top of or alongside analytics platforms, crawlers, and content systems, orchestrating actions through AI agents.
At a high level, agentic SEO tools can be grouped into three broad types.
Types of Agentic SEO Tools
Audit agents
Audit agents continuously monitor a website’s SEO health. Instead of running one-time audits, they repeatedly scan for issues such as broken links, indexing problems, content decay, technical errors, or ranking drops. What makes them “agentic” is their ability to prioritize issues, identify root causes, and recommend—or even implement—fixes based on impact.
Content agents
Content agents focus on planning, creating, and improving content. They analyze search intent, identify content gaps, refresh outdated pages, optimize on-page elements, and sometimes generate or update content automatically. More advanced content agents can track performance and iterate over time, learning which changes lead to better rankings or engagement.
Optimization agents
Optimization agents are responsible for ongoing improvements across the site. This can include internal linking, metadata optimization, schema updates, keyword targeting adjustments, and page-level refinements. These agents often work continuously, making small but frequent improvements rather than large, infrequent changes.
What to Look for in an Agentic SEO Tool
Because agentic SEO involves a higher level of autonomy, choosing the right tool requires more caution than traditional SEO software.
Transparency is critical. You should be able to understand what the agent is doing, why it made a decision, and what data it used. Black-box systems increase risk and reduce trust.
Control is equally important. Good agentic SEO tools allow marketers to set goals, define boundaries, approve actions, or pause automation when needed. Human oversight should always be possible.
Explainability separates reliable tools from risky ones. The tool should clearly explain recommendations and outcomes, helping marketers learn—not just automate blindly.
In short, the best agentic SEO tools don’t remove marketers from the process; they augment decision-making while keeping humans in charge.
The Future of Agentic SEO
The future of SEO is no longer just about ranking pages—it’s about orchestrating intelligent systems that adapt, predict, and act in real time. As search engines evolve into generative and intent-driven platforms, Agentic SEO will become a core capability for marketers who want to stay competitive. Let’s explore what’s coming next.

Agentic SEO + Generative Search
Search is rapidly shifting from “ten blue links” to generative search experiences, where users receive synthesized answers instead of lists of pages. In this environment, Agentic SEO plays a crucial role by continuously aligning content with how AI-driven search engines interpret and generate responses.
Agentic systems can analyze how generative engines summarize topics, identify which sources are being cited, and autonomously adjust content structure, clarity, and authority signals. Instead of optimizing solely for rankings, Agentic SEO will optimize for visibility within AI-generated answers, ensuring brands are accurately represented when search engines generate responses on behalf of users.
Predictive SEO & Self-Healing Websites
One of the most transformative aspects of Agentic SEO is its predictive capability. Rather than reacting to traffic drops or ranking losses, agentic systems will anticipate changes before they happen.
By monitoring historical trends, SERP volatility, algorithm updates, and user behavior, agentic agents can forecast potential performance issues and take preemptive action. This leads to the concept of self-healing websites—sites that automatically update outdated content, fix technical SEO issues, adjust internal linking, and optimize pages without manual intervention. SEO becomes an always-on system that improves itself continuously.
Human + Agent Collaboration Models
The future of Agentic SEO is not fully autonomous—it’s collaborative. Humans will define goals, brand guidelines, ethical boundaries, and strategic priorities, while AI agents handle execution, analysis, and iteration at scale.
In this model, marketers act as strategists and supervisors, reviewing decisions, validating outputs, and refining direction. Agentic systems become tireless teammates that surface insights, test hypotheses, and recommend actions—freeing humans to focus on creativity, storytelling, and long-term growth strategy.
How SEO Roles Will Evolve
As Agentic SEO matures, SEO roles will shift dramatically. Routine tasks like keyword research, audits, and on-page optimization will increasingly be automated. In their place, new roles will emerge: SEO strategists, AI workflow designers, prompt engineers, and quality controllers.
Successful SEOs will be those who understand both search fundamentals and agentic systems—professionals who can guide intelligent agents rather than compete with them. In short, the future SEO is not replaced by AI, but augmented by intelligent agents working in continuous collaboration.
How to Get Started with Agentic SEO
Adopting Agentic SEO doesn’t mean handing over your entire website to autonomous AI on day one. For most marketers, the smartest approach is gradual adoption—combining human judgment with AI agents that learn, act, and improve under clear supervision. This section walks you through a practical, low-risk roadmap to get started.
Start with Assisted Agentic SEO
If you’re new to Agentic SEO, begin with assisted workflows rather than full autonomy. In this model, AI agents analyze data, generate recommendations, and suggest actions—but humans approve or refine those actions before execution.
For example, an agent might:
- Identify underperforming pages
- Suggest keyword adjustments
- Recommend internal links or content updates
You remain in control, using the agent as a decision support system rather than a fully independent executor. This helps you understand how agentic systems think, where they perform well, and where human judgment is still essential.
Set Clear Goals & Guardrails
Agentic SEO systems work best when they are goal-driven. Before deploying any agent, define what success looks like. Common goals include:
- Improving rankings for specific topic clusters
- Increasing organic traffic to blog content
- Reducing technical SEO issues over time
Equally important are guardrails—rules that limit what the agent can and cannot do. Guardrails may include:
- Pages or sections the agent is not allowed to edit
- Brand tone and content quality standards
- Approval requirements for major changes
Clear goals and boundaries prevent over-optimization and ensure the agent aligns with your brand and SEO strategy.
Test on Low-Risk Pages
Avoid experimenting with Agentic SEO on your most critical pages at the start. Instead, test on low-risk assets such as:
- Older blog posts
- Informational articles
- Low-traffic landing pages
These pages allow you to observe how agents make decisions, optimize content, and respond to performance feedback—without risking core revenue or brand visibility. Think of this phase as a sandbox for learning, not a shortcut to instant results.
Measure, Learn, and Scale
Agentic SEO is not a “set it and forget it” system. Continuously track performance metrics such as:
- Ranking changes
- Organic traffic growth
- Engagement and conversion signals
Use these insights to refine goals, tighten guardrails, and increase autonomy gradually. As confidence grows, you can scale agentic workflows across larger sections of your site—moving from assisted decision-making to more autonomous optimization where appropriate.
In short, successful Agentic SEO starts small, learns fast, and scales responsibly. Marketers who treat AI agents as collaborators—not replacements—will see the most sustainable long-term gains.
Final Thoughts: Agentic SEO Is a Shift, Not a Shortcut
Agentic SEO is not a magic button you press to get rankings overnight. It’s not “set it and forget it” SEO, and it’s definitely not a shortcut around strategy, quality, or user intent. Instead, agentic SEO represents a fundamental shift in how SEO work is planned, executed, and improved over time.

At its core, agentic SEO introduces a new operating model—one where AI agents don’t just assist humans but actively analyze situations, make decisions, take action, and learn from results. This changes SEO from a periodic, manual process into a continuous, always-on system. Rankings are no longer something you check once a month; they become signals that intelligent systems respond to in real time.
However, this doesn’t make human marketers obsolete. In fact, it raises the bar. Marketers move from executing repetitive tasks to setting goals, defining guardrails, validating outcomes, and shaping strategy. The real advantage comes from combining human judgment with autonomous execution—not replacing one with the other.
Those who treat agentic SEO as a shortcut risk poor-quality output, brand inconsistency, or even search penalties. But marketers who invest time in understanding how agentic systems work—and how to control them responsibly—gain a powerful edge. As search grows more complex and competitive, early adopters who learn, test, and adapt will be best positioned to win in the long term.
Agentic SEO isn’t about doing less thinking. It’s about thinking differently—and scaling that thinking intelligently.

